Abstract
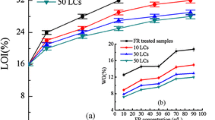
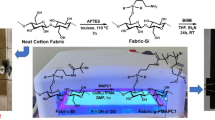
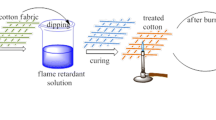
Phosphorus- and nitrogen-containing compounds were grafted on a cotton fabric surface by three steps. Firstly, the cotton fabric was oxidized by sodium periodate to form aldehyde groups, and then the aldehyde groups were reacted with the organic amine to generate Schiff bases. Finally, the Schiff bases were reacted with dimethyl phosphate by the phosphine hydride addition reaction. The chemical structure of grafted cotton fabric was characterized and confirmed. The results demonstrated that the limiting oxygen index (LOI) value of the modified cotton fabric dramatically increased from 19.5% for pure cotton fabric to 28.1% due to the chemical grafted on the cotton surface. After washing, the LOI value slightly decreased to 27.4%, which indicated that the prepared cotton fabric possessed superior washing durability. Thermogravimetry and cone calorimetry results demonstrated that the grafted flame retardant stimulated the thermal degradation and charring of cotton fabric ahead of time and formed sufficient char residue at high temperature, which efficiently prevented the underlying cotton fabric from degradation and combustion. Consequently, the flame retardancy of the cotton fabric was enhanced.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alongi J, Ciobanu M, Malucelli G (2011) Novel flame retardant finishing systems for cotton fabrics based on phosphorus-containing compounds and silica derived from sol–gel processes. Carbohydr Polym 85(3):599–608
Alongi J, Colleoni C, Rosace G et al (2013a) The role of pre-hydrolysis on multi step sol–gel processes for enhancing the flame retardancy of cotton. Cellulose 20(1):525–535
Alongi J, Colleoni C, Rosace G et al (2013b) Phosphorus-and nitrogen-doped silica coatings for enhancing the flame retardancy of cotton: synergisms or additive effects. Polym Degrad Stab 98(2):579–589
Alongi J, Carosio F, Malucelli G (2014) Current emerging techniques to impart flame retardancy to fabrics: an overview. Polym Degrad Stab 106:138–149
Azzam F, Galliot M, Putaux JL et al (2015) Surface peeling of cellulose nanocrystals resulting from periodate oxidation and reductive amination with water-soluble polymers. Cellulose 22(6):3701–3714
Bogdanova VV, Kobets OI, Kirlitsa VP (2016) The mechanism of action and the synergistic effect of nitrogen and phosphorus-containing fire retardants in fire protection and wood and peat fire suppression. Russ J Phys Chem B 10(2):306–312
Boukhriss A, Gmouh S, Hannach H et al (2016) Treatment of cotton fabrics by ionic liquid with PF6 − anion for enhancing their flame retardancy and water repellency. Cellulose 23(5):3355–3364
Cheema HA, El-Shafei A, Hauser PJ (2013) Conferring flame retardancy on cotton using novel halogen-free flame retardant bifunctional monomers: synthesis, characterizations and applications. Carbohydr Polym 92(1):885–893
Deh S, Gähr F (2016) Synergistic effects in the pyrolysis of phosphorus-based flame-retardants: the role of Si-and N-based compounds. Polym Degrad Stab 130:155–164. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2016.06.009
Dong C, Lu Z, Zhang F et al (2016) Combustion behaviors of cotton fabrics treated by a novel nitrogen- and phosphorus-containing polysiloxane flame retardant. J Therm Anal Calorim 123(1):535–544
Gaan S, Sun G (2007) Effect of phosphorus and nitrogen on flame retardant cellulose: a study of phosphorus compounds. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 78(2):371–377
Gao WW, Zhang GX, Zhang FX (2015) Enhancement of flame retardancy of cotton fabrics by grafting a novel organic phosphorous-based flame retardant. Cellulose 22(4):2787–2796
Hou Q, Liu W, Liu Z et al (2008) Characteristics of antimicrobial fibers prepared with wood periodate oxycellulose[J]. Carbohydr Polym 74(2):235–240
Lecoeur E, Vroman I, Bourbigot S et al (2001) Flame retardant formulations for cotton. Polym Degrad Stab 74(3):487–492
Lessan F, Montazer M, Moghadam MB (2011) A novel durable flame-retardant cotton fabric using sodium hypophosphite, nano TiO2 and maleic acid. Thermochim Acta 520(1):48–54
Li X, Chen H, Wang W et al (2015) Synthesis of a formaldehyde-free phosphorus–nitrogen flame retardant with multiple reactive groups and its application in cotton fabrics. Polym Degrad Stab 120:193–202
Liu X, Xu Y (2014) Preparation process and antimicrobial properties of cross-linking chitosan onto periodate-oxidized bamboo pulp fabric. Fibers Polym 15(9):1887–1894
Nikolic T, Milanovic J, Kramar A et al (2014) Preparation of cellulosic fibers with biological activity by immobilization of trypsin on periodate oxidized viscose fibers. Cellulose 21(3):1369–1380
Shariatinia Z, Javeri N, Shekarriz S (2015) Flame retardant cotton fibers produced using novel synthesized halogen-free phosphoramide nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 118:183–198
Shaver LA (2008) Determination of phosphates by the gravimetric quimociac technique[J]. J Chem Educ 85(8):1097
Sirvio J, Hyvakko U, Liimatainen H et al (2011) Periodate oxidation of cellulose at elevated temperatures using metal salts as cellulose activators. Carbohydr Polym 83(3):1293–1297
Tsafack MJ, Levalois-Grützmacher J (2006) Plasma-induced graft-polymerization of flame retardant monomers onto PAN fabrics. Surf Coat Technol 200(11):3503–3510
Vasiljević J, Jerman I, Jakša G et al (2015) Functionalization of cellulose fibres with DOPO-polysilsesquioxane flame retardant nanocoating. Cellulose 22(3):1893–1910
Wang LH, Ren YL, Wang XL, Zhao JY, Zhang Y, Zeng Q, Gu YT (2016a) Fire retardant viscose fiber fabric produced by graft polymerization of phosphorus and nitrogen-containing monomer. Cellulose 23:2689–2700. doi:10.1007/s10570-016-0970-6
Wang S, Sui X, Li Y, Li J, Xu H, Zhong Y, Zhang L, Mao Z (2016b) Durable flame retardant finishing of cotton fabrics with organosilicon functionalized cyclotriphosphazene. Polym Degrad Stab 128:22–28. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2016.02.009
Xie K, Gao A, Zhang Y (2013) Flame retardant finishing of cotton fabric based on synergistic compounds containing boron and nitrogen. Carbohydr Polym 98(1):706–710
Yang JC, Liao W, Deng SB et al (2016) Flame retardation of cellulose-rich fabrics via a simplified layer-by-layer assembly. Carbohydr Polym 151:434–440
Zhang D, Xie Q et al (2015) Synthesis and flame retardant properties of solicon- contained phosphoramide. J Donghua University (natural science) 215–220:252
Zhao P, Liu S, Xiong K et al (2016) Highly flame retardancy of cotton fabrics with a novel phosphorus/nitrogen/silicon flame-retardant treating system. Fibers Polym 17(4):569–575
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for funding supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 31370709), and Heilongjiang Major Research Projects (GA12A102, GA15A101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Xu, M., Wang, Q. et al. A novel durable flame retardant cotton fabric produced by surface chemical grafting of phosphorus- and nitrogen-containing compounds. Cellulose 24, 4069–4081 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1391-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1391-x