Abstract
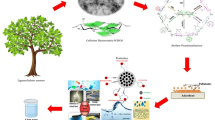
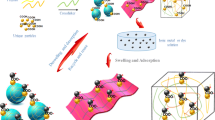
A lignocellulose-based composite hydrogel, as a novel biosorbent, was prepared for Cu2+ removal from wastewater. TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibrils (TOCN) were dispersed in a 7 wt% NaOH/12 wt% urea aqueous solution at room temperature. Meanwhile, the dissolved cellulose was obtained in the same system at subzero temperature. The composite hydrogels were prepared by blending the dissolved cellulose solution, TOCN dispersion, and alkali lignin solution in an NaOH/urea aqueous solution. The composite hydrogel exhibits excellent adsorption capacity for heavy metals, which can be attributed to the synergistic effects of physical adsorption (porous 3D structure) and chemical adsorption (active sites: carboxyl and phenolic groups). The maximum amount of adsorbed Cu2+ onto composite hydrogel can reach 541 mg/g, which was achieved after 45 min. The adsorption behavior is well-described by the pseudo-second-order kinetics and the Freundlich model (R2 > 0.999). Furthermore, the composite hydrogel exhibits high-strength properties, indicating that the presence of TOCN and lignin contributes to mechanical improvements.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmaruzzaman M (2011) Industrial wastes as low-cost potential adsorbents for the treatment of wastewater laden with heavy metals. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 166:36–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2011.04.005
Cai J, Zhang L (2005) Rapid dissolution of cellulose in LiOH/urea and NaOH/urea aqueous solutions. Macromol Biosci 5:539–548. https://doi.org/10.1002/mabi.200400222
Carro L, Barriada JL, Herrero R, Sastre de Vicente ME (2015) Interaction of heavy metals with Ca-pretreated Sargassum muticum algal biomass: characterization as a cation exchange process. Chem Eng J 264:181–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.11.079
Ciesielczyk F, Bartczak P, Klapiszewski Ł, Jesionowski T (2017) Treatment of model and galvanic waste solutions of copper(II) ions using a lignin/inorganic oxide hybrid as an effective sorbent. J Hazard Mater 328:150–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.01.009
Dai L, Zhang L, Wang B et al (2017) Multifunctional self-assembling hydrogel from guar gum. Chem Eng J 330:1044–1051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.08.041
Duan C, Zhao N, Yu X et al (2013) Chemically modified kapok fiber for fast adsorption of Pb2+, Cd2+, Cu2+ from aqueous solution. Cellulose 20:849–860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-9875-9
Erdtman H (1972) Lignins: occurrence, formation, structure and reactions, K. V. Sarkanen and C. H. Ludwig, Eds., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 1971. 916pp. $35.00. J Polym Sci [B] 10:228–230. https://doi.org/10.1002/pol.1972.110100315
Fujisawa S, Togawa E, Hayashi N (2016) Orientation control of cellulose nanofibrils in all-cellulose composites and mechanical properties of the films. J Wood Sci 62:174–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10086-015-1533-4
Gautam RK, Mudhoo A, Lofrano G, Chattopadhyaya MC (2014) Biomass-derived biosorbents for metal ions sequestration: adsorbent modification and activation methods and adsorbent regeneration. J Environ Chem Eng 2:239–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.12.019
Ge Y, Xiao D, Li Z, Cui X (2014) Dithiocarbamate functionalized lignin for efficient removal of metallic ions and the usage of the metal-loaded bio-sorbents as potential free radical scavengers. J Mater Chem A 2:2136–2145. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA14333C
Gidh AV, Decker SR, Vinzant TB et al (2006) Determination of lignin by size exclusion chromatography using multi angle laser light scattering. J Chromatogr A 1114:102–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.02.044
Guerra A, Gaspar AR, Contreras S et al (2007) On the propensity of lignin to associate: a size exclusion chromatography study with lignin derivatives isolated from different plant species. Phytochemistry 68:2570–2583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.05.026
Guo X, Zhang S, Shan X (2008) Adsorption of metal ions on lignin. J Hazard Mater 151:134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.05.065
Hajeeth T, Vijayalakshmi K, Gomathi T, Sudha PN (2013) Removal of Cu(II) and Ni(II) using cellulose extracted from sisal fiber and cellulose-g-acrylic acid copolymer. Int J Biol Macromol 62:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.08.029
Ho Y (2006) Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J Hazard Mater 136:681–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.12.043
Hokkanen S, Repo E, Suopajärvi T et al (2014) Adsorption of Ni(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by amino modified nanostructured microfibrillated cellulose. Cellulose 21:1471–1487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0240-4
Isobe N, Chen X, Kim U-J et al (2013) TEMPO-oxidized cellulose hydrogel as a high-capacity and reusable heavy metal ion adsorbent. J Hazard Mater 260:195–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.05.024
Isogai A, Saito T, Fukuzumi H (2011) TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers. Nanoscale 3:71–85. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0NR00583E
Jung KA, Woo SH, Lim S-R, Park JM (2015) Pyrolytic production of phenolic compounds from the lignin residues of bioethanol processes. Chem Eng J 259:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.07.126
Kamel S, Hassan EM, El-Sakhawy M (2006) Preparation and application of acrylonitrile-grafted cyanoethyl cellulose for the removal of copper (II) ions. J Appl Polym Sci 100:329–334. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.23317
Kumar PS, Ramalingam S, Kirupha SD et al (2011) Adsorption behavior of nickel(II) onto cashew nut shell: equilibrium, thermodynamics, kinetics, mechanism and process design. Chem Eng J 167:122–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.12.010
Li Z, Kong Y, Ge Y (2015a) Synthesis of porous lignin xanthate resin for Pb2+ removal from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 270:229–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.123
Li Z, Xiao D, Ge Y, Koehler S (2015b) Surface-functionalized porous lignin for fast and efficient lead removal from aqueous solution. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:15000–15009. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b03994
Lindströmn T (1979) The colloidal behaviour of kraft lignin. Colloid Polym Sci 257:277–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01382370
Liu L, Wang R, Yu J et al (2016) Robust self-standing chitin nanofiber/nanowhisker hydrogels with designed surface charges and ultralow mass content via gas phase coagulation. Biomacromolecules 17:3773–3781. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.6b01278
Liu Y, Deng L, Zhang C et al (2018) Tunable physical properties of ethylcellulose/gelatin composite nanofibers by electrospinning. J Agric Food Chem 66:1907–1915. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b06038
Ma J, Zhou G, Chu L et al (2017) Efficient removal of heavy metal ions with an EDTA functionalized chitosan/polyacrylamide double network hydrogel. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:843–851. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02181
Ma J, Liu Y, Ali O et al (2018) Fast adsorption of heavy metal ions by waste cotton fabrics based double network hydrogel and influencing factors insight. J Hazard Mater 344:1034–1042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.11.041
Mahfoudhi N, Boufi S (2017) Nanocellulose as a novel nanostructured adsorbent for environmental remediation: a review. Cellulose 24:1171–1197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1194-0
Minu K, Jiby KK, Kishore VVN (2012) Isolation and purification of lignin and silica from the black liquor generated during the production of bioethanol from rice straw. Biomass Bioenergy 39:210–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.01.007
Mohammadi Z, Shangbin S, Berkland C, Liang J (2017) Chelator-mimetic multi-functionalized hydrogel: highly efficient and reusable sorbent for Cd, Pb, and As removal from waste water. Chem Eng J 307:496–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.121
Mohan D, Pittman CU, Steele PH (2006) Single, binary and multi-component adsorption of copper and cadmium from aqueous solutions on Kraft lignin—a biosorbent. J Colloid Interface Sci 297:489–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.11.023
Mushi NE, Kochumalayil J, Cervin NT et al (2016) Nanostructurally controlled hydrogel based on small-diameter native chitin nanofibers: preparation, structure, and properties. ChemSusChem 9:989–995. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201501697
Pagnanelli F, Mainelli S, Vegliò F, Toro L (2003) Heavy metal removal by olive pomace: biosorbent characterisation and equilibrium modelling. Chem Eng Sci 58:4709–4717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2003.08.001
Pang Y, Wang S, Qiu X et al (2017) Preparation of lignin/sodium dodecyl sulfate composite nanoparticles and their application in pickering emulsion template-based microencapsulation. J Agric Food Chem 65:11011–11019. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03784
Qi H, Cai J, Zhang L, Kuga S (2009) Properties of films composed of cellulose nanowhiskers and a cellulose matrix regenerated from alkali/urea solution. Biomacromolecules 10:1597–1602. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm9001975
Qian S, Sheng K (2017) PLA toughened by bamboo cellulose nanowhiskers: role of silane compatibilization on the PLA bionanocomposite properties. Compos Sci Technol 148:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.05.020
Safwat E, Hassan ML, Saniour S et al (2018) Injectable TEMPO-oxidized nanofibrillated cellulose/biphasic calcium phosphate hydrogel for bone regeneration. J Biomater Appl. https://doi.org/10.1177/0885328218763866
Sehaqui H, de Larraya UP, Liu P et al (2014) Enhancing adsorption of heavy metal ions onto biobased nanofibers from waste pulp residues for application in wastewater treatment. Cellulose 21:2831–2844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0310-7
Shi Z, Yang Q, Kuga S, Matsumoto Y (2015) Dissolution of wood pulp in aqueous NaOH/urea solution via dilute acid pretreatment. J Agric Food Chem 63:6113–6119. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b01714
Simonin J-P (2016) On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chem Eng J 300:254–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.079
Sotto A, Kim J, Arsuaga JM et al (2014) Binary metal oxides for composite ultrafiltration membranes. J Mater Chem A 2:7054–7064. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA15347A
Srivastava SK, Singh AK, Sharma A (1994) Studies on the uptake of lead and zinc by lignin obtained from black liquor—a paper industry waste material. Environ Technol 15:353–361. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593339409385438
Suhas Gupta VK, Carrott PJM et al (2016) Cellulose: a review as natural, modified and activated carbon adsorbent. Bioresour Technol 216:1066–1076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.05.106
Wang Z, Liu S, Matsumoto Y, Kuga S (2012) Cellulose gel and aerogel from LiCl/DMSO solution. Cellulose 19:393–399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9651-2
Wang Q, Shi X, Xu J et al (2016) Highly enhanced photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI) on AgI/TiO2 under visible light irradiation: influence of calcination temperature. J Hazard Mater 307:213–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.12.050
Wang Z, Yu J, Zhang L et al (2017) Cellulose laurate ester aerogel as a novel absorbing material for removing pollutants from organic wastewater. Cellulose 24:5069–5078. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1489-1
Weber WJ, Morris JC (1963) Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J Sanit Eng Div 89:31–60
Xiong J, Jiao C, Li C et al (2014) A versatile amphiprotic cotton fiber for the removal of dyes and metal ions. Cellulose 21:3073–3087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0318-z
Xu Y, Li K, Zhang M (2007) Lignin precipitation on the pulp fibers in the ethanol-based organosolv pulping. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Asp 301:255–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.12.078
Xu X, Liu F, Jiang L et al (2013) Cellulose nanocrystals vs. cellulose nanofibrils: a comparative study on their microstructures and effects as polymer reinforcing agents. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:2999–3009. https://doi.org/10.1021/am302624t
Xu Z, Gao G, Pan B et al (2015) A new combined process for efficient removal of Cu(II) organic complexes from wastewater: Fe(III) displacement/UV degradation/alkaline precipitation. Water Res 87:378–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.09.025
Zeng L, Chen Y, Zhang Q et al (2015) Adsorption of Cd(II), Cu(II) and Ni(II) ions by cross-linking chitosan/rectorite nano-hybrid composite microspheres. Carbohydr Polym 130:333–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.05.015
Zhang L, Yan L, Wang Z et al (2015) Characterization of lignin derived from water-only and dilute acid flowthrough pretreatment of poplar wood at elevated temperatures. Biotechnol Biofuels 8:203. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-015-0377-x
Zhang N, Zang G-L, Shi C et al (2016) A novel adsorbent TEMPO-mediated oxidized cellulose nanofibrils modified with PEI: preparation, characterization, and application for Cu(II) removal. J Hazard Mater 316:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.05.018
Zhang L, Lu H, Yu J et al (2017) Dissolution of lignocelluloses with a high lignin content in a N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide monohydrate solvent system via simple glycerol-swelling and mechanical pretreatments. J Agric Food Chem 65:9587–9594. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03429
Zhao W, Yang L, He L, Zhang S (2016) Simultaneous enrichment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and Cu2+ in water using tetraazacalix[2]arene[2]triazine as a solid-phase extraction selector. J Agric Food Chem 64:6233–6239. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.6b03083
Zhu Q, Li Z (2015) Hydrogel-supported nanosized hydrous manganese dioxide: synthesis, characterization, and adsorption behavior study for Pb2+, Cu2+, Cd2+ and Ni2+ removal from water. Chem Eng J 281:69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.06.068
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for financial support from National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFD0601005), as well as the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31870565), the Doctorate Fellowship Foundation of Nanjing Forestry University, the Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX17_0845) and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Lu, H., Yu, J. et al. Synthesis of lignocellulose-based composite hydrogel as a novel biosorbent for Cu2+ removal. Cellulose 25, 7315–7328 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2077-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2077-8