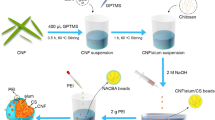
Abstract
Treating water pollution, especially dye-contaminated wastewater, in an economical and efficient manner remains a challenge as the surface charge diversity of contaminants. This work designed a nanocellulose-based amphoteric adsorbent based on 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinyl-1-oxyl (TEMPO)-oxidized cellulose nanofibrils (TOCNs) with in situ polymerization of diallyl dimethyl ammonium chloride (PDMDAAC). To explore the adsorption capacity of the amphoteric adsorbent (TOCN/PDMDAAC) for negatively and positively charged contaminants, methyl orange (MO, an anionic dye) and methylene blue (MB, a cationic dye) were employed as adsorbates. The effect of adsorbent on the adsorption performance at different pH, initial concentration of dye, contact time and ionic strength were investigated by batch treatment method. Equilibrium isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics of dyes onto TOCN/PDMDAAC were examined, which implied that the adsorption behavior was monolayer and the adsorption process was spontaneous endothermic. The adsorption mechanisms are hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions between the dye and the active site on the adsorbent. The adsorption behavior of the binary blended dye system of MO and MB has also been investigated, and the addition of the other dye of higher concentration showed a synergistic adsorption behavior. According to the Langmuir model, at pH 7, 298 K, the equilibrium adsorption of MO and MB onto TOCN/PDMDAAC was as high as 404.86 mg g−1 and 520.83 mg g−1, respectively. These results indicated that TOCN/PDMDAAC was an effective amphoteric adsorbent, which offered a promising strategy for the adsorption of multicomponent dyes in an eco-friendly way.
Graphic Abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysis during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abouzeid RE, Khiari R, El-Wakil N, Dufresne A (2019) Current state and new trends in the use of cellulose nanomaterials for wastewater treatment. Biomacromol 20(2):573–597. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.8b00839
Aimonen K, Imani M, Hartikainen M, Suhonen S, Vanhala E, Moreno C, Rojas OJ, Norppa H, Catalán J (2022) Surface functionalization and size modulate the formation of reactive oxygen species and genotoxic effects of cellulose nanofibrils. Part Fibre Toxicol 19(1):19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12989-022-00460-3
Al-Ghouti MA, Da’ana DA (2020) Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: A review. J Hazard Mater 393:122383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122383
An YY, Xiao P, Zheng HL, Zhao R, Han MX, Mao WW, Li YS (2021) Multi-functionalized self-floating microspheres for dyes capture: amphoteric adsorption and rapid surface solid-liquid separation. J Clean Prod 296:126535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126535
Andreas A, Winata ZG, Santoso SP, Angkawijaya AE, Yuliana M, Soetaredjo FE, Ismadji S, Hsu H-Y, Go AW, Ju Y-H (2021) Biocomposite hydrogel beads from glutaraldehyde-crosslinked phytochemicals in alginate for effective removal of methylene blue. J Mol Liq 329:115579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.115579
Antoniw JM, Hallman MT, Kiriakou MV, Morse T, Cranston ED (2023) Colloidal stability window for carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals: considerations for handling, characterization, and formulation. Langmuir 39(30):10321–10334. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.3c00319
Azha SF, Sellaoui L, Shamsudin MS, Ismail S, Bonilla-Petriciolet A, Ben Lamine A, Ert A (2018) Synthesis and characterization of a novel amphoteric adsorbent coating for anionic and cationic dyes adsorption: Experimental investigation and statistical physics modelling. Chem Eng J 351:221–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.06.092
Celestino GG, Henriques RR, Shiguihara AL, Constantino VRL, Melo RD, Amim J (2019) Adsorption of gallic acid on nanoclay modified with poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride). Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:28444–28454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3505-x
Chang CY, Zhang LN (2011) Cellulose-based hydrogels: Present status and application prospects. Carbohydr Polym 84(1):40–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.12.023
Chen F, Zhao E, Kim T, Wang JX, Hableel G, Reardon PJT, Wang TY, Ananthakrishna SJ, Arconada-Alvarez S, Knowles JC, Jokerst JV (2017) Organosilica nanoparticles with an intrinsic secondary amine: an efficient and reusable adsorbent for dyes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(18):15566–15576. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b0418
Chen B, Long FX, Chen SJ, Cao YR, Pan XJ (2020a) Magnetic chitosan biopolymer as a versatile adsorbent for simultaneous and synergistic removal of different sorts of dyestuffs from simulated wastewater. Chem Eng J 385:123926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123926
Chen CJ, Kuang YD, Zhu SZ, Burgert I, Keplinger T, Gong A, Li T, Berglund L, Eichhorn SJ, Hu LB (2020b) Structure-property-function relationships of natural and engineered wood. Nat Rev Mater 5(9):642–666. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-020-0195-z
Chen Y, Huang SA, Yu K, Guo JZ, Wang YX, Li B (2023) Adsorption of lead ions and methylene blue on acrylate-modified hydrochars. Bioresour Technol 379:129067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2023.129067
Cheng F, Liu CY, Wei XJ, Yan TS, Li HB, He JM, Huang YD (2017) Preparation and characterization of 2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl (TEMPO)-oxidized cellulose nanocrystal/alginate biodegradable composite dressing for hemostasis applications. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(5):3819–3828. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02849
de Oliveira GR, Fernandes NS, de Meloa JV, da Silva DR, Urgeghe C, Martinez-Huitle CA (2011) Electrocatalytic properties of Ti-supported Pt for decolorizing and removing dye from synthetic textile wastewaters. Chem Eng J 168(1):208–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.12.070
Dong X, Zhang Z et al (2022) Bio-inspired non-iridescent structural coloration enabled by self-assembled cellulose nanocrystal composite films with balanced ordered/disordered arrays. Compos Part B-Eng 229:109456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109456
Fraschini C, Chauve G, Bouchard J (2017) TEMPO-mediated surface oxidation of cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs). Cellulose 24:2775–2790. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1319-5
French AD (2017) Glucose, not cellobiose, is the repeating unit of cellulose and why that is important. Cellulose 24:4605–4609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1450-3
Gan S, Zakaria S, Chia CH, Kaco H (2018) Effect of graphene oxide on thermal stability of aerogel bio-nanocomposite from cellulose-based waste biomass. Cellulose 25(9):5099–5112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1946-5
Gomes AS, Leal MVG, Tolosa GR, Cabrera FC, Dognani G, Job AE (2023) Cationic dialdehyde cellulose microfibers for efficient removal of eriochrome black T from aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 380:129096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2023.129096
Gupta SV, Kulkarni VV, Ahmaruzzaman M (2024) Fabrication of a bio-adsorbent material by grafting CeO2 quantum dots (QDts) over Areca nut shell biochar using Saccharum officinarum extract as a solvent/capping agent for adsorption of Methylene blue dye: Synthesis, material analyses, adsorption kinetics and isotherms studies. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 680:132611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2023.132611
Gurav R, Bhatia SK, Choi T-R, Choi Y-K, Kim HJ, Song H-S, Lee SM, Park SL, Lee HS, Koh J, Jeon J-M, Yoon J-J, Yang Y-H (2021) Application of macroalgal biomass derived biochar and bioelectrochemical system with Shewanella for the adsorptive removal and biodegradation of toxic azo dye. Chemosphere 264(2):128539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128539
He T, Hua JQ, Chen R-P, Yu L (2021) Adsorption characteristics of methylene blue by a dye-degrading and extracellular polymeric substance-producing strain. J Environ Manage 288:112446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112446
Hu ZY, Guo C, Wang P, Guo R, Liu XW, Tian Y (2022) Electrochemical degradation of methylene blue by Pb modified porous SnO2 anode. Chemosphere 305:135447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135447
Hubbe MA (2021) Insisting upon meaningful results from adsorption experiments. Sep Purif Rev 51(2):212–225. https://doi.org/10.1080/15422119.2021.1888299
Hubbe MA, Azizian S, Douven S (2019) Implications of apparent pseudo-second-order adsorption kinetics onto cellulosic materials: a review. Bioresour 14, 7582–7626. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.14.3.7582-7626
Isogai A (2021) Emerging nanocellulose technologies: recent developments. Adv Mater 33(28):2000630. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202000630
Isogai A, Sait T, Fukuzumi H (2011) TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers. Nanoscale 3(1):71–85. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0NR00583E
Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS, Reghioua A, Yaseen ZM (2020) Zwitterion composite chitosan-epichlorohydrin/zeolite for adsorption of methylene blue and reactive red 120 dyes. Int J Biol Macromol 163:756–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.014
Jia X, Qian MH, Peng WH, Xu X, Zhang YJ, Zhao XL (2023) Synthesis and demulsification properties of poly (DMDAAC-co-DAMBAC) (9:1) copolymer. Polymers 15(3):562. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030562
Jin YH, Liu F, Li YH, Du QJ, Song FL, Chen B, Chen KW, Zhang Y, Wang MZ, Wang DC (2023) Efficient adsorption of azo anionic dye Congo Red by micro-nanometal-organic framework MIL-68(Fe) and MIL-68(Fe)/chitosan composite sponge: Preparation, characterization and adsorption performance. Int J Biol Macromol 120:88–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126198
Kaur P, Shin MS, Park JS, Verma G, Sekhon SS (2018) Supramolecular modification of Carbon Nanofibers with Poly(diallyl dimethylammonium) chloride and Triton X-100 for electrochemical application. Int J Hydrog Energy 43(13):6575–6585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.02.075
Kayan GO, Kayan A (2021) Composite of natural polymers and their adsorbent properties on the dyes and heavy metal ions. J Polym Environ 29(11):3477–3496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02154-x
Khasevani SG, Shahsavari S, Gholami MR (2021) Green synthesis of ternary carbon dots (CDs)/MIL-88B (Fe)/Bi2S3 nanocomposite via MOF templating as a reusable heterogeneous nanocatalyst and nano-photocatalyst. Mater Res Bull 138:111204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2021.111204
Li N, Yang H (2021) Construction of natural polymeric imprinted materials and their applications in water treatment: A review. J Hazard Mate 403(5):123643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123643
Li Y, Xiao HN, Pan YF, Wang LD (2018) Novel composite adsorbent consisting of dissolved cellulose fiber/microfibrillated cellulose for dye removal from Aqueous Solution. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(5):6994–7002. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b00829
Li HJ, Miao L, Zhao GQ, Jia WZ, Zhu ZR (2022) Preparation of high-performance chitosan adsorbent by cross-linking for adsorption of Reactive Red 2 (RR2) dye wastewater. J Environ Chem Eng 10(6):108872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108872
Ma J, Ma Y, A, Yu F, (2018) Novel One-Pot Route for Large-Scale Synthesis of Novel Magnetic CNTs/Fe@C Hybrids and Their Applications for Binary Dye Removal. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(7):8178–8191. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b04668
Mittal H, Babu R, Alhassan SM (2020) Utilization of gum xanthan based superporous hydrogels for the effective removal of methyl violet from aqueous solution. Int J Biol Macromol 143:413–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.11.008
Mittal H, Al Alili A, Morajkar PP, Alhassan SM (2021) GO crosslinked hydrogel nanocomposites of chitosan/carboxymethyl cellulose-A versatile adsorbent for the treatment of dyes contaminated wastewater. Int J Biol Macromol 167:1248–1261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.11.079
Momina, Ahmad K (2023) Feasibility of the adsorption as a process for its large scale adoption across industries for the treatment of wastewater: Research gaps and economic assessment. J Clean Prod 388:136014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136014
Munk M, Camargo LSA, Quintão CCR, Silva SR, Souza ED, Raposo NRB, Marconcini JM, Jorio A, Ladeira LO, Brandão HM (2016) Biocompatibility assessment of fibrous nanomaterials in mammalian embryos. Nanomedicine 12(5):1151–1159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2016.01.006
Nan BF, Wu K, Qu ZC, Xiao LQ, Xu CG, Shi J, Lu MG (2020) A multifunctional thermal management paper based on functionalized graphene oxide nanosheets decorated with nanodiamond. Carbon 161:132–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.01.056
Oyarce E, Butter B, Santander P, Sánchez J (2021) Polyelectrolytes applied to remove methylene blue and methyl orange dyes from water via polymer-enhanced ultrafiltration. J Environ Chem Eng 9(6):106297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106297
Pandey A (2021) Pharmaceutical and biomedical applications of cellulose nanofibers: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19(3):2043–2055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-021-01182-2
Pathania D, Araballi A, Fernandes F, Shivanna JM, Sriram G, Kurkuri M, Hegde G, Aminabhavi TM (2023) Cost effective porous areca nut carbon nanospheres for adsorptive removal of dyes and their binary mixtures. Environ Res 224:115521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.115521
Routoula E, Patwardhan SV (2020) Degradation of anthraquinone dyes from effluents: A review focusing on enzymatic dye degradation with industrial potential. Environ Sci Technol 54(2):647–664. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b03737
Shan H, Poredos P, Ye ZY, Qu H, Zhang YX, Zhou MJ, Wang RZ, Tan SC (2023) All-Day Multicyclic Atmospheric Water Harvesting Enabled by Polyelectrolyte Hydrogel with Hybrid Desorption Mode. Adv Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202302038
Sheha RR, El-Zahhar AA (2008) Synthesis of some ferromagnetic composite resins and their metal removal characteristics in aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 150(3):795–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.05.042
Shi YW, Chang Q, Zhang TW, Song GB, Sun Y, Ding GH (2022a) A review on selective dye adsorption by different mechanisms. J Environ Chem Eng 10(6):108639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108,639
Shi YW, Song GB, Li AQ, Wang J, Wang HA, Sun Y, Ding GH (2022b) Graphene oxide-chitosan composite aerogel for adsorption of methyl orange and methylene blue: Effect of pH in single and binary systems. Colloid Surface A 641:128595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.128595
Surendran G, Sherje AP (2022) Cellulose nanofibers and composites: An insight into basics and biomedical applications. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 75:103601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2022.103601
Tan Q, Jia XY, Dai R, Chang HQ, Woo MW, Chen H (2023) Synthesis of a novel magnetically recyclable starch-based adsorbent for efficient adsorption of crystal violet dye. Sep Purif Technol 320(1):124157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.124157
Tran HN, You SJ, Hosseini-Bandegharaei A, Chao HP (2017) Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: a critical review. Water Res 120:88–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.04.014
Uddin F (2021) Environmental hazard in textile dyeing wastewater from local textile industry. Cellulose 28(17):10715–10739. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04228-4
Wang JL, Guo X (2020) Adsorption kinetic models: Physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. J Hazard Mater 390:122156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122156
Wang JL, Guo X (2022) Rethinking of the intraparticle diffusion adsorption kinetics model: Interpretation, solving methods and applications. Chemosphere 309(2):136732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136732
Wang JL, Guo X (2023) Adsorption kinetics and isotherm models of heavy metals by various adsorbents: an overview. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 53(21):1837–1865. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2023.2221157
Webber TW, Chakkravorti RK (1974) Pore and solid diffusion models for fixed-bed adsorbers. AIChE J 20:228–238. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.690200204
Wei JJ, Zhou CL, Zeng ZH, Pan F, Wang FQ, Lei LW, Nyström G, Fu ZY (2022) Bioinspired cellulose-integrated MXene-based hydrogels for multifunctional sensing and electromagnetic interference shielding. Interdiscip Mater 1(4):495–506. https://doi.org/10.1002/idm2.12026
Wu T, Song YH, Shi ZQ, Liu DN, Chen SL, Xiong CX, Yang QL (2021) High-performance nanogenerators based on flexible cellulose nanofibril/MoS2 nanosheet composite piezoelectric films for energy harvesting. Nano Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.105541
Xiang YF, Banks MK, Wu RX, Xu WJ, Chen S (2018) Synthesis of thermo-sensitive PDDA-co-PNIPAM/graphene hybrid via electrostatic interactions and its thermal modulated phase transition. Mater Chem Phys 220:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.08.070
Xu DS, Kong QM, Wang XJ, Lou T (2022) Preparation of carboxymethyl cellulose/chitosan-CuO giant vesicles for the adsorption and catalytic degradation of dyes. Carbohydr Polym 291:119630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119630
Xue JH, Zhu EW, Zhu HF, Liu DN, Cai HP, Xiong CX, Yang QL, Shi ZQ (2022) Dye adsorption performance of nanocellulose beads with different carboxyl group content. Cellulose 30(3):1623–1636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04964-1
You JY, Liu C, Feng X, Lu BW, Xia L, Zhuang XP (2022) In situ synthesis of ZnS nanoparticles onto cellulose/chitosan sponge for adsorption-photocatalytic removal of Congo red. Carbohydr Polym 288:119332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119332
Yu SJ, Pang HW, Huang SY, Tang H, Wang SQ, Qiu MQ, Chen ZS, Yang H, Song G, Fu D, Hu BW, Wang XX (2021) Recent advances in metal-organic framework membranes for water treatment: A review. Sci Total Environ 800:149662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149662
Zhan YF, Yang L, Lan JW, Shang JJ, Chen SQ, Guan XM, Li WX, Lin SJ (2021) Mussel-inspired polydopamine decorated pomelo peel as a durable biosorbent for adsorption of cationic dyes. Cellulose 28(1):453–470. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03541-8
Zhao HY, Dong WX, Deng Y, Chen LF, Zhang CF, Zhang CL, Zhou J, Qu LF, Li YS, Li DJ, Yu SH (2022) Biomass-based biomimetic-oriented Janus nanoarchitecture for efficient heavy-metal enrichment and interfacial solar water sanitation. Interdiscip Mater 1(4):537–547. https://doi.org/10.1002/idm2.12057
Zhou YB, Hu YH, Huang WW, Cheng G, Cui CZ, Lu J (2018) A novel amphoteric beta-cyclodextrin-based adsorbent for simultaneous removal of cationic/anionic dyes and bisphenol A. Chem Eng J 341:47–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.155
Zhu HF, Zhu EW, Xie YY, Liu DN, Hu Y, Shi ZQ, Xiong CX, Yang QL (2022) Hydrangea-like nanocellulose microspheres with high dye adsorption and drug encapsulation prepared by emulsion method. Carbohydr Polym 296:119947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119947
Acknowledgments
The research was financially supported by the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. ZR20210302328).
Funding
Funding was provided by the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. ZR20210302328).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ru Song: Writing—original draft, Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis. Enwen Zhu: Writing—review & editing, Validation, Investigation, Data curation, Visualization. Runqing Hou: Investigation. Fukun Niu: Investigation. Jiangkai Bao: Investigation. Dan Chen: Investigation. Zhuqun Shi: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Writing—review & editing, Supervision. Quanling Yang: Investigation, Writing—review & editing. Chuanxi Xiong: Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Compliance with Ethical Standards.
Consent for publication
All authors were informed and agreed to publish in Cellulose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, R., Zhu, E., Hou, R. et al. Nanocellulose-based composite beads as the amphoteric adsorbent for effective adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes. Cellulose (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05835-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05835-7