Abstract
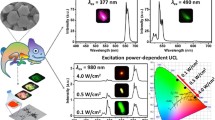
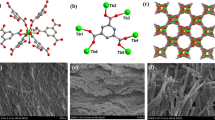
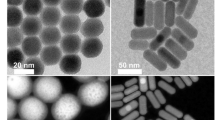
We report a novel near-infrared (NIR) and visible dual emissive transparent Yb3+-nanopaper, which is produced from Yb3+-CQDs grafted oxidized nanofibrillated cellulose (Yb3+-CQDs-ONFC) using a press-controlled extrusion film-making method. The Yb3+-nanopaper exhibits excellent properties, including high transparency (90%), good flexibility, visible fluorescence and NIR phosphorescence. The morphology and chemical structures of Yb3+-nanopaper are investigated with SEM, TEM, XRD, XPS, ICP-OES and FT-IR spectroscopy. The experimental results show that the Yb3+-CQDs have been successfully grafted onto ONFC matrix, and the Yb3+-CQDs are well dispersed in nanopaper with strong visible-NIR dual emission under only one UV excitation. In the Yb3+-nanopaper, CQDs not only act as visible fluorescence “emitter” but also as “antenna” sensitizing Yb3+ ions with NIR characteristic luminescence. And the sensitization of the energy transfer pathway is mainly through singlet state (1LC). Furthermore, the surface passivation of Yb3+-CQDs with ONFC produces an enhanced NIR luminescence by eight times in intensity. Of importance here is that high level security codes of Yb3+-nanopaper can be achieved in three fashions including colour tuning from blue to yellow, NIR/visible spectra, and nanosecond/microsecond lifetime. In addition, aqueous solution of Yb3+-CQDs-ONFC being colourless and transparent can be applied as water-based security ink and spread on the currency note or filter paper, and the spread patterns on the filter paper are stable under water or moist environment.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archer RD, Chen H, Thompson LC (1998) Synthesis, characterization, and luminescence of europium (III) schiff base complexes. Inorg Chem 37:2089–2095. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic960244d
Balkel DE, Becker RS (1968) Relation between the absorption and excitation spectra and relative quantum yields of fluorescence of all-trans-retinal. J Am Chem Soc 90:6710–6711. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01026a026
Bünzli J-CG, Eliseeva SV (2013) Intriguing aspects of lanthanide luminescence. Chem Sci 4:1939–1949. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3SC22126A
Carnall WT, Fields PR, Rajnak K (1968) Electronic energy levels of the trivalent lanthanide aquo ions Gd3+. J Chem Phys 49:4443–4446. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1669894
Chen L, Lai C, Marchewka R, Berry RM, Tam KC (2016) Use of CdS quantum dot-functionalized cellulose nanocrystal films for anti-counterfeiting applications. Nanoscale 8:13288–13296. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NR03039D
Das RK, Mohapatra S (2017) Highly luminescent, heteroatom-doped carbon quantum dots for ultrasensitive sensing of glucosamine and targeted imaging of liver cancer cells. J Mater Chem B 511:2190–2197. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TB03141B
Dexter DL (1953) A theory of sensitized luminescence in solids. J Chem Phys 21:836–850. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1699044
Diez I, Eronen P, Osterberg M, Linder MB, Ikkala O, Ras RHA (2011) Functionalization of nanofibrillated cellulose with silver nanoclusters: fluorescence and antibacterial activity. Macromol Biosci 11:1185–1191. https://doi.org/10.1002/mabi.201100099
Ding H, Yu S-B, Wei J-S, Xiong H-M (2016) Full-color light-emitting carbon dots with a surface-state-controlled luminescence mechanism. ACS Nano 10:484–491. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b05406
Divya V, Biju S, Varma RL, Reddy M (2010) Highly efficient visible light sensitized red emission from europium tris[1-(4-biphenoyl)-3-(2-fluoroyl)propanedione](1,10-phenanthroline) complex grafted on silica nanoparticles. J Mater Chem 20:5220–5227. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0JM00588F
Du BB, Zhu YX, Pan M, Yue MQ, Hou YJ, Wu K, Zhang LY, Chen L, Yin SY, Fan YN, Su CY (2015) Direct white-light and a dual-channel barcode module from Pr (III)-MOF crystals. Chem Commun 51:12533–12536. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CC04468E
Feng WX, Yin SY, Pan M, Wang HP, Fan YN, Lü XQ, Su CY (2017) PMMA-copolymerized color tunable and pure white-light emitting Eu3+–Tb3+ containing Ln-Metallopolymers. J Mater Chem C 5:1742–1750. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TC04851J
Filpponen I, Argyropoulos DS (2010) Regular linking of cellulose nanocrystals via click chemistry: synthesis and formation of cellulose nanoplatelet gels. Biomacromolecules 11:1060–1066. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm1000247
Galland S, Berthold F, Prakobna K, Berglund LA (2015) Holocellulose nanofibers of high molar mass and small diameter for high-strength nanopaper. Biomacromolecules 16:2427–2435. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.5b00678
Gao MX, Liu CF, Wu ZL, Zeng QL, Yang XX, Wu WB, Li YF, Huang CZ (2013) A surfactant-assisted redox hydrothermal route to prepare highly photoluminescent carbon quantum dots with aggregation-induced emission enhancement properties. Chem Commun 49:8015–8017. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CC44624G
Guo J, Liu D, Filpponen I, Johansson L-S, Malho J-M, Quraishi S, Liebner F, Santos HA, Rojas OJ (2017) Photoluminescent hybrids of cellulose nanocrystals and carbon quantum dots as cytocompatible probes for in vitro bioimaging. Biomacromolecules 18:2045–2055. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.7b00306
Hu L, Sun Y, Li S, Wang X, Hu K, Wang L, Liang X, Wu Y (2014) Multifunctional carbon dots with high quantum yield for imaging and gene delivery. Carbon 67:508–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.10.023
Jiang K, Zhang L, Lu J, Xu C, Cai C, Lin H (2016) Triple-mode emission of carbon dots: applications for advanced anti-counterfeiting. Angew Chem Int Ed 55:7231–7235. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201602445
Junka K, Guo J, Filpponen I, Laine J, Rojas OJ (2014) Modification of cellulose nanofibrils with luminescent carbon dots. Biomacromolecules 15:876–881. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.7b00306
Kumar P, Singh S, Gupta BK (2016) Future prospects of luminescent nanomaterial based security inks: from synthesis to anti-counterfeiting applications. Nanoscale 8:14297–14340. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NR06965C
Lim SY, Shen W, Gao ZQ (2015) Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem Soc Rev 44:362–381. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS00269E
Lin N, Dufresne A (2014) Surface chemistry, morphological analysis and properties of cellulose nanocrystals with gradiented sulfation degrees. Nanoscale 6:5384–5393. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR06761K
Liu K, Chen L, Huang L, Lai Y (2016) Evaluation of ethylenediamine-modified nanofibrillated cellulose/chitosan composites on adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solution. Carbohyd Polym 151:1115–1119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.06.071
Lu Y, Yan B (2014) Luminescent lanthanide barcodes based on postsynthetic modified nanoscale metal-organic frameworks. J Mater Chem C 2:7411–7416. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TC01077A
Lu S, Sui L, Liu J, Zhu S, Chen A, Jin M, Yang B (2017) Near-infrared photoluminescent polymer-carbon nanodots with two-photon fluorescence. Adv Mater 29:1603443–1603446. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201603443
Miao M, Zhao J, Feng X, Cao Y, Cao S, Zhao Y, Ge X, Sun L, Shi L, Fang J (2015) Fast fabrication of transparent and multi-luminescent TEMPO-oxidized nanofibrillated cellulose nanopaper functionalized with lanthanide complexes. J Mater Chem C 3:2511–2517. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TC02622E
Missoum K, Bras J, Belgacem MN (2012) Organization of aliphatic chains grafted on nanofibrillated cellulose and influence on final properties. Cellulose 19:1957–1973. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9780-7
Ngo YH, Li D, Simon GP, Garnier G (2011) Paper surfaces functionalized by nanoparticles. Adv Colloid Interface 163:23–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2011.01.004
Osterberg M, Vartiainen J, Lucenius J, Hippi U, Seppala J, Serimaa R, Laine J (2013) A fast method to produce strong NFC films as a platform for barrier and functional materials. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:4640–4647. https://doi.org/10.1021/am401046x
Pan J, Zheng Z, Yang J, Wu Y, Lu F, Chen Y, Gao W (2017) A novel and sensitive fluorescence sensor for glutathione detection by controlling the surface passivation degree of carbon quantum dots. Talanta 166:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.01.033
Raj DBA, Francis B, Reddy MLP, Butorac RR, Lynch VM, Cowley AH (2010) Highly luminescent poly(methyl methacrylate)-incorporated europium complex supported by a carbazole-based fluorinated β-diketonate ligand and a 4,5-bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene oxide co-ligand. Inorg Chem 49:9055–9063. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic1015324
Retot H, Bessiere A, Viana B, Galtayries A (2011) Location of trivalent lanthanide dopant energy levels in (Lu0.5Gd0.5)2O3. J Appl Phys 109:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3597788
Robert JM, Ashlie M, John N, John S, Jeff Y (2011) Cellulose nanomaterials review: structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem Soc Rev 40:3941–3994. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CS00108B
Sanchez C, Belleville P, Popallad M, Nicole L (2011) Applications of advanced hybrid organic–inorganic nanomaterials: from laboratory to market. Chem Soc Rev 40:696–753. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CS00136H
Sehaqui H, Zhou Q, Ikkala O, Berglund LA (2011) Strong and tough cellulose nanopaper with high specific surface area and porosity. Biomacromolecules 12:3638–3644. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm2008907
Song Z, Lin T, Lin L, Lin S, Fu F, Wang X, Guo L (2016) Invisible security ink based on water-soluble graphitic carbon nitride quantum dots. Angew Chem Int Ed 55:2773–2777. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201510945
Song N, Jiao D, Cui S, Hou X, Ding P, Shi L (2017) Highly anisotropic thermal conductivity of layer-by-layer assembled nanofibrillated cellulose/graphene nanosheets hybrid films for thermal management. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:2924–2932. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b11979
Steemers FJ, Verboom W, Reinhoudt DN, Tol vander EB, Verhoeven JW (1995) New sensitizer-modified calix [4] arenes enabling near-UV excitation of complexed luminescent lanthanide ions. J Am Chem Soc 117:9408–9414. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00142a004
Vandenabeele P, Edwards HGM, Jehlička J (2014) The role of mobile instrumentation in novel applications of raman spectroscopy: archaeometry, geosciences, and forensics. Chem Soc Rev 43:2628–2649. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60263J
Weber MJ (1968) Radiative and multiphonon relaxation of rare-earth ions in Y2O3. J Phys Rev 171:283–291. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.171.283
White KA, Gogick D, Stehman J, Rosi NL, Petoud S (2009) Near-infrared luminescent lanthanide MOF barcodes. J Am Chem Soc 131:18069–18071. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja907885m
Wu F, Su H, Zhu X, Wang K, Zhang Z, Wong W-K (2016) Near-infrared emissive lanthanide hybridized carbon quantum dots for bioimaging applications. J Mater Chem B 4:6366–6372. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TB01646D
Xu Y, Jia X-H, Yin X-B, He X-W, Zhang Y-K (2014) Carbon quantum dot stabilized gadolinium nanoprobe prepared via a one-pot hydrothermal approach for magnetic resonance and fluorescence dual-modality bioimaging. Anal Chem 86:12122–12129. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac503002c
Xu S, Chen R, Zheng C, Huang W (2016) Excited state modulation for organic afterglow: materials and applications. Adv Mater 28:9920–9940. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201602604
Xue J, Song F, Yin X, Wang X, Wang Y (2015) Let it shine: a transparent and photoluminescent foldable nanocellulose/quantum dot paper. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:10076–10079. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b02011
Yin SY, Chen L, Pan M, Wang Z, Zhang LY, Wang HP, YaNan Fan SuCY (2016) A mathematically-tuning model of multicolor and white light upconversion in lanthanide-doped ZrO2 macroporous matrix. ChemistrySelect 1:3136–3143. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201600344
Youssef H (2014) Key advances in the chemical modification of nanocelluloses. Chem Soc Rev 43:1519–1542. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60204D
Zhang Z, Feng WX, Su PY, Lü XQ, Song JR, Fan DD, Wong W-K, Jones RA, Su CY (2014) Near-infrared luminescent PMMA-supported metallopolymers based on Zn–Nd schiff-base complexes. Inorg Chem 53:5950–5960. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic500132n
Zhang Z, He Y-N, Liu L, Lü X-Q, Zhu X-J, Wong W-K, Pan M, Su C-Y (2016) Pure white-light and colour-tuning of Eu3+–Gd3+-containing metallopolymer. Chem Commun 52:3713–3716. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CC09946C
Zhao J, Wei Z, Feng X, Miao M, Sun L, Cao S, Shi L, Fang J (2014) Luminescent and transparent nanopaper based on rare-earth up-converting nanoparticle grafted nanofibrillated cellulose derived from garlic skin. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:14945–14951. https://doi.org/10.1021/am5026352
Zhao Y, Wei R, Feng X, Sun L, Liu P, Su Y, Shi L (2016) Dual-mode luminescent nanopaper based on ultrathin g–C3N4 nanosheets grafted with rare-earth upconversion nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:21555–21562. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b06254
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31370578, 21703131), Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of Shaanxi University of Science and Technology (2016BJ-40, BJ15-26). X.Z. thanks the supports from Hong Kong Research Grants Council (HKBU 22304115), Hong Kong Baptist University (FRG2/16-17/024, FRG1/15-16/052, RC-IRMS/16/17/02CHEM and RC-ICRS/1617/02C-CHEM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Chang, H., Xue, B. et al. Near-infrared and visible dual emissive transparent nanopaper based on Yb(III)–carbon quantum dots grafted oxidized nanofibrillated cellulose for anti-counterfeiting applications. Cellulose 25, 377–389 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1594-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1594-1