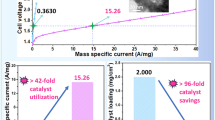
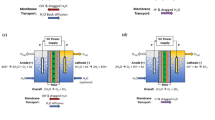
Abstract
A series of nanocomposites based on quaternized polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and nanocellulose (NC) from oil palm empty fruit bunch have been used as anion exchange membranes (AEM) for direct alcohol-hydrogen peroxide fuel cell (DAHPFC) applications. The PVA and NC are individually quaternized with hexadecyltrimethyl ammonium bromide (HDT) and glycidyltrimethyl ammonium chloride (GAC), cross-linked, and cast to form quaternized polyvinyl alcohol/quaternized nanocellulose (QPVA/QNC) membranes following thermal treatment. We observe that an increase of QNC quaternization degree increases quaternary ammonium content and the dimensional stability of the QPVA/QNC membranes while inhibiting PVA matrix crystallinity, decreasing both HDT dispersal and membrane thermal stability. We determine that QPVA/QNCGAC30% membranes exhibit a maximum ion conductivity of 9.85 ± 0.07 mS/cm at room temperature and 29.07 ± 1.76 mS/cm at 80 °C with an ion exchange capacity of approximately 1.14 meq/g. Addition of QNC also enhances the alkaline stability of the optimized QPVA/QNC membrane with less ion conductivity loss. Optimized QPVA/QNC membranes have been demonstrated as an AEM in DAHPFCs without the use of platinum based catalysts. Compared with other membranes, we believe this nanocomposite membrane with comparable performances can promise AEM application in DAHPFCs.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AEM :
-
Anion exchange membrane
- DAFC :
-
Direct alcohol fuel cell
- DAHPFC :
-
Direct alcohol-hydrogen peroxide fuel cell
- FE-TEM :
-
Field emission transmission electron microscopy
- FT-IR :
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- GAC :
-
Glycidyltrimethyl ammonium chloride
- HDT :
-
Hexadecyltrimethyl ammonium bromide
- IEC :
-
Ion exchange capacity
- NC :
-
Nanocellulose
- OPEFB :
-
Oil palm empty fruit bunch
- PVA :
-
Polyvinyl alcohol
- QNC :
-
Quaternized nanocellulose
- QPVA :
-
Quaternized polyvinyl alcohol
- SEM :
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- TGA :
-
Thermo gravimetric analysis
- XPS:
-
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
- XRD :
-
X-ray diffraction
References
Abdullah Mirzaie R, Eshghi A (2014) Study of methanol electro-oxidation on Ni and Ni-Pt/carbon paper electrodes for direct methanol fuel cell applications. Surf Eng 30:263–267. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743294414Y.0000000248
Amirfakhri SJ, Binny D, Meunier JL, Berk D (2014) Investigation of hydrogen peroxide reduction reaction on graphene and nitrogen doped graphene nanoflakes in neutral solution. J Power Sources 257:356–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.01.114
An L, Zhao TS, Zeng L, Yan XH (2014) Performance of an alkaline direct ethanol fuel cell with hydrogen peroxide as oxidant. Int J Hydrogen Energy 39:2320–2324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.11.072
Bolto B, Tran T, Hoang M, Xie Z (2009) Crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes. Prog Polym Sci 34:969–981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2009.05.003
Cheng X, Wang J, Liao Y et al (2018) Enhanced conductivity of anion-exchange membrane by incorporation of quaternized cellulose nanocrystal. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:23774–23782. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b05298
Das G, Park BJ, Yoon HH (2016) A bionanocomposite based on 1,4-diazabicyclo-[2.2.2]-octane cellulose nanofiber cross-linked-quaternary polysulfone as an anion conducting membrane. J Mater Chem A 4:15554–15564. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta05611c
Fadzillah DM, Kamarudin SK, Zainoodin MA, Masdar MS (2019) Critical challenges in the system development of direct alcohol fuel cells as portable power supplies: an overview. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44:3031–3054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.11.089
Fahma F, Iwamoto S, Hori N et al (2010) Isolation, preparation, and characterization of nanofibers from oil palm empty-fruit-bunch (OPEFB). Cellulose 17:977–985. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-010-9436-4
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
French AD (2017) Glucose, not cellobiose, is the repeating unit of cellulose and why that is important. Cellulose 24:4605–4609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1450-3
French AD, Johnson GP (2009) Cellulose and the twofold screw axis: modeling and experimental arguments. Cellulose 16:959–973. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-009-9347-4
Gaur SS, Dhar P, Sonowal A et al (2017) Thermo-mechanically stable sustainable polymer based solid electrolyte membranes for direct methanol fuel cell applications. J Memb Sci 526:348–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.12.030
Gautam SP, Bundela PS, Pandey AK et al (2010) A review on systematic study of cellulose. J Appl Nat Sci 2:330–343. https://doi.org/10.31018/jans.v2i2.143
Gopi KH, Peera SG, Bhat SDD et al (2014) Preparation and characterization of quaternary ammonium functionalized poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) as anion exchange membrane for alkaline polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Int J Hydrogen Energy 39:2659–2668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.12.009
Gopi KH, Bhat SD, Sahu AK, Sridhar P (2016) Quaternized poly(phenylene oxide) anion exchange membrane for alkaline direct methanol fuel cells in KOH-free media. J Appl Polym Sci 133:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.43693
Goto T, Zaccaron S, Bacher M et al (2021) On nitrogen fixation and “residual nitrogen content” in cellulosic pulps. Carbohydr Polym 253:117235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117235
Hari Gopi K, Bhat SD (2018) Anion exchange membrane from polyvinyl alcohol functionalized with quaternary ammonium groups via alkyl spacers. Ionics 24:1097–1109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2272-x
Hari Gopi K, Dhavale VM, Bhat SD (2019) Development of polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan blend anion exchange membrane with mono and di quaternizing agents for application in alkaline polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Mater Sci Energy Technol 2:194–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mset.2019.01.010
Hou C, Wu Y, Wang T et al (2019) preparation of quaternized bamboo cellulose and its implication in direct air capture of CO2. Energy Fuels 33:1745–1752. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.8b02821
Imaan DU, Mir FQ, Ahmad B (2021) Synthesis and characterization of a novel poly(vinyl alcohol)-based zinc oxide (PVA-ZnO) composite proton exchange membrane for DMFC. Int J Hydrogen Energy 46:12230–12241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.05.008
Ioelovich M (2018) Determination of distortions and sizes of cellulose nanocrystallites. Res J Nanosci Eng 2:23–27. https://doi.org/10.22259/2637-5591.0201004
Ioelovich M (2021) Adjustment of hydrophobic properties of cellulose materials. Polymers. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13081241
Jiang GP, Zhang J, Qiao JL et al (2015) Bacterial nanocellulose/Nafion composite membranes for low temperature polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J Power Sources 273:697–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.09.145
Jose J, Thomas V, Vinod V et al (2019) Nanocellulose based functional materials for supercapacitor applications. J Sci Adv Mater Devices 4:333–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2019.06.003
Kumar SR, Ma WT, Lu HC et al (2017) Surfactant-assisted perovskite nanofillers incorporated in quaternized poly(vinyl alcohol) composite membrane as an effective hydroxide-conducting electrolyte. Energies 10:1–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10050615
Kyle S, Jessop ZM, Al-Sabah A et al (2018) Characterization of pulp derived nanocellulose hydrogels using AVAP® technology. Carbohydr Polym 198:270–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.06.091
Lei L, Zhu X, Xu J et al (2017) Highly stable ionic-covalent cross-linked sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) for direct methanol fuel cells. J Power Sources 350:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.03.046
Lin JS, Kumar SR, Ma WT et al (2017) Gradiently distributed iron oxide@graphene oxide nanofillers in quaternized polyvinyl alcohol composite to enhance alkaline fuel cell power density. J Memb Sci 543:28–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2017.08.045
Lu Y, Armentrout AA, Li J et al (2015) A cellulose nanocrystal-based composite electrolyte with superior dimensional stability for alkaline fuel cell membranes. J Mater Chem A 3:13350–13356. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ta02304a
Mahendra IP, Wirjosentono B, Tamrin et al (2019) Thermal and morphology properties of cellulose nanofiber from TEMPO-oxidized lower part of empty fruit bunches (LEFB). Open Chem 17:526–536. https://doi.org/10.1515/chem-2019-0063
Mandal A, Chakrabarty D (2011) Isolation of nanocellulose from waste sugarcane bagasse (SCB) and its characterization. Carbohydr Polym 86:1291–1299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.06.030
Mandal A, Chakrabarty D (2014) Studies on the mechanical, thermal, morphological and barrier properties of nanocomposites based on poly(vinyl alcohol) and nanocellulose from sugarcane bagasse. J Ind Eng Chem 20:462–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.05.003
Mansur HS, Sadahira CM, Souza AN, Mansur AAP (2008) FTIR spectroscopy characterization of poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel with different hydrolysis degree and chemically crosslinked with glutaraldehyde. Mater Sci Eng C 28:539–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2007.10.088
Matsuoka K, Iriyama Y, Abe T et al (2005) Alkaline direct alcohol fuel cells using an anion exchange membrane. J Power Sources 150:27–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2005.02.020
Merle G, Wessling M, Nijmeijer K (2011) Anion exchange membranes for alkaline fuel cells: a review. J Memb Sci 377:1–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2011.04.043
Merle G, Hosseiny SS, Wessling M, Nijmeijer K (2012) New cross-linked PVA based polymer electrolyte membranes for alkaline fuel cells. J Memb Sci 409–410:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2012.03.056
Muhmed SA, Nor NAM, Jaafar J et al (2020) Emerging chitosan and cellulose green materials for ion exchange membrane fuel cell: a review. Energy Ecol Environ 5:85–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-019-00127-4
Murmu R, Roy D, Patra SC et al (2022) Preparation and characterization of the SPEEK/PVA/Silica hybrid membrane for direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC). Polym Bull 79:2061–2087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-03602-3
Okahisa Y, Furukawa Y, Ishimoto K et al (2018) Comparison of cellulose nanofiber properties produced from different parts of the oil palm tree. Carbohydr Polym 198:313–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.06.089
Okahisa Y, Matsuoka K, Yamada K, Wataoka I (2020) Comparison of polyvinyl alcohol films reinforced with cellulose nanofibers derived from oil palm by impregnating and casting methods. Carbohydr Polym 250:116907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116907
Pan ZFF, An L, Zhao TSS, Tang ZKK (2018) Advances and challenges in alkaline anion exchange membrane fuel cells. Prog Energy Combust Sci 66:141–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2018.01.001
Pei A, Butchosa N, Berglund LA, Zhou Q (2013) Surface quaternized cellulose nanofibrils with high water absorbency and adsorption capacity for anionic dyes. Soft Matter 9:2047–2055. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2sm27344f
Poux T, Bonnefont A, Ryabova A et al (2014) Electrocatalysis of hydrogen peroxide reactions on perovskite oxides: experiment versus kinetic modeling. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:13595–13600. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cp00341a
Rajesh Kumar S, Juan CH, Liao GM et al (2016) fumed silica nanoparticles incorporated in quaternized poly(vinyl alcohol) nanocomposite membrane for enhanced power densities in direct alcohol alkaline fuel cells. Energies. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9010015
Rhim J-W, Park HB, Lee C-S et al (2004) Crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes containing sulfonic acid group: proton and methanol transport through membranes. J Memb Sci 238:143–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2004.03.030
Rong N, Chen C, Ouyang K et al (2021) Adsorption characteristics of directional cellulose nanofiber/chitosan/montmorillonite aerogel as adsorbent for wastewater treatment. Sep Purif Technol 274:119120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119120
Rynkowska E, Fatyeyeva K, Marais S et al (2019) Chemically and thermally crosslinked PVA-based membranes: effect on swelling and transport behavior. Polymers 11:7–9. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111799
Shaari N, Kamarudin SK, Zakaria Z (2019) Enhanced alkaline stability and performance of alkali-doped quaternized poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes for passive direct ethanol fuel cell. Int J Energy Res 43:5252–5265. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.4513
Shang Z, An X, Seta FT et al (2019) Improving dispersion stability of hydrochloric acid hydrolyzed cellulose nano-crystals. Carbohydr Polym 222:115037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115037
Shettigar RR, Misra NM, Patel K (2018) Cationic surfactant (CTAB) a multipurpose additive in polymer-based drilling fluids. J Pet Explor Prod Technol 8:597–606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13202-017-0357-8
Slade RCT, Varcoe JR (2005) Investigations of conductivity in FEP-based radiation-grafted alkaline anion-exchange membranes. Solid State Ionics 176:585–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2004.09.044
Syverud K, Xhanari K, Chinga-Carrasco G et al (2011) Films made of cellulose nanofibrils: surface modification by adsorption of a cationic surfactant and characterization by computer-assisted electron microscopy. J Nanoparticle Res 13:773–782. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-0077-1
Tasci TO, Herson PS, Neeves KB, Marr DWM (2016) Surface-enabled propulsion and control of colloidal microwheels. Nat Commun 7:10225. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10225
Varcoe JR, Atanassov P, Dekel DR et al (2014) Anion-exchange membranes in electrochemical energy systems. Energy Environ Sci 7:3135–3191. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ee01303d
Vilčiauskas L, Kreuer K-D (2011) Comment on “mixed grotthuss and vehicle transport mechanism in proton conducting polymers from ab initio molecular dynamics simulations.” Chem Mater 23:3377–3378. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm200865v
Vilela C, Silvestre AJD, Figueiredo FML, Freire CSR (2019) Nanocellulose-based materials as components of polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J Mater Chem A 7:20045–20074. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TA07466J
Xiong Y, Fang J, Zeng QH, Liu QL (2008) Preparation and characterization of cross-linked quaternized poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes for anion exchange membrane fuel cells. J Memb Sci 311:319–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2007.12.029
Xu F, Su Y, Lin B (2020) progress of alkaline anion exchange membranes for fuel cells: the effects of micro-phase separation. Front Mater 7:1–7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2020.00004
Yan XH, Zhao TS, An L et al (2016) A direct methanol-hydrogen peroxide fuel cell with a Prussian Blue cathode. Int J Hydrogen Energy 41:5135–5140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.01.066
Yang CC (2012) Alkaline direct methanol fuel cell based on a novel anion-exchange composite polymer membrane. J Appl Electrochem 42:305–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-012-0395-3
Yang C-C, Chiu S-J, Lee K-T et al (2008) Study of poly(vinyl alcohol)/titanium oxide composite polymer membranes and their application on alkaline direct alcohol fuel cell. J Power Sources 184:44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.06.011
Yang W, Qi G, Kenny JM et al (2020) Effect of cellulose nanocrystals and lignin nanoparticles on mechanical, antioxidant and water vapour barrier properties of glutaraldehyde crosslinked pva films. Polymers 12:1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061364
Yu EH, Krewer U, Scott K (2010) Principles and materials aspects of direct alkaline alcohol fuel cells. Energies 3:1499–1528. https://doi.org/10.3390/en3081499
Yunphuttha C, Porntheeraphat S, Wongchaisuwat A et al (2016) Characterization of La1−xSrx MnO3 perovskite catalysts for hydrogen peroxide reduction. Phys Chem Chem Phys 18:16786–16793. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP02338J
Yunphuttha C, Porntheeraphat S, Midpanon S et al (2018) Improving the catalytic activity of lanthanum manganese oxide with strontium doping for hydrogen peroxide reduction reaction in micro direct alcohol-hydrogen peroxide fuel cell. J Power Sources 392:251–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.04.072
Zakaria Z, Kamarudin SK (2020) A review of quaternized polyvinyl alcohol as an alternative polymeric membrane in DMFCs and DEFCs. Int J Energy Res 44:6223–6239. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.5314
Zakaria Z, Shaari N, Kamarudin SK (2018) Preliminary study of alkaline direct ethanol fuel cell by using crosslinked quaternized poly(vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide membrane (kajian awal sel fuel etanol langsung beralkali menggunakan membran elektrolit berasaskan alkohol polivinil terkuaternisasi/grafin oksida). J Kejuruter 30:219–227. https://doi.org/10.17576/jkukm-2018-30(2)
Zeng G, Han J, Dai B et al (2017) preparation and characterization of alkaline anion exchange membrane for fuel cells application. J Nanotechnol 2017:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3701378
Zhang J, Wu J, Yu J et al (2017) Application of ionic liquids for dissolving cellulose and fabricating cellulose-based materials: state of the art and future trends. Mater Chem Front 1:1273–1290. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6qm00348f
Zhou T, Wang M, He X, Qiao J (2019) Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) anion-exchange membrane modified with multiwalled carbon nanotubes for alkaline fuel cells. J Mater 5:286–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmat.2019.01.012
Zhu H, Zhang M, Cai S et al (2014) In situ growth of Rh nanoparticles with controlled sizes and dispersions on the cross-linked PVA-PEI nanofibers and their electrocatalytic properties towards H2O2. RSC Adv 4:794–804. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ra44834g
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Office of the Ministry of Higher Education, Science, Research and Innovation and the Thailand Science Research and Innovation through the Kasetsart University Reinventing University Program 2021. We are grateful to the Department of Chemistry at Faculty of Science, Scientific Equipment Center and Center of Excellence-Oil Palm, Kasetsart University Research and Development Institute, Kasetsart University, and Suksomboon Palm Oil Co., Ltd. for their support.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Office of the Ministry of Higher Education, Science, Research and Innovation and the Thailand Science Research and Innovation through the Kasetsart University (Reinventing University Program 2021). Other supports were received from the Department of Chemistry at Faculty of Science, Scientific Equipment Center and Center of Excellence-Oil Palm, Kasetsart University Research and Development Institute, Kasetsart University, and Suksomboon Palm Oil Co., Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the work by designing the research, analyzing data, troubleshooting, and giving discussion. Material preparation, data collection, and writing the draft were performed by CY (the first author). All authors commented the draft and gave the suggestion. The first author and the corresponding author edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare they have no financial interests. Disclosure of Conflict of Interest Statement is enclosed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yunphuttha, C., Midpanon, S., Marr, D.W.M. et al. Polyvinyl alcohol/nanocellulose nanocomposites from oil palm empty fruit bunch as anion exchange membranes for direct alcohol-hydrogen peroxide fuel cells. Cellulose 31, 1569–1601 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05692-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05692-w