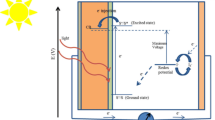
Abstract
Cellulose-based material for novel and functional application, has attracted more attention, due to its degradable, renewable and green nature. In this research, a conductive regenerated cellulose film (CRCF) was developed as an effective counter electrode (CE) for preparing dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). The CRCF presented desirable surface morphologies and structure and low resistance, and the resultant DSSC showed a high power conversion efficiency of 8.11%, which was comparable to that of traditional platinum-CE DSSC. Our discovery opens a new avenue for promoting cellulose application, as well as fabrication of cost-effective and eco-friendly DSSCs.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaoumead A, Park HD, Joo BH, Kwak DJ, Park MW, Sung YM (2013) Structural and electrical properties of titanium-doped indium oxide films deposited by RF sputtering. Energy Procedia 34:572–581
Chen L, Guo C, Zhang Q, Lei Y, Xie J, Ee S, Guai G, Song Q, Li C (2013) Graphene quantum-dot-doped polypyrrole counter electrode for high-performance dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:2047–2051
Cheng D, An X, Zhang J, Tian X, He Z, Wen Y, Ni Y (2017) Facile preparation of regenerated cellulose film from cotton linter using organic electrolyte solution (OES). Cellulose 24(4):1631–1639
Dai L, Long Z, Chen J, An X, Cheng D, Khan A, Ni Y (2017) Robust guar gum/cellulose nanofibrils multilayer films with good barrier properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(6):5477–5485
Hu L, Zheng G, Yao J, Liu N, Weil B, Eskilsson M, Karabulut E, Ruan Z, Fan S, Bloking J, McGehee M, Wågberg L, Cui Y (2013) Transparent and conductive paper from nanocellulose fibers. Energy Environ Sci 6:513–518
Khondoker MAH, Yang SY, Mun SC, Kim J (2012) Flexible and conductive ITO electrode made on cellulose film by spin-coating. Synth Met 162:1972–1976
Lee J, Lim D, Yang K, Choi W (2011) Influence of different plasma treatments on electrical and optical properties on sputtered AZO and ITO films. J Cryst Growth 326:50–57
Lee CP, Lai KY, Lin CA, Li CT, Ho KC, Wu CI, Laue SP, He JH (2017) A paper-based electrode using a graphene dot/PEDOT: PSS composite for flexible solar cells. Nano Energy 36:260–267
Li J, Ma X, Duan C, Liu Y, Zhang H, Ni Y (2016) Enhanced removal of hemicelluloses from cellulosic fibers by poly (ethylene glycol) during alkali treatment. Cellulose 23:231–238
Li C, Lee CP, Chiu I, Ramamurthy V, Huang Y, Chen T, Pang H, Lin J, Ho K (2017) Hierarchical TiO 1.1 Se 0.9-wrapped carbon cloth as the TCO-free and Pt-free counter electrode for iodide-based and cobalt-based dye-sensitized solar cells. J Mater Chem A 5:14079–14091
Liu X, Pang J, Zhang X, Wu Y, Sun R (2013) Regenerated cellulose film with enhanced tensile strength prepared with ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate (EMIMAc). Cellulose 20:1391–1399
Liu Y, Sun B, Li J, Cheng D, An X, Yang B, He Z, Lutes R, Khan A, Ni Y (2018) An aqueous dispersion of carbon fibers and expanded graphite stabilized from the addition of cellulose nanocrystals to produce highly conductive cellulose composites. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:3291–3298
Ma X, Yang X, Zheng X, Chen L, Huang L, Cao S, Akinosho H (2015) Toward a further understanding of hydrothermally pretreated holocellulose and isolated pseudo lignin. Cellulose 22:1687–1696
Mi H, Liu CH, Chang TH, Seo JH, Zhang H, Sang JC, Nader B, Ma Z, Yao C, Cai Z, Gong S (2016) Characterizations of biodegradable epoxy-coated cellulose nanofibrils (CNF) thin film for flexible microwave applications. Cellulose 23:1–7
Morfa AJ, Rödlmeier T, Jürgensen N, Stolz S, Hernandez-Sosa G (2016) Comparison of biodegradable substrates for printed organic electronic devices. Cellulose 23:1–9
Tang Y, He Z, Mosseler JA, Ni Y (2014) Production of highly electro-conductive cellulosic paper via surface coating of carbon nanotube/graphene oxide nanocomposites using nanocrystalline cellulose as a binder. Cellulose 21:4569–4581
Tian C, Zheng L, Miao Q, Cao C, Ni Y (2014) Improving the reactivity of kraft-based dissolving pulp for viscose rayon production by mechanical treatments. Cellulose 21:3647–3654
Ummartyotin S, Juntaro J, Sain M, Manuspiya H (2012) Development of transparent bacterial cellulose nanocomposite film as substrate for flexible organic light emitting diode (OLED) display. Ind Crops Prod 35:92–97
Wang H, Hu M, Fei G, Wang L, Fan J (2015) Preparation and characterization of polypyrrole/cellulose fiber conductive composites doped with cationic polyacrylate of different charge density. Cellulose 22:3305–3319
Weerasinghe HC, Huang F, Cheng YB (2013) Fabrication of flexible dye sensitized solar cells on plastic substrates. Nano Energy 2:174–189
Wu R, Wang X, Li F, Li H, Wang Y (2009) Green composite films prepared from cellulose, starch and lignin in room-temperature ionic liquid. Bioresour Technol 100:2569–2572
Wu J, Lan Z, Lin J, Huang M, Huang Y, Fan L, Luo G, Lin Y, Xie Y, Wei Y (2017) Counter electrodes in dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem Soc Rev 46:5975–5982
Yun S, Hagfeldt A, Ma T (2014) Pt-free counter electrode for dye-sensitized solar cells with high efficiency. Adv Mater 26:6210–6237
Zhu H, Zhu S, Jia Z, Parvinian S, Li Y, Vaaland O, Hu L, Li T (2015) Anomalous scaling law of strength and toughness of cellulose nanopaper. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:8971–8976
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21674123, 31700520), New Century Excellent Talents in Fujian Province University (KLa17009A), International cooperation project of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (KXGH17003), and the Distinguished Young Scholars of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (xjq201729).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Yang, H., Huang, K. et al. Conductive regenerated cellulose film as counter electrode for efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Cellulose 25, 5113–5122 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1913-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1913-1