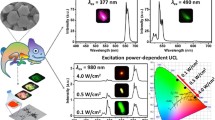
Abstract
The anti-counterfeiting label with multiple fluorescent colors plays an important role in information encryption and decryption. It is urgent to develop new materials for improving the security level of secret information. In this study, novel lanthanide (Ln)-based nanopapers (Ln-nanopapers, Ln = Eu and Tb) were prepared by Ln metal–organic frameworks (Ln-MOFs) self-assembling on 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinyl-1-oxide (TEMPO) cellulose nanofibrils (tCNFs). Due to ligand energy absorption, hetero Ln-nanopapers exhibited high efficiency and brightness in characteristic luminescence and color tuning. Based on the adjusting energy absorption mode of hetero Ln-nanopapers, we selectively lit up Eu3+ (red emission) and Tb3+ (green emission) or [Eu3+ and Tb3+] (yellow emission), respectively. And, using the characteristic absorption mode of Ln3+ ions can effectively avoid the influence of fluorescent brightener on anti-counterfeiting performance. In addition, the characteristic absorption and emission spectra of Ln3+ ions were obtained by using the reversible energy level transition (7FJ ↔ 5Dk) of Ln3+ ions, which could be used for mirror-like encryption. The Ln-nanopapers realizes the advanced anti-counterfeiting with adjustable color, selective lighting and visual recognition.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data is available upon request.
References
Afzal S, Maitra U (2022) Sensitized lanthanide photoluminescence-based sensors–a review. Helv Chim Acta 105(2):202100194. https://doi.org/10.1002/hlca.202100194
Akhmetshina TG, Blatov VA (2017) Topological methods for complex intermetallics. Zkrist- Cryst Mater 232:497–506. https://doi.org/10.1515/zkri-2016-2027
Bernot K, Daiguebonne C, Calvez G et al (2021) A journey in lanthanide coordination chemistry: from evaporable dimers to magnetic materials and luminescent devices. Accounts Chem Res 54(2):427–440. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00684
Brodin FW, Gregersen ØW, Syverud K (2014) Cellulose nanofibrils: challenges and possibilities as a paper additive or coating material–A review. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 29(1):156–166. https://doi.org/10.3183/npprj-2014-29-01-p156-166
Brunckova H, Mudra E, Rocha L et al (2021) Preparation and characterization of isostructural lanthanide Eu/Gd/Tb metal-organic framework thin films for luminescent applications. Appl Surf Sci 542:148731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.148731
Einchhorn SJ, Dufresne A, Aranguren MM et al (2010) Review: current international research into cellulose nanofibres and nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 45:1–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3874-0
Gao R, Zhao M, Guan Y et al (2014) Ordered and flexible lanthanide complex thin films showing up-conversion and color-tunable luminescence. J Mater Chem C 2:9579–9586. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4tc01213e
Gu Z, Wang B, Pang C et al (2012) Syntheses, characterization and fluorescent properties of lanthanide-containing ionic liquids [Cnmim][Ln(NO3)4]. Acta Chim Sinica 70(24):2501. https://doi.org/10.6023/a12090695
Guillou O, Daiguebonne C, Calvez G et al (2016) A long journey in lanthanide chemistry: from fundamental crystallogenesis studies to commercial anticounterfeiting taggants. Accounts Chem Res 49(5):844–856. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00058
Guo X, Zhu G, Li Z et al (2006) Rare earth coordination polymers with zeolite topology constructed from 4-connected building units. Inorg Chem 45(10):4065–4070. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic060116h
Han S, Bae HJ, Kim J et al (2012) Lithographically encoded polymer microtaggant using high-capacity and error-correctable QR code for anti-counterfeiting of drugs. Adv Mater 24:5924–5929. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201201486
Huang H, Chen J, Liu Y et al (2020) Lanthanide-doped core@ multishell nanoarchitectures: multimodal excitable upconverting/downshifting luminescence and high-level anti-counterfeiting. Small 16(19):2000708. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202000708
Jie B, Lin H, Zhai Y et al (2022) Mechanism, design and application of fluorescent recognition based on metal organic frameworks in pollutant detection. Chem Eng J 454:139931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.139931
Jin K, Ji X, Yang T et al (2021) Facile access to photo-switchable, dynamic-optical, multi-colored and solid-state materials from carbon dots and cellulose for photo-rewritable paper and advanced anti-counterfeiting. Chem Eng J 406:126794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126794
Ju D, Song F, Zhang J et al (2019) Enhancing the emission color sensitivity of bulk microcrystals in response to excitation power density and NIR wavelength by introducing Li+/Lu3+ for anti-counterfeiting. J Alloy Compd 770:1181–1188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.08.227
Kaur S, Deopa N, Prasad A et al (2018) Intense green emission from Tb3+ ions doped zinc lead alumino borate glasses for laser and W-LEDs applications. Opt Mater 84:318–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2018.07.020
Kokado K (2017) Network polymers derived from the integration of flexible organic polymers and rigid metal–organic frameworks. Polym J 49(4):345–353. https://doi.org/10.1038/pj.2016.122
Kumar P, Singh S, Gupta BK (2016) Future prospects of luminescent nanomaterial-based security inks: from synthesis to anti-counterfeiting applications. Nanoscale 8(30):14297–14340. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5nr06965c
Li M, Ren G, Wang F et al (2019) Two metal–organic zeolites for highly sensitive and selective sensing of Tb3+. Inorg Chem Front 6(5):1129–1134. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8qi01406j
Li X, Hu Y (2019) Luminescent films functionalized with cellulose nanofibrils/CdTe quantum dots for anti-counterfeiting applications. Carbohyd Polym 203:167–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.09.028
Liu L, Shi J, Li Y et al (2022) Disguise as fluorescent powder: Ultraviolet-B persistent luminescence material without visible light for advanced information encryption and anti-counterfeiting applications. Chem Eng J 430:132884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.132884
Lu YT, Chi S (2003) Compact, reliable asymmetric optical configuration for cost-effective fabrication of multiplex dot matrix hologram in anti-counterfeiting applications. Optik 114(4):161–167. https://doi.org/10.1078/0030-4026-00241
Muthamma K, Sunil D, Shetty P (2021) Carbon dots as emerging luminophores in security inks for anti-counterfeit applications - an up-to-date review. Appl Mater Today 23:101050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2021.101050
Kerbellec N, Kustaryono D, Haquin V et al (2009) An unprecedented family of lanthanide-containing coordination polymers with highly tunable emission properties. Inorg Chem Front 48(7):2837–2843. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic801616y
Oliver J, Yago D, Cante J et al (2019) Variational approach to relaxed topological optimization: Closed form solutions for structural problems in a sequential pseudo-time framework. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 355:779–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2019.06.038
Othong J, Boonmak J, Promarak V et al (2019) Sonochemical synthesis of carbon dots/lanthanoid MOFs hybrids for white light-emitting diodes with high color rendering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(47):44421–44429. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b13814
Park KW, Jang HS, Cho SH (2022) Prediction of Ln3+−4f energy levels in β-NaYF4:Ln3+ and understanding of absorption behaviors. Mater Chem Phys 275:125317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.125317
Park SJ, Je BS, Jang JW et al (2019) Green and red emitting YBO3: Ln3+ (Ln= Eu, Tb) phosphors for detection of latent fingerprint. J Alloy Compd 789:367–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.03.029
Roberts CM (2006) Radio frequency identification (RFID). Comput Secur 25(1):18–26. https://doi.org/10.1108/02634500810847174
Singh D, Bhagwan S, Dalal A et al (2020) Synthesis and investigation of enhanced luminescence of Ln(III)-complexes containing fluorinated β-diketone and oxygen donor ancillary ligands for efficient advanced displays. J Lumin 223:117255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2020.117255
Song B, Wang H, Zhong Y et al (2018) (2018) Fluorescent and magnetic anti-counterfeiting realized by biocompatible multifunctional silicon nanoshuttle-based security ink. Nanoscale 10(4):1617–1621. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nr06337g
Sun CY, Wang XL, Zhang X et al (2013) Efficient and tunable white-light emission of metal-organic frameworks by iridium-complex encapsulation. Nat Commun 4(1):2717. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3717
Sun XY, Fan XX, He JJ et al (2020) Preparation and photoluminescence properties of CaLuBO4: Tb3+ phosphor. Chinese J Lumin 41(3):265–270. https://doi.org/10.3788/fgxb20204103.0265
Viana RS, Oliveira CAF, Chojnacki J et al (2017) Structural and spectroscopic investigation of new luminescent hybrid materials based on calix [4] arene-tetracarboxylate and Ln3+ ions (Ln=Gd, Tb or Eu). J Solid State Chem 251:26–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2017.04.002
Wen J, Wang Y, Jang GS et al (2020) Thermodynamic stabilities and transition levels of native defects and lanthanide ions in Sr2MgSi2O7. Chinese J Lumin 41:655–663. https://doi.org/10.3788/fgxb20204106.0655
Wu Y, Zhao X, Zhang Z et al (2021) Dual-mode dichromatic SrBi4Ti4O15: Er3+ emitting phosphor for anti-counterfeiting application. Ceram Int 47(11):15067–15072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.02.064
Xu M, Ge W, Shi J et al (2021) Stretchable and flexible Bi2Ti4O11: Yb3+, Er3+ @TPU film stimulated by near infrared for dynamic and multimodal anti-counterfeiting. J Alloy Compd 884:161164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.161164
Yoshihara H, Yoshinobu M (2014) Effects of specimen configuration and measurement method of strain on the characterization of tensile properties of paper. J Wood Sci 60:287–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10086-014-1398-y
Zhang G, Zheng H, Guo M et al (2016) Synthesis of polymeric fluorescent brightener based on coumarin and its performances on paper as light stabilizer, fluorescent brightener and surface sizing agent. Appl Surf Sci 367:167–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.01.110
Zhang K, Zhang Y, Yan D et al (2018) Enzyme-assisted mechanical production of cellulose nanofibrils: thermal stability. Cellulose 25:5049–5061. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1928-7
Zhang Q, Yang L, Han Y et al (2022) A pH-sensitive ESIPT molecule with aggregation-induced emission and tunable solid-state fluorescence multicolor for anti-counterfeiting and food freshness detection. Chem Eng J 428:130986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130986
Zhang Z, Chang H, Xue B et al (2017) Near-infrared and visible dual emissive transparent nanopaper based on Yb(III)–carbon quantum dots grafted oxidized nanofibrillated cellulose for anti-counterfeiting applications. Cellulose 25:377–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1594-1
Zhang Z, Ma N, Yao S et al (2021) Transparent and Hazy EuxTb1–x-Nanopaper with Color-Tuning, Photo-Switching, and White Light-Emitting Properties for Anti-counterfeiting and Light-Softened WLEDs. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 9(17):5827–5837. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c08741
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22171170, 21703131), Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (No. 2021JQ-555, 2022GY-279), Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of Shaanxi University of Science & Technology (No. 2016BJ-40, 2019BJ-34), Guangxi Key Laboratory of Clean Pulp & Papermaking and Pollution Control (NO. 2019KF18, 2019KF33), State Key Laboratory of Biobased Material and Green Papermaking (NO. KF201918).
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22171170, 21703131), Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (No. 2021JQ-555, 2022GY-279), Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of Shaanxi University of Science & Technology (No. 2016BJ-40, 2019BJ-34), Guangxi Key Laboratory of Clean Pulp & Papermaking and Pollution Control (NO. 2019KF18, 2019KF33), State Key Laboratory of Biobased Material and Green Papermaking (NO. KF201918).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by ZZ, XL, and ZZ. The frist draft of the manuscript was written by ZZ and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. XD corrected grammatical errors in the manuscript. All author read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This manuscript has not been published or presented elsewhere in part or in entirety and is not under consideration by another journal. The authors also confirm that they have prepared the manuscript in compliance with the Ethics in Publishing Policy as described in the Guide for Authors.
Consent for publication
All authors have approved the manuscript and agree with submission to this journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Li, X., Han, W. et al. Color-tuning, mirror-like encryption and selective lighting of lanthanide-based nanocellulose nanopaper for multichannel anti-counterfeiting. Cellulose 30, 9741–9756 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05474-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05474-4