Abstract
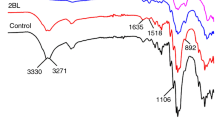
Cotton fabrics were treated with Gelatin (GEL)/Adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP) by layer-by-layer (LBL) assembly coatings and SiO2 sol–gel coatings to improve flame retardancy. Functional groups, surface element compositions, crystal structures, surface microscopic morphologies and element distributions of original and treated cotton fabrics were characterized by techniques including Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Scanning electron microscopy–Energy dispersive spectrometer (SEM–EDX). The results of FTIR, XPS, XRD and SEM–EDX show that the composite coatings are successfully deposited onto cotton fiber surfaces. Thermogravimetric, limiting oxygen index (LOI) experiments, vertical flammability tests (VFTs) and cone calorimetry tests (CCTs) were used to assess the thermal stabilities, flame retardancy levels and reaction-to-fire properties of cotton fabrics. The washing durability, air permeability and hydrophobicity levels were investigated by American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists, Chinese national standard and water contact angle tests. Results show that the 10BL-SiO2@COT exhibits optimum flame retardancy level. Its char residue rate at 700.0 ℃ increases by 506.7% when comparing with original cotton fabric. It has a LOI value of 30.3% (non-flammable level). It can self-extinguish with a char length of only 4.4 cm during a VFT. Its total heat release and peak heat release rate reduce by 18.7% and 50.4% when comparing with original cotton fabric. Its fire growth rate value decreases to 2.2 kW/(m2·s) with a synergistic effectiveness parameter of 1.3 (≥ 1.0). In addition, its LOI value decreases by 26.1% after 10 laundering cycles, but its air permeability enhances by 5.8% as compared with original cotton fabric. Also, it is very hydrophilic. GEL/AMP LBL assembly and SiO2 gel coatings play more synergistic roles in providing physical barriers and structural supports, promoting and reinforcing char formations, cooling burning zones, diluting oxygen and gaseous products.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All of the data and materials are owned by the authors and no permissions are required.
References
An W, Ma JZ, Xu QN, Fan QQ (2020) Flame retardant, antistatic cotton fabrics crafted by layer-by-layer assembly. Cellulose 27:8457–8469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03356-7
Anne D, Thierry A, Naira Q, Filip M, Veronique SL (2015) Gelatin structure and composition linked to hard capsule dissolution: a review. Food Hydrocoll 43:360–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2014.06.006
Aziz B, Aicha B, Said G (2020) Flame-retardant and water-repellent coating on cotton fabric by titania-boron sol-gel method. J Sol Gel Sci Technol 94:719–730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-020-05224-z
Chan SY, Si L, Lee KI, Ng PF, Chen L, Yu B, Hu Y, Yuen RKK, Xin JH, Fei B (2018) A novel boron-nitrogen intumescent flame retardant coating on cotton with improved washing durability. Cellulose 25:843–857. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1577-2
Chen HQ, Xu YJ, Jiang ZM, Jin X, Liu Y, Zhang L, Zhang CJ, Yan C (2020) The thermal degradation property and flame-retardant mechanism of coated knitted cotton fabric with chitosan and APP by LBL assembly. J Therm Anal Calorim 140:591–602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08834-0
Cheng XW, Guan JP, Yang XH, Tang RC, Fan Y (2020a) Phytic acid/silica organic-inorganic hybrid sol system: a novel and durable flame retardant approach for wool fabric. J Mater Res Technol 9:700–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.11.011
Cheng XW, Tang RC, Guan JP, Zhou SQ (2020b) An eco-friendly and effective flame retardant coating for cotton fabric based on phytic acid doped silica sol approach. Prog Org Coat. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2020.105539
Cheng XW, Wu YX, Hu BQ, Guan JP (2020c) Facile preparation of an effective intumescent flame-retardant coating for cotton fabric. Surf Innov 8:315–322. https://doi.org/10.1680/jsuin.20.00021
Cheng XW, Wu YX, Huang YT, Jiang JR, Xu JT, Guan JP (2020d) Synthesis of a reactive boron-based flame retardant to enhance the flame retardancy of silk. React Funct Polym 156:104731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2020.104731
Fang YC, Sun WH, Li L, Wang Q (2021) Bio-based phytic acid/chitosan and polycarboxylic acid for eco-friendly flame retardant and anti-crease of cotton fabric. J Nat Fibers. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2021.1964123
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
Gao DG, Zhang YH, Lyu B, Wang PP, Ma JZ (2019) Nanocomposite based on poly(acrylic acid)/attapulgite towards flame retardant of cotton fabrics. Carbohyd Polym 206:245–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.10.113
Guo YB, Xiao MY, Ren YL, Liu YS, Wang Y, Guo X, Liu XH (2021a) Synthesis of an effective halogen-free flame retardant rich in phosphorus and nitrogen for lyocell fabric. Cellulose 28:7355–7372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03975-8
Guo QQ, Yang YF, Li L, Sun J, Liu W, Gu XY, Li HF, Zhang S (2021b) Construction of bio-safety flame retardant coatings on polyethylene terephthalate fabric with ammonium phytate and cyclodextrin. Polym Adv Technol 32:4440–4449. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.5447
Lazar ST, Kolibaba TJ, Grunlan JC (2020) Flame-retardant surface treatments. Nat Rev Mater 5:259–275. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-019-0164-6
Li SS, Lin XH, Liu Y, Li R, Ren XH, Huang TS (2019a) Phosphorus-nitrogen-silicon-based assembly multilayer coating for the preparation of flame retardant and antimicrobial cotton fabric. Cellulose 26:4213–4223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02373-5
Li SS, Ding F, Lin XH, Li ZG, Ren XH (2019b) Layer-by-layer self-assembly of organic-inorganic hybrid intumescent flame retardant on cotton fabrics. Fibers Polym 20:538–544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-019-8914-z
Li P, Liu C, Xu YJ, Jiang ZM, Liu Y, Zhu P (2020) Novel and eco-friendly flame-retardant cotton fabrics with lignosulfonate and chitosan through LbL: flame retardancy, smoke suppression and flame-retardant mechanism. Polym Degrad Stab 181:109302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2020.109302
Li P, Liu C, Wang B, Tao Y, Xu YJ, Liu Y, Zhu P (2021) Eco-friendly coating based on an intumescent flame-retardant system for viscose fabrics with multi-function properties: flame retardancy, smoke suppression, and antibacterial properties. Prog Org Coat 159:106400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2021.106400
Li G, You F, Zhou ST, Wang ZH, Li D, Zhang XF, Zhou C, Zhuang CH, Zhao YP (2022a) Preparations, characterizations, thermal and flame retardant properties of cotton fabrics finished by boron-silica sol–gel coatings. Polym Degrad Stab 202:110011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2022.110011
Li D, Wang ZH, Zhu YS, You F, Zhou ST, Li G, Zhang XF, Zhou C (2022b) Synergistically improved flame retardancy of the cotton fabric finished by silica-coupling agent-zinc borate hybrid sol. J Ind Text 51(5S):8297S-8322S. https://doi.org/10.1177/15280837211028800
Liang TY, Jiang ZL, Wang CS, Liu JL (2017) A facile one-step synthesis of flame-retardant coatings on cotton fabric via ultrasound irradiation. J Appl Polym Sci 134:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/APP.45114
Liao Y, Chen Y, Wan CY, Zhang GX, Zhang FX (2021) An eco-friendly N-P flame retardant for durable flame-retardant treatment of cotton fabric. Int J Biol Macromol 187:251–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.07.130
Ling C, Guo L (2020) A novel, eco-friendly and durable flame-retardant cotton-based hyperbranched polyester derivative. Cellulose 27:2357–2368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02923-x
Liu Y, Pan YT, Wang X, Acuña P, Zhu P, Wagenknecht U, Heinrich G, Zhang XQ, Wang R, Wang DY (2016) Effect of phosphorus-containing inorganic-organic hybrid coating on the flammability of cotton fabrics: synthesis, characterization and flammability. Chem Eng J 294:167–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.02.080
Liu LX, Huang ZC, Pan Y, Wang X, Song L, Hu Y (2018) Finishing of cotton fabrics by multi-layered coatings to improve their flame retardancy and water repellency. Cellulose 25:4791–4803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1866-4
Liu M, Huang S, Zhang GX, Zhang FX (2019) Synthesis of P–N–Si synergistic flame retardant based on a cyclodiphosphazane derivative for use on cotton fabric. Cellulose 26:7553–7567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02608-5
Liu J, Dong CH, Zhang Z, Sun H, Kong DZ, Lu Z (2020a) Durable flame retardant cotton fabrics modified with a novel silicon-phosphorus-nitrogen synergistic flame retardant. Cellulose 27:9027–9043. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03370-9
Liu LX, Pan Y, Zhao YY, Cai W, Gui Z, Hu Y, Wang X (2020b) Self-assembly of phosphonate-metal complex for superhydrophobic and durable flame-retardant polyester-cotton fabrics. Cellulose 27:6011–6025. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03148-z
Liu XH, Zhang QY, Peng B, Ren YL, Cheng B, Ding C, Su XW, He J, Lin SG (2020c) Flame retardant cellulosic fabrics via layer-by-layer self-assembly double coating with egg white protein and phytic acid. J Clean Prod 243:118641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118641
Liu BW, Zhao HB, Chen L, Chen L, Wang XL, Wang YZ (2021) Eco-friendly synergistic cross-linking flame-retardant strategy with smoke and melt-dripping suppression for condensation polymers. Compos Part B Eng 211:108664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.108664
Luo QL, Gao P, Zhou J, Zhang J, Wu W, Cao JD, Reddy N, Ma H (2020) Imparting flame resistance to citric acid-modified cotton fabrics using DNA. J Eng Fiber Fabr 15:1925850691. https://doi.org/10.1177/1558925020922217
Malucelli G (2020a) Flame-retardant systems based on chitosan and its derivatives: state of the art and perspectives. Molecules 25:4046. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184046
Malucelli G (2020b) Sol–gel and layer-by-layer coatings for flame-retardant cotton fabrics: recent advances. Coatings 10:333. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10040333
Neelam A, Omm-e-Hany SJ, Mahmood SI (2018) Properties and thermal degradation studies of gelatin-based film-exploring the biopolymer for plastic advancement. Int J Food Sci Nutr 5:69–73. https://doi.org/10.15436/2377-0619.18.1847
Nirmala D, Chayanika D, Tarun M, Dilip K (2016) Gelatin and gelatin-polyelectrolyte complexes: drug delivery. Encycl Biomed Polym Polym Biomater 11:3557–3569. https://doi.org/10.1081/E-EBPP-120049954
Peng L, Wang HX, Dai HJ, Fu Y, Ma L, Zhu HK, Yu Y, Li L, Wang Q, Zhang YH (2021) Preparation and characterization of gelatin films by transglutaminase cross-linking combined with ethanol precipitation or hofmeister effect. Food Hydrocoll 113:106421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106421
Periyasamy AP, Venkataraman M, Kremenakova D, Militky J, Zhou Y (2020) Progress in sol-gel technology for the coatings of fabrics. Materials 13:1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13081838
Piao JX, Ren JY, Wang YF, Feng TT, Wang YX, Liu W et al (2022) Green P–N coating by mechanochemistry: efficient flame retardant for cotton fabric. Cellulose 29:2711–2729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04436-6
Qiu XQ, Li ZW, Li XH, Zhang ZJ (2018) Flame retardant coatings prepared using layer by layer assembly: a review. Chem Eng J 334:108–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.194
Rao WH, Shi JJ, Yu CB, Zhao HB, Wang YZ (2021) Highly efficient, transparent, and environment-friendly flame-retardant coating for cotton fabric. Chem Eng J 424:130556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130556
Sun JX, Shi LX, Song TT, Sun CY (2021) Flame resistance of cotton fabric finishing with N-hydroxymethylacrylamide spirophosphate. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4:1155–1165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00348-4
Sykam K, Försth M, Sas G, Restás Á, Das O (2021) Phytic acid: a bio-based flame retardant for cotton and wool fabrics. Ind Crops Prod 164:113349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113349
Wan CY, Liu SD, Chen Y, Zhang FX (2020) Facile, one-pot, formaldehyde-free synthesis of reactive N-P flame retardant for a biomolecule of cotton. Int J Biol Macromol 163:1659–1668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.174
Wang ZH, Wei P, Qian Y, Liu JP (2014) The synthesis of a novel graphene-based inorganic-organic hybrid flame retardant and its application in epoxy resin. Compos Part B Eng 60:341–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.12.033
Wang X, Lu Y, Zhang QR, Wang KL, Carmalt CJ, Parkin IP, Zhang ZJ, Zhang X (2021) Durable fire retardant, superhydrophobic, abrasive resistant and air/UV stable coatings. J Colloid Interface Sci 582:301–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.07.084
Xu F, Zhong L, Zhang C, Wang P, Zhang FX, Zhang GX (2019) Novel high-efficiency casein-based P–N-containing flame retardants with multiple reactive rroups for cotton fabrics. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:13999–14008. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b02474
Xu DH, Wang SJ, Wang YM, Yun L, Dong CH, Jiang ZM, Zhu P (2020) Preparation and mechanism of flame-retardant cotton fabric with phosphoramidate siloxane polymer through multistep coating. Polymers 12:1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071538
Xu F, Zhang G, Wang P, Dai FY (2021) A novel ε-polylysine-derived durable phosphorus-nitrogen-based flame retardant for cotton fabric. Cellulose 28:3807–3822. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03714-z
Yang LR, Luo X, Yan L, Zhou YW, Yu SQ, Ju H, Wang Y, Zhang L (2022) Efficient selective adsorption of uranium using a novel eco-friendly chitosan-grafted adenosine 5′-monophosphate foam. Carbohydr Polym 285:119157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119157
Zhang QH, Zhang W, Huang JY, Lai YK, Xing TL, Chen GQ, Jin W, Liu HZ, Sun B (2015) Flame retardance and thermal stability of wool fabric treated by boron containing silica sols. Mater Des 85:796–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.07.163
Zhang Z, Kong DZ, Sun H, Sun L, Dong CH, Lu Z (2020) Synthetic novel, convenient and eco-friendly Si/P/N synergistic treatment agent to improve the flame retardancy and thermal stability of cotton fabrics. Cellulose 27:10473–10487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03488-w
Zhang LP, Li XC, Zhang SD, Gao QQ, Lu QW, Peng RH, Xu P, Shang HH, Yuan YL, Zou HW (2021a) Micro-FTIR combined with curve fitting method to study cellulose crystallinity of developing cotton fibers. Anal Bioanal Chem 413:1313–1320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-03094-6
Zhang AN, Zhao HB, Cheng JB, Li ME, Li SL, Cao M, Wang YZ (2021b) Construction of durable eco-friendly biomass-based flame-retardant coating for cotton fabrics. Chem Eng J 410:128361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.128361
Zhang XF, Wang ZH, Zhou ST, You F, Li D, Zhou C, Pan Y, Wang JQ (2022) Enhanced flame retardancy level of a cotton fabric treated by an ammonium pentaborate doped silica-KH570 sol. J Ind Text 52:1–29. https://doi.org/10.1177/15280837221116590
Zhao B, Kolibaba TJ, Lazar S, Grunlan JC (2021) Environmentally-benign, water-based covalent polymer network for flame retardant cotton. Cellulose 28:5855–5866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03874-y
Zhou TC, Xu HD, Cai L, Wang JJ (2020) Construction of anti-flame network structures in cotton fabrics with pentaerythritol phosphate urea salt and nano SiO2. Appl Surf Sci 507:145175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.145175
Zhu FL, Chen L, Feng QQ (2022) Waste gelatin based layer by layer assembly for sustainable solution to cotton fabrics flame retardancy. Prog Org Coat 163:106688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2021.106688
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51376089 and 50906039) and the 2019 Key Project of The Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (19KJA520007, A Class).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XZ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing-original draft, Writing-review & editing. DL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing-original draft. FY: Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Writing-review & editing. GL: Investigation, Data curation. CZ: Resources, Visualization. DC: Resources, Visualization. YP: Resources, Investigation. JW: Conceptualization, Methodology. JM: Resources, Investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no conflicts of competing interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All authors state that they adhere to the Ethical Responsibilities of Authors. The authors claim the compliance with the ethical standards.
Consent for publication
All authors listed in this article agree to be published.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Li, D., You, F. et al. Improved thermal stability and flame retardancy levels of cotton fabrics treated by GEL/AMP layer-by-layer assembly and silica gel composite coatings. Cellulose 30, 6695–6718 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05278-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05278-6