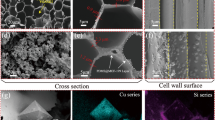
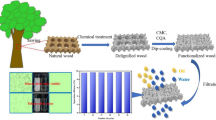
Abstract
Oily wastewater causes a serious threat to the ecological environment and human health, how to effectively treat oily wastewater is a big concern. In recent years, the treatment of oil–water emulsions has considerably advanced through the development of separation membranes with special wettability, However, these membranes involve problems, such as complex preparation processes and material contamination, so developing an economical and environmentally friendly, high-performance membrane is a significant challenge. In this work, a wood-based membrane was easily prepared by a simple dipping process using aramid nanofibers (ANFs) to modify the surface of wood. Compared to synthetic hydrogel membranes, the wet ANF/wood membrane exhibits higher tensile strength (1.69 ± 0.32 MPa). More importantly, the membrane presents underwater superoleophobic properties and fouling resistance under complex environmental conditions (acid, alkali, seawater, and high temperature) and effectively separates various oil–water emulsions with high separation efficiency (> 99.3%) and flux (> 227 L m−2 h−1). More excitingly, the membrane retains its original separation properties after 13 cycles of oil–water emulsion separation. Therefore, the inexpensive, environmentally friendly and easily prepared ANF/wood membrane is well tolerated under extreme conditions, presents excellent separation performance and provides a material basis for the treatment of actual oily wastewater.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Ahmad N, Rasheed S, Ahmed K, Musharraf SG, Najam-ul-Haq M, Hussain D (2023) Facile two-step functionalization of multifunctional superhydrophobic cotton fabric for UV-blocking, self cleaning, antibacterial, and oil-water separation. Sep Purif Technol 306:122626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122626
Annabi N, Shin SR, Tamayol A, Miscuglio M, Bakooshli MA, Assmann A, Mostafalu P, Sun JY, Mithieux S, Cheung L (2016) Highly elastic and conductive human-based protein hybrid hydrogels. Adv Mater 28:40–49. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201503255
Bai X, Shen Y, Tian H, Yang Y, Feng H, Li J (2019) Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic wood slice for effective water-in-oil emulsion separation. Sep Purif Technol 210:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.08.010
Cai Z, Chen F, Tian Y, Zhang D, Lian Z, Cao M (2022) Programmable droplet transport on multi-bioinspired slippery surface with tridirectionally anisotropic wettability. Chem Eng J 449:137831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.137831
Cao H, Gu W, Fu J, Liu Y, Chen S (2017) Preparation of superhydrophobic/oleophilic copper mesh for oil-water separation. Appl Surf Sci 412:599–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.04.012
Chen C, Li Z, Hu Y, Huang Q, Li X, Qing Y, Wu Y (2022) Rosin acid and SiO2 modified cotton fabric to prepare fluorine-free durable superhydrophobic coating for oil-water separation. J Hazard Mater 440:129797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129797
Chen G, Li T, Chen C, Kong W, Jiao M, Jiang B, Xia Q, Liang Z, Liu Y, He S et al (2021) Scalable wood hydrogel membrane with nanoscale channels. ACS Nano 15:11244–11252. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c10117
Deng Y, Peng C, Dai M, Lin D, Ali I, Alhewairini SS, Zheng X, Chen G, Li J, Naz I (2020) Recent development of super-wettable materials and their applications in oil-water separation. J Clean Prod 266:121624. https://doi.org/10.1616/j.jclepro.2020.121624
Dong D, Zhu Y, Fang W, Ji M, Wang A, Gao S, Lin H, Huang R, Jin J (2022) Double-defense design of super-anti-fouling membranes for oil/water emulsion separation. Adv Funct Mater 32:2113247. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.2021132m.202113247
Songfeng E, Geng B, Ji X, Ning D, Ma Q, Zhao R, Sha L, Lu Z (2023) In-situ assembling inorganic nanoparticles on the surface of aramid nanofibers for the enhanced mechanical and insulation performances of the prepared nanopapers. Compos Sci Technol 235:110026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2023.110026
Fu Q, Ansari F, Zhou Q, Berglund LA (2018) Wood nanotechnology for strong, mesoporous, and hydrophobic biocomposites for selective separation of oil/water mixtures. ACS Nano 12:2222–2230. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b00005
Gao J, Wang J, Xu Q, Wu S, Chen Y (2021) Regenerated cellulose strongly adhered by a supramolecular adhesive onto the PVDF membrane for a highly efficient oil/water separation. Green Chem 23:5633–5646. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1GC01998H
Guo Y, Gong L, Gao S, Zhu Y, Zhang F, Li J, Jin J (2020) Cupric phosphate mineralized polymer membrane with superior cycle stability for oil/water emulsion separation. J Membrane Sci 612:118427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2020.118427
Han M, Zhang J, Chu W, Chen J, Zhou G (2019) Research progress and prospects of marine oily wastewater treatment: a review. Water 11:2517. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122517
Huang J, Zhang Z, Weng J, Yu D, Liang Y, Xu X, Qiao Z, Zhang G, Yang H, Wu X (2020) Molecular understanding and design of porous polyurethane hydrogels with ultralow-oil-adhesion for oil–water separation. ACS Appl Mater Inter 12:56530–56540. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c18825
Jia C, Li Y, Yang Z, Chen G, Yao Y, Jiang F, Kuang Y, Pastel G, Xie H, Yang B (2017) Rich mesostructures derived from natural woods for solar steam generation. Joule 1:588–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2017.09.011
Jiang Y, Xian C, Xu X, Zheng W, Zhu T, Cai W, Huang J, Lai Y (2023) Robust PAAm-TA hydrogel coated PVDF membranes with excellent crude-oil antifouling ability for sustainable emulsion separation. J Membrane Sci 667:121166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2022.121166
Kim S, Kim K, Jun G, Hwang W (2020) Wood-nanotechnology-based membrane for the efficient paurification of oil-in-water emulsions. ACS Nano 14:17233–17240. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c07206
Kong Q, Ren X, Li Z (2023) Three-dimensional porous structure on cotton fabric through the breath figure method with functions of self-cleaning and oil/water separation. Cellulose 30:3915–3930. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05087-x
Li F, Kong W, Zhao X, Pan Y (2020) Multifunctional TiO2-based superoleophobic/superhydrophilic coating for oil–water separation and oil purification. ACS Appl Mater Inter 12:18074–18083. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b22625
Li X, Gui Q, Wei Y, Feng L (2021a) Novel superwetting nanofibrous skins for removing stubborn soluble oil in emulsified wastewater. J Mater Chem A 9:26127–26134. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1TA08628F
Li X, Liu J, Qu R, Zhang W, Liu Y, Zhai H, Wei Y, Hu H, Feng L (2021b) Universal and tunable liquid–liquid separation by nanoparticle-embedded gating membranes based on a self-defined interfacial parameter. Nat Commun 12:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20369-9
Liu T, Liu Z, Zhou Z, Shi SQ, Aladejana JT, Gong S, Fang Z, Li J (2023) A novel sol-gel strategy for constructing wood fibers and aramid nanofiber nanocomposite with strong, tough and recyclable properties. Compos Sci Technol 238:109975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2023.109975
Liu Y, Yin J, Fu Y, Zhao P, Zhang Y, He B, He P (2020) Underwater superoleophobic APTES-SiO2/PVA organohydrogel for low-temperature tolerant, self-healing, recoverable oil/water separation mesh. Chem Eng J 382:122925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122925
Mosadegh-Sedghi S, Rodrigue D, Brisson J, Iliuta MC (2014) Wetting phenomenon in membrane contactors–causes and prevention. J Membrane Sci 452:332–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.09.055
Nayak K, Tripathi BP (2021) Molecularly grafted PVDF membranes with in-air superamphiphilicity and underwater superoleophobicity for oil/water separation. Sep Purif Technol 259:118068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.118068
Shi G, Shen Y, Mu P, Wang Q, Yang Y, Ma S, Li J (2020) Effective separation of surfactant-stabilized crude oil-in-water emulsions by using waste brick powder-coated membranes under corrosive conditions. Green Chem 22:1345–1352. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9GC04178H
Su L, Ma X, Zhou J, Liu X, Du F, Teng C (2022) Large-scale preparation of high-performance boron nitride/aramid nanofiber dielectric composites. Nano Res 15:8648–8655. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4456-6
Su M, Liu Y, Li S, Fang Z, He B, Zhang Y, Li Y, He P (2019) A rubber-like, underwater superoleophobic hydrogel for efficient oil/water separation. Chem Eng J 361:364–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.12.082
Teng C, Xie D, Wang J, Zhu Y, Jiang L (2016) A strong, underwater superoleophobic PNIPAM–clay nanocomposite hydrogel. J Mater Chem A 4:12884–12888. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA03548E
Wang J, Ma X, Su L, Zhang C, Dong X, Teng C, Jiang L, Yu C (2022a) Eco-friendly perforated kelp membrane with high strength for efficient oil/water separation in a complex environment. Sep Purif Technol 282:120114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.120114
Wang J, Ma X, Zhou J, Du F, Teng C (2022b) Bioinspired, high-strength, and flexible mxene/aramid fiber for electromagnetic interference shielding papers with joule heating performance. ACS Nano 16:6700–6711. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c01323
Wang Y, Liu Z, Wei X, Liu K, Wang J, Hu J, Lin J (2021a) An integrated strategy for achieving oil-in-water separation, removal, and anti-oil/dye/bacteria-fouling. Chem Eng J 413:127493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127493
Wang Y, Wang J, Ding Y, Zhou S, Liu F (2021b) In situ generated micro-bubbles enhanced membrane antifouling for separation of oil-in-water emulsion. J Membrane Sci 621:119005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2020.119005
Wang Z, Guo P, Heng L, Jiang L (2021c) Nano/submicrometer-emulsion oily wastewater treatment inspired by plant transpiration. Matter 4:1274–1286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matt.2021.01.017
Wei W, Sun M, Zhang L, Zhao S, Wu J, Wang J (2017) Underwater oleophobic PTFE membrane for efficient and reusable emulsion separation and the influence of surface wettability and pore size. Sep Purif Technol 189:32–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.07.074
Wu J, Wei W, Li S, Zhong Q, Liu F, Zheng J, Wang J (2018) The effect of membrane surface charges on demulsification and fouling resistance during emulsion separation. J Membrane Sci 563:126–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msci.2018.05.065
Xu M, Zhang H, Peng W, Ruan X, Chen L, Dai X, Dai J (2023) Eco-friendly fabrication of porphyrin@hyperbranched polyamide-amine@phytic acid/PVDF membrane for superior oil-water separation and dye degradation. Appl Surf Sci 608:155075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.155075
Yan L, Liu C, Xia J, Chao M, Wang W, Gu J, Chen T (2020) CNTs/TiO2 composite membrane with adaptable wettability for on-demand oil/water separation. J Cleaner Prod 275:124011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124011
Yang M, Cao K, Sui L, Qi Y, Zhu J, Waas A, Arruda EM, Kieffer J, Thouless M, Kotov NA (2011) Dispersions of aramid nanofibers: A new nanoscale building block. ACS Nano 5:6945–6954. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn2014003
Yang S, Chen L, Wang S, Liu S, Xu Q, Zhu J, Zhang Q, Zhao P (2022) Honeycomb-like cobalt hydroxide nanosheets induced basalt fiber fabrics with robust and durable superhydrophobicity for anti-icing and oil-water separation. J Hazard Mater 429:128284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128284
Yang Y, Zhao X, Ye L (2023) Facile construction of durable superhydrophobic cellulose paper for oil–water separation. Cellulose 30:3255–3265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05074-2
Yong J, Chen F, Huo J, Fang Y, Yang Q, Bian H, Li W, Wei Y, Dai Y, Hou X (2018) Green, biodegradable, underwater superoleophobic wood sheet for efficient oil/water separation. ACS Omega 3:1395–1402. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.7b02064
Zeng F, Chen X, Xiao G, Li H, Xia S, Wang J (2020) A bioinspired ultratough multifunctional mica-based nanopaper with 3D aramid nanofiber framework as an electrical insulating material. ACS Nano 14:611–619. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b07192
Zhang H, Shen Y, Li M, Zhu G, Feng H, Li J (2019) Egg shell powders-coated membrane for surfactant-stabilized crude oil-in-water emulsions efficient separation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:10880–10887. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b01756
Zhang N, Cheng K, Zhang J, Li N, Yang X, Wang Z (2022a) A dual-biomimetic strategy to construct zwitterionic anti-fouling membrane with superior emulsion separation performance. J Membrane Sci 660:120829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2022.120829
Zhang X, Mo Z, Arenal R, Li W, Wang C (2023a) Efficient oil-water separation by a robust superhydrophobic coating prepared directly from commercial lacquer using silanized multi-walled carbon nanotubes as filler. Appl Surf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.155208
Zhang Y, Tan L, Han N, Tian S, Li W, Wang W, Wu Y, Sun Z, Zhang X (2023b) Janus ZIF-8/P(AN-MA) hybrid microfiltration membrane with selected wettability for highly efficient separation of water/oil emulsions. Sep Purif Technol 304:122273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122273
Zhang Y, Xi J, Meng L, Lou Y, Jiang S, Xiao H, Wu W (2022b) Underwater superoleophobic paper-based materials with controllable pore structure for emulsified oil separation. Cellulose 30:277–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04885-z
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support from National Natural Science Foundation of China (22075161), Project funded by Shandong Postdoctoral Science Foundation (SDBX2022038) and the Qingdao University of Science and Technology Graduate Student Independent Research Innovation Project (S2022KY006); (S2022KY024).
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China (22075161), Project funded by Shandong Postdoctoral Science Foundation (SDBX2022038) and the Qingdao University of Science and Technology Graduate Student Independent Research Innovation Project (S2022KY006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XZ, CT: Investigation, Methodology, Software Writing-Original Draft; RZ, LJ, JW, JZ and RW: Formal analysis, Validation, Visualization; HW, XW and XM: Data curation and Writing-Review and Editing and Funding acquisition.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Teng, C., Zhai, R. et al. Easy preparation of wood-base membrane with fouling resistance in complex environments for efficient oil–water emulsion separation. Cellulose 30, 11041–11054 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05497-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05497-x