Abstract
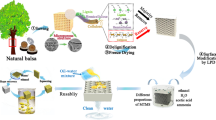
As the amount of oily wastewater discharged from industrial and domestic sources increases, materials used for oil/water separation have received widespread research attention in recent years. However, many reported separation materials with special wetting properties require complex and environmentally unfriendly preparation processes. Therefore, green and efficient materials for oily wastewater and emulsion separation are urgently needed. In this paper, inspired by the scrobiculate and honeycomb-shaped porous structure of natural balsa wood, functionalized wood was designed as an oil/water separation and emulsion purification material by delignification and a simple surface modification process. A deep eutectic solvent (DES) was used to remove the lignin and hemicellulose components. Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and chitosan quaternary ammonium salt (CQA) were used to functionalize and obtain the superhydrophilic/underwater superoleophobic wood material. The water contact angle of the functionalized wood in air reached 0°, while the underwater contact angles for different kinds of oil were greater than 150°. Various oils were effectively separated with a high separation efficiency (> 99.2%). Moreover, the separation efficiency of kerosene from water still reached 99.5% after 30 separation test cycles. After long-term immersion in different pH and salt solutions, the separation efficiency for a kerosene/water mixture was still greater than 99%. Rapid and continuous oil/water separation was achieved conveniently. More importantly, the selective wetting properties and complex porous structure of the functionalized wood enabled the purification of unstable and surfactant-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions with high separation efficiencies. The functionalized wood material also showed promising antibacterial properties, with a good inhibitory effect on the growth of both Gram-positive S.aureus and Gram-negative E.coli. This will effectively prevent contamination and the decrease in separation efficiency caused by mold on the surface. Therefore, this green, efficient, easily prepared, and durable functionalized wood shows excellent potential for application as a separation material for oily wastewater.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Zhang, X. Yang, Y. Wang, Y. Qi, Y. Zhang, J. Luo, P. Cui, W. Jiang, A review on oil/water emulsion separation membrane material, Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. (2022), 107257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107257
H. Zhang, G. Zhang, H. Zhu, F. Wang, G. Xu, H. Shen, J. Wang, Multiscale kapok/cellulose aerogels for oil absorption: the study on structure and oil absorption properties. Ind. Crops Prod. 171, 113902 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113902
Y. Zhu, Y. Lu, H. Yu, G. Jiang, X. Zhao, C. Gao, L. Xue, Super-hydrophobic F-TiO2@ PP membranes with nano-scale “coral”-like synapses for waste oil recovery. Sep. Purif. Technol. 267, 118579 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118579
M. Ardani, M. Imani, A. Tadjarodi, Core shell Fe3O4@ TiO2/silica aerogel nanocomposite; synthesis and study of structural, magnetic and photocatalytic properties. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 338, 111757 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2022.111757
Zh. Tan, L. Hu, D. Yang, D. Zheng, X. Qiul, Lignin: Excellent hydrogel swelling promoter used in cellulose aerogel for efficient oil/water separation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 629, 422–433 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.08.185
J. Zhang, W. Qu, X. Li, Z. Wang, Demulsifier-inspired superhydrophilic/underwater superoleophobic membrane modified with polyoxypropylene polyoxyethylene block polymer for enhanced oil/water separation properties. Molecules 28(3), 1282 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122340
D. Wang, H. Yang, Q. Wang, Y. Lu, J. Yan, W. Cheng, J. Orlando, G. Han, Composite membranes of polyacrylonitrile cross-linked with cellulose nanocrystals for emulsion separation and regeneration. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 164, 107300 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2022.107300
Y. Wang, G. Yue, D. Li, L. Hou, X. Zhao, Z. Cui, J. Bai, N. Wang, Y. Zhao, A robust carbon nanotube and PVDF-HFP nanofiber composite superwettability membrane for high-efficiency emulsion separation. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 41(10), 2000089 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.202000089
C. Liu, L. Wei, L. Zhang, Z. Li, X. Jia, X. Gen, Preparation of carbon-based nanodemulsifiers derived from zif-8 and their demulsification performance for water-in-oil emulsions. ChemistrySelect 7(41), e202203135 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202203135
D. Zou, W. Fan, J. Xu, E. Drioli, X. Chen, M. Qiu, Y. Fan, One-step engineering of low-cost kaolin/fly ash ceramic membranes for efficient separation of oil-water emulsions. J. Membr. Sci. 621, 118954 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2020.118954
G. Parisi, S. Narayan, Using a fluorine-free copper mesh with dynamically tunable wetting properties for high-flux separation of oil-water mixtures. Journal of Water Process Engineering 44, 102365 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102365
L. Qiu, J. Zhang, Z. Guo, W. Liu, Asymmetric superwetting stainless steel meshes for on-demand and highly effective oil-water emulsion separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 273, 118994 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118994
X. Zhang, C. Hu, J. Lin, H. Yin, J. Shi, J. Tang, B. Ma, T. Li, K. Ren, Fabrication of recyclable, superhydrophobic-superoleophilic quartz sand by facile two-step modification for oil-water separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 10(1), 107019 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.107019
J. Wu, J. Tian, Z. Qian, J. Huang, D. Sun, Highly robust separation for aqueous oils enabled by balsa wood-based cellulose aerogel with intrinsic superior hydrophilicity. Sep. Purif. Technol. 315, 123688 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.123688
L. Shen, X. Wang, Z. Zhang, X. Jin, M. Jiang, J. Zhang, Design and fabrication of the evolved zeolitic imidazolate framework-modified polylactic acid nonwoven fabric for efficient oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13(12), 14653–14661 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c22090
M. Zhang, M. Wang, J. Chen, L. Dong, Y. Tian, Z. Cui, J. Li, B. He, F. Yan, Self-assembled silica aerogel-coated polylactic acid membrane for water-in-oil emulsion separation. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 105(3), 694–700 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031282
J. Yang, J. Cui, A. Xie, J. Dai, C. Li, Y. Yan, Facile preparation of superhydrophilic/underwater superoleophobic cellulose membrane with CaCO3 particles for oil/water separation. Colloids Surf. A 608, 125583 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125583
Y. Yang, Z. Guo, Y. Li, Y. Qing, W. Wang, Z. Ma, S. You, W. Li, Multifunctional superhydrophobic self-cleaning cotton fabrics with oil-water separation and dye degradation via thiol-ene click reaction, Separation and Purification Technology, 282(2022), 12012, .https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.120123
J. Wu, Y. Fu, H. Li, M. Tan, Y. Zhang, Fabrication of superhydrophilic mask non-woven fabric with cellulose GO composite coating for oil water separation. Colloids and Surfaces C: Environmental Aspects 1, 100003 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsuc.2023.100003
R. Yang, Q. Cao, Y. Liang, S. Hong, C. Xia, Y. Wu, J. Li, L. Cai, C. Sonne, Q. Le, S. Lam, High capacity oil absorbent wood prepared through eco-friendly deep eutectic solvent delignification. Chem. Eng. J. 401, 126150 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126150
Z. Chen, X. Su, W. Wu, S. Chen, X. Zhang, Y. Wu, H. Xie, K. Li, Superhydrophobic PDMS@TiO2 wood for photocatalytic degradation and rapid oil-water separation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 434, 128182 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2022.128182
W. Huang, L. Zhang, X. Lai, H. Li, X. Zen, Highly hydrophobic F-rGO@ wood sponge for efficient clean-up of viscous crude oil. Chem. Eng. J. 386, 123994 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123994
Y. Cai, Y. Yu, J. Wu, K. Wang, Y. Dong, J. Qu, J. Hu, L. Zhang, Q. Fu, J. Li, Q. Zhang, D. Tian, Durable, flexible, and super-hydrophobic wood membrane with nanopore by molecular cross-linking for efficient separation of stabilized water/oil emulsions. EcoMat 4(6), e12255 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/eom2.12255
L. Zhang, X. Li, S. Chen, J. Guan, Y. Guo, W. Yu, 3D chitosan/GO/ZnO hydrogel with enhanced photocorrosion-resistance and adsorption for efficient removal of typical water-soluble pollutants. Catal. Commun. 176, 106627 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2023.106627
P. Lin, L. Liu, G. He, T. Zhang, M. Yang, J. Cai, L. Fan, S. Tao, Preparation and properties of carboxymethyl chitosan/oxidized hydroxyethyl cellulose hydrogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 162, 1692–1698 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.282
R. Gao, Y. Huang, W. Gan, S. Xiao, Y. Gao, B. Fang, X. Zhang, B. Lyu, R. Huang, J. Li, X. Wei, Y. Deng, Y. Lu, Superhydrophobic elastomer with leaf-spring microstructure made from natural wood without any modification chemicals. Chem. Eng. J. 442, 136338 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.136338
Y. Jia, K. Guan, L. Zhang, Y. Lin, Q. Shen, P. Zhang, H. Matsuyama, Enabling polyketone membrane with underwater superoleophobicity via a hydrogel-based modification for high-efficiency oil-in-water emulsion separation. J. Membr. Sci. 618, 11870 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2020.118705
J. Zhang, W. Qu, X. Li, Z. Wang, Surface engineering of filter membranes with hydrogels for oil-in-water emulsion separation, Separation and Purification Technology, (2022), 122340, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122340
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Graduate Innovation Project of North Minzu University (No. YCX22146), the Ningxia Natural Science Foundation (No. 2023AAC03312), the Research Projects of North Minzu University (No. 2023XYZCL03), the Key Research Development Program of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region of China (No. 2022BDE92037), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21564001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JW: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing-review and editing. HL: Original draft preparation, Investigation, Project administration. PW: Validation, Data curation. YZ: Performance testing. MT: Formal analysis, Validation. WQ: Performance testing, Validation. XH: Performance testing. SL: Performance testing. YT: Formal analysis, Validation. SZ: Formal analysis, Validation. JD: Formal analysis, Validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file2 (MP4 178205 KB)
Supplementary file3 (MP4 523198 KB)
Supplementary file4 (MP4 20481 KB)
Supplementary file5 (MP4 24855 KB)
Supplementary file6 (MP4 18912 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Li, H., Wang, P. et al. Natural polyelectrolyte-functionalized superhydrophilic and antibacterial wood for efficient oil/water separation. J Porous Mater 31, 709–725 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-023-01548-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-023-01548-7