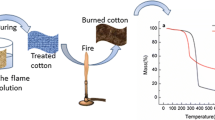
Abstract
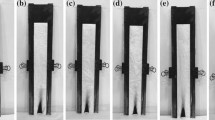
A new phosphorus/nitrogen flame retardant (FR) containing reactive –P–O−NH4+ groups was synthesized from glycerol, phosphoric acid, and urea. At high temperatures, the –P–O−NH4+ group decomposed into –P–O−H+ group, which produced phosphonic anhydride under the action of dicyandiamide catalyst. Phosphonic anhydride dehydrated and condensed with a hydroxyl group on the 6-position carbon atom in the glucose ring of cotton fiber, firmly binding the FR molecule to the fiber through a strong P–O–C bond. The structure of the FR was determined by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H NMR, 13C NMR, and 31P NMR). The effects of FR treatment on the flame retardancy, durability, and thermal stability of cotton fabrics were systematically investigated by measuring limiting oxygen index (LOI) and performing UL-94 vertical burning, cone calorimetry (CONE), thermogravimetric (TG), and differential scanning calorimetry tests. In addition, scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive spectroscopy, FT-IR, and X-ray photoelectron spectrometry studies verified that FR molecules were grafted onto cotton fabrics. X-ray diffraction showed that FR did not affect their crystal structure. The treated cotton fabric with a weight gain of 25.3% exhibited an LOI of 40.5%, which was significantly higher than that obtained for the untreated cotton (17.0%); additionally, the treated cotton showed good self-extinguishing properties during the UL-94 vertical burning test. Furthermore, the results of CONE analysis indicated that the peak heat release rate of the untreated cotton reduced from 171.1 to 15.1 kW/m2 after FR treatment, and its total heat release decreased from 6.3 to 1.1 MJ/m2. TG data revealed that FR finishing reduced the initial thermal degradation temperature of the untreated cotton under heating conditions to 225.9 and 221.8 °C in N2 and air atmospheres, respectively, while the whiteness and mechanical properties of the treated cotton remained in the usable range. Analysis of the flame retardation mechanism of the FR showed that the dense phosphorus/nitrogen char layer that formed in the condensed phase effectively hindered the release of heat and diffusion of flammable volatile substances. This study provides new insights into the design and manufacturing of environmentally friendly FR-treated cotton fabrics with excellent flame retardancy and durability.
Graphical abstract





















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data and material have authenticity, every experimental data in the manuscript is tested by the author, which is reliable.
References
Abidi N, Cabrales L, Hequet E (2009) Functionalization of a cotton fabric surface with titania nanosols: applications for self-cleaning and UV-protection properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 1:2141–2146. https://doi.org/10.1021/am900315t
Abou-Okeil A, El-Sawy SM, Abdel-Mohdy FA (2013) Flame retardant cotton fabrics treated with organophosphorus polymer. Carbohydr Polym 92:2293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.12.008
Ahmed HM, Abdellatif MM, Ibrahim S, Abdellatif FHH (2019) Mini-emulsified copolymer/silica nanocomposite as effective binder and self-cleaning for textiles coating. Prog Org Coating 129:52–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2019.01.002
Alongi J, Colleoni C, Rosace G, Malucelli G (2013) Phosphorus- and nitrogen-doped silica coatings for enhancing the flame retardancy of cotton: synergisms or additive effects? Polym Degrad Stab 98:579–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2012.11.017
Alongi J, Malucelli G (2012) State of the art and perspectives on sol-gel derived hybrid architectures for flame retardancy of textiles. J Mater Chem 22:21805–21809. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm32513f
Annalisa C, Francesca B, Giulio M, Chiara M, Monica P (2016) DNA-chitosan cross-linking and photografting to cotton fabrics to improve washing fastness of the fire-resistant finishing. Cellulose 23:3963–3984. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1067-y
Basak S, Wazed Ali S (2018) Fire resistant behaviour of cellulosic textile functionalized with wastage plant bio-molecules: a comparative scientific report. Int J Biol Macromol 114:169–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.03.109
Bentis A, Boukhriss A, Grancaric AM, El Bouchti M, El Achaby M, Gmouh S (2019) Flammability and combustion behavior of cotton fabrics treated by the sol gel method using ionic liquids combined with different anions. Cellulose 26:2139–2153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2206-4
Bosco F, Casale A, Gribaudo G, Mollea C, Malucelli G (2017) Nucleic acids from agro-industrial wastes: a green recovery method for fire retardant applications. Ind Crops Prod 108:208–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.06.035
Carosio F, Alongi J, Malucelli G (2013) Flammability and combustion properties of ammonium polyphosphate-/poly(acrylic acid)-based layer by layer architectures deposited on cotton, polyester and their blends. Polym Degrad Stab 98:1626–1637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2013.06.019
Carosio F, Ghanadpour M, Alongi J, Wagberg L (2018) Layerby-layer-assembled chitosan/phosphorylated cellulose nanofibrils as a bio-based and flame protecting nano-exoskeleton on PU foams. Carbohydr Polym 202:479–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.09.005
Chen L, Wang XH, Yang HP, Lu Q, Li D, Yang Q, Chen HP (2015) Study on pyrolysis behaviors of non-woody lignins with TG-FTIR and Py-GC/MS. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 113:449–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2015.03.018
Chen XL, Huo LL, Jiao CM, Li SX (2013) TG-FTIR characterization of volatile compounds from flame retardant polyurethane foams materials. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 100:186–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2012.12.017
Dutkiewicz M, Przybylak M, Januszewski R, Maciejewski H (2018) Synthesis and flame retardant efficacy of hexakis(3- (triethoxysilyl)propyloxy)cyclotriphosphazene/silica coatings for cotton fabrics. Polym Degrad Stab 148:10–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2017.11.018
Emam HE (2019) Generic strategies for functionalization of cellulosic textiles with metal salts. Cellulose 26:1431–1447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2185-5
Fang F, Zhang X, Meng Y, Ding X, Bao C, Li S et al (2016) Boron-containing intumescent multilayer nanocoating for extinguishing flame on cotton fabric. Cellulose 23:2161–2172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0928-8
Fang Y, Liu X, Tao X (2019) Intumescent flame retardant and anti-dripping of PET fabrics through layer-by-layer assembly of chitosan and ammonium polyphosphate. Prog Org Coat 134:162–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2019.05.010
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
Fu J, Yang FC, Chen GP, Zhang GF, Huang C, Guo ZG (2019) A facile coating with water-repellent and flame-retardant properties on cotton fabric. N J Chem 43:10183–10189. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nj02240f
Ge LL, Duan HJ, Zhang XG, Chen C, Tang JH, Li ZM (2012) Synergistic effect of ammonium polyphosphate and expandable graphite on flame-retardant properties of acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene. J Appl Polym Sci 126:1337–1343. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.36997
Ghosh B, Chellappan KV, Urban MW (2011) Self-healing inside a scratch of oxetane-substituted chitosan-polyurethane (OXE-CHI-PUR) networks. J Mater Chem 21:14473. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1jm12321a
Gorham J, Torres J, Wolfe G, Agostino AD’, Fairbrother DH, (2005) Surface reactions of molecular and atomic oxygen with carbon phosphide films. J Phys Chem B 109:20379–20386. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0521196
Guo WW, Wang X, Huang JL, Zhou YF, Cai W, Wang JL, Song L, Hu Y (2020) Construction of durable flame-retardant and robust superhydrophobic coatings on cotton fabrics for water-oil separation application. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125661
He WT, Song PA, Yu B, Fang ZP, Wang H (2020) Flame retardant polymeric nanocomposites through the combination of nanomaterials and conventional flame retardants. Prog Mater Sci 114:100687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2020.100687
Huang NH, Wang JQ (2009) A TGA-FTIR study on the effect of CaCO3 on the thermal degradation of EBA copolymer. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 84:124–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2009.01.001
Hussain SMS, Kamal MS, Fogang LT (2019) Synthesis and physicochemical investigation of betaine type polyoxyethylene zwitterionic surfactants containing different ionic headgroups. J Mol Struct 1178:83–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.09.094
Jiang W, Jin FL, Park SJ (2015) Synthesis of a novel phosphorus-nitrogen-containing intumescent flame retardant and its application to fabrics. J Ind Eng Chem 27:40–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2015.01.010
Jiang W, Li JF, Li ZY, Zhang XY, Jin FL, Park SJ (2021) A novel synthesis of ditrimethylolpropane biphosphoramide diethyleneamine as flame retardant and antistatic textiles. Korean J Chem Eng 38:872–884. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-021-0744-1
Jiang ZM, Li H, He YW, Liu Y, Dong CH, Zhu P (2019) Flame retardancy and thermal behavior of cotton fabrics based on a novel phosphorus-containing siloxane. Appl Surf Sci 479:765–775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.02.159
Jiao C, Chen X (2010) Flammability and thermal degradation of intumescent flame-retardant polypropylene composites. Polym Eng Sci 50:767–772. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.21583
Kundu CK, Wang X, Hou YB, Hu Y (2018) Construction of flame-retardant coating on polyamide 6.6 via UV grafting of phosphorylated chitosan and sol-gel process of organo-silane. Carbohydr Polym 181:833–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.11.069
Kwak W, Oh M, Gong M (2015) Preparation of silver-coated cotton fabrics using silver carbamate via thermal reduction and their properties. Carbohydr Polym 115:317–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.08.070
Lee HC, Lee S (2018) Flame retardancy for cotton cellulose treated with H3PO3. J Appl Polym Sci 135:46497. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.46497
Li JF, Jiang W (2021) Synthesis of a novel P-N flame retardant for preparing flame retardant and durable cotton fabric. Ind Crop Prod 174:114205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.114205
Li X, Chen H, Wang W, Liu Y, Zhao P (2015) Synthesis of a formaldehyde-free phosphorusenitrogen flame retardant with multiple reactive groups and its application in cotton fabrics. Polym Degrad Stabil 120:193–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2015.07.003
Lin D, Zeng X, Li H, Lai X, Wu T (2019) One-pot fabrication of superhydrophobic and flame-retardant coatings on cotton fabrics via sol-gel reaction. J Colloid Interface Sci 533:198–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.08.060
Liu J, Zhang Z, Sun L, Dong CH, Kong DZ, Wang S, Lu Z (2021) Synthesis of a novel synergistic flame retardant based on cyclopolysiloxane and its flame retardant coating on cotton fabric. Cellulose 28:9505–9523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04127-8
Liu L, Huang Z, Pan Y, Wang X, Song L, Hu Y (2018a) Finishing of cotton fabrics by multi-layered coatings to improve their flame retardancy and water repellency. Cellulose 25:4791–4803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1866-4
Liu W, Chen L, Wang YZ (2012) A novel phosphorus-containing flame retardant for the formaldehyde-free treatment of cotton fabrics. Polym Degrad Stab 97:2487–2491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2012.07.016
Liu X, Zhang Y, Cheng B, Ren Y, Zhang Q, Ding C, Peng B (2018b) Preparation of durable and flame retardant lyocell fibers by a one-pot chemical treatment. Cellulose 25:6745–6758. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2005-y
Liu Z, Xu M, Wang Q, Li B (2017) A novel durable flame retardant cotton fabric produced by surface chemical grafting of phosphorus- and nitrogen-containing compounds. Cellulose 24:4069–4081. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1391-x
Malucelli G, Bosco F, Alongi J, Carosio F, Blasio AD et al (2014) Biomacromolecules as novel green flame retardant systems for textiles: an overview. RSC Adv 4:46024–46039. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA06771A
Mao H, Liu X, Qian X, An X (2015) Preparation and dedoping-resistant effect of self-doped polyaniline/cellulose fibers (spani/cf) hybrid. Cellulose 22:2641–2650. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0689-9
Mohamed AL, El-Sheikh MA, Waly AI (2014) Enhancement of flame retardancy and water repellency properties of cotton fabrics using silanol based nano composites. Carbohydr Polym 102:727–737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.10.097
Mohammad N, Yasser Z, Parvin K (2015) Nanoparticles as effective flame retardants for natural and synthetic textile polymers: application, mechanism, and optimization. Polym Rev 55:531–560. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583724.2014.980427
Molaba TP, Chapple S, John MJ (2016) Aging studies on flame retardant treated lignocellulosic fibers. J Appl Polym Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.44175
Nabipour H, Wang X, Song L, Hu Y (2020) Hydrophobic and flame-retardant finishing of cotton fabrics for water-oil separation. Cellulose 27:4145–4159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03057-1
Naebe M, Li QX, Onur A, Denning R (2016) Investigation of chitosan adsorption onto cotton fabric with atmospheric helium/oxygen plasma pre-treatment. Cellulose 23:2129–2142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0915-0
Nguyen TM, Chang SC, Condon B, Thomas TP, Azadi P (2014) Thermal decomposition reactions of cotton fabric treated with piperazine-phosphonates derivatives as a flame retardant. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 110:122–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2014.08.006
Pan Y, Liu L, Wang X, Song L, Hu Y (2018) Hypophosphorous acid cross-linked layer-by-layer assembly of green polyelectrolytes on polyester-cotton blend fabrics for durable flame-retardant treatment. Carbohyd Polym 201:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.08.044
Pethsangave DA, Khose RV, Wadekar PH, Some S (2017) Deep eutectic solvent functionalized graphene composite as an extremely high potency flame retardant. ACS Appl Mater Inter 9:35319–35324. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b09587
Qi LY, Qiu SL, Xi JC, Yu B, Hu Y, Xing WY (2022) Construction of super-hydrophobic, highly effective flame retardant coating for cotton fabric with superior washability and abrasion resistance. J Colloid Interf Sci 607:2019–2028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.10.021
Rao WH, Shi JJ, Yu CB, Zhao HB, Wang YZ (2021) Highly efficient, transparent, and environment-friendly flame-retardant coating for cotton fabric. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2021.130556
Rosace G, Castellano A, Trovato V, Iacono G, Malucelli G (2018) Thermal and flame retardant behaviour of cotton fabrics treated with a novel nitrogen-containing carboxyl-functionalized organophosphorus system. Am Mineral 196:348–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.05.012
Rosace G, Colleoni C, Trovato V, Iacono G, Malucelli G (2017) Vinylphosphonic acid/methacrylamide system as a durable intumescent flame retardant for cotton fabric. Cellulose 24:3095–3108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1294-x
Shafizadeh F, Bradbury AG, De Groot WF, Aanerud TW (1982) Role of inorganic additives in the smoldering combustion of cotton cellulose. Ind Eng Chem Prod Res Dev 27:97–101. https://doi.org/10.1021/i300005a021
Shahidi S, Ghoranneviss M (2013) Effect of plasma pretreatment followed by nanoclay loading on flame retardant properties of cotton fabric. J Fusion Energy 33:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-013-9645-6
Sharma V, Basak S, Rishabh K, Umaria H, Ali SW (2018) Synthesis of zinc carbonate nanoneedles, a potential flame retardant for cotton textiles. Cellulose 25:6191–6205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1962-5
Tao Y, Liu C, Li P, Wang B, Xu YJ, Jiang ZM, Liu Y, Zhu P (2021) A flame-retardant PET fabric coating: flammability, anti-dripping properties, and flame-retardant mechanism. Prog Org Coat 150:105971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2020.105971
Tsai KC, Kuan HC, Chou HW, Kuan CF, Chen CH, Chiang CL (2011) Preparation of expandable graphite using a hydrothermal method and flame-retardant properties of its halogen-free flame-retardant HDPE composites. J Polym Res 18:483–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-010-9440-2
Tudu BK, Sinhamahapatra A, Kumar A (2020) Surface modification of cotton fabric using TiO2 nanoparticles for selfcleaning, oil-water separation, antistain, anti-water absorption, and antibacterial properties. ACS Omega 5:7850–7860. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b04067
Vahabi H, Kandola BK, Saeb MR (2019) Flame retardancy index for thermoplastic composites. Polymers 11:407. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030407
Vince J, Orel B, Vilcnik A, Fir M, Vuk AS, Jovanovski V, Simoncic B (2006) Structural and water-repellent properties of a urea/poly(dimethylsiloxane) sol-gel hybrid and its bonding to cotton fabric. Langmuir 22:6489–6497. https://doi.org/10.1021/la060694a
Wang JL, Zhang Y, Cai W, Yao CX, Hu Y, Hu WZ (2019) Construction of multifunctional boron nitride nanosheet towards reducing toxic volatiles (CO and HCN) generation and fire hazard of thermoplastic polyurethane. J Hazard Mater 362:482–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.009
Wang P, Xiao H, Duan C, Wang B, Li Z (2020) Sulfathiazole derivative with phosphaphenanthrene group: synthesis, characterization and its high flame retardant activity on epoxy resin. Polym Degrad Stabil 173:109078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2020.109078
Wang S, Kong DZ, Chen HF, Wang Z, Lu Z (2022) Construction of a novel B/N/Si synergistic flame retardant system and its application on cotton fabric. Ind Crop Prod 178:114574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.114574
Wang S, Sui X, Li Y, Li J, Xu H et al (2016) Durable flame retardant finishing of cotton fabrics with organosilicon functionalized cyclotriphosphazene. Polym Degrad Stabil 128:22–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2016.02.009
Wang SH, Sun L, Li YY, Wang HX, Liu J, Zhu P, Dong CH (2021) Properties of flame-retardant cotton fabrics: Combustion behavior, thermal stability and mechanism of Si/P/N synergistic effect. Ind Crop Prod 173:114157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.114157
Wang X, Romero M, Zhang XQ, Wang R, Wang DY (2015) Intumescent multilayer hybrid coating for flame retardant cotton fabrics based on layer-by-layer assembly and sol-gel process. RSC Adv 5:10647–10655. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra14943b
Wu X, Gou TT, Zhao QY, Chen L, Wang P (2021) High-efficiency durable flame retardant with ammonium phosphate ester and phosphine oxide groups for cotton cellulose biomacromolecule. Int J Biol Macromol 194:945–953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.11.149
Yoshioka-Tarver M, Condon BD, Santiago Cintron M, Chang S, Easson MW, Fortier CA (2012) Enhanced flame retardant property of fiber reactive halogen-free organophosphonate. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:11031–11037. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie300964g
Yuan H, Xing W, Zhang P, Song L, Hu Y (2012) Functionalization of cotton with UV Cured flame retardant coatings. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:5394–5401. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie202468u
Zhang DQ, Williams BL, Shrestha SB, Nasir Z, Becher EM et al (2017) Flame retardant and hydrophobic coatings on cotton fabrics via sol-gel and self-assembly techniques. J Colloid Interf Sci 505:892–899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.06.087
Zhang Y, Ren Y, Liu X, Huo T, Qin Y (2018) Preparation of durable flame retardant PAN fabrics based on amidoximation and phosphorylation. Appl Surf Sci 428:395–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.09.155
Zhao P, Rao WH, Luo HQ, Wang L, Liu YL, Yu CB (2020) Novel organophosphorus compound with amine groups towards self-extinguishing epoxy resins at low loading. Mater Des 193:108838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108838
Funding
This work was supported by the 2013 Science and Technology Fund Project (20130206070 GX) of Jilin Provincial Department of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL: Participating in the synthesis and selection of flame retardants, planning the concept, design and analysis. Responsible for the synthesis experiment of flame retardant, post-processing of treated cotton, data testing, sorting. Writing-original draft and revise the article, writing-review & editing. WJ: Being the manager of the whole project, participating in market research, drug selection, article guidance, data processing and proposing novel methods for this article. ML: Market Research on flame retardants and cotton fabric, and participated in the experimental process of synthesis and sample preparation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethics approval
We submit a manuscript entitled "Durable phosphorus/nitrogen flame retardant for cotton fabric". This manuscript does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors, and there is no ethical issue. In line with ethical standards, no conflict of interest.
Consent to participate
We declare that this manuscript entitled "Durable phosphorus/nitrogen flame retardant for cotton fabric" has not been published before; that it is not under consideration for publication anywhere else; that its publication has been approved by all co-authors. The publisher will not be held legally responsible should there be any claims for compensation.
Consent for publication
We declare that this manuscript entitled "Durable phosphorus/nitrogen flame retardant for cotton fabric" is original and has never been published before, and we do not consider publishing it elsewhere at present. We confirm that all the authors have read and approved this manuscript, and we further confirm that the order of authors listed in the manuscript has been approved by all of us. We agree that this manuscript will be published in cellulose, we know that the corresponding author is the only contact in the editing process, and she is responsible for communicating progress with another author, submitting revisions and finally approving proofs.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Jiang, W. & Liu, M. Durable phosphorus/nitrogen flame retardant for cotton fabric. Cellulose 29, 4725–4751 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04558-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04558-x