Abstract
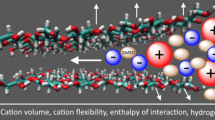
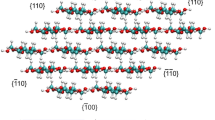
Cellulose is the most abundant natural polymer on the earth, and effective solvents are essential for its wide application. Among various solvents such as alkali/urea or ionic liquids, cations all play a very important role on the cellulose dissolution. In this work, the influence of cation on the cellulose dissolution in alkali/urea via a cooling process was investigated with a combination of MD simulation and experiments, including differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and NMR diffusometry (PFG-SE NMR). The results of DSC proved that the dissolution of cellulose in both solvents was a process within a temperature range, starting at above 0 °C and completing at low temperature (−5 °C for LiOH/urea and −20 °C for NaOH/urea), indicating the necessity of low temperature for the cellulose dissolution. Molecular dynamic (MD) simulation suggested that the electrostatic force between OH− and cellulose dominated the inter-molecular interactions. In our findings, Li+ could penetrate closer to cellulose, and displayed stronger electrostatic interaction with the biomacromolecule than Na+, thus possessed a greater “stabilizing” effect on the OH−/cellulose interaction. PFG-SE NMR demonstrated a more significant binding fraction of Li+ than Na+ to cellulose, which was consistent with MD. These results indicated that the direct interactions existed between the cations and cellulose, and Li+ exhibited stronger interaction with cellulose, leading to stronger dissolving power.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berendsen HJC, Postma JPM, van Gunsteren WF et al (1984) Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J Chem Phys 81:3684–3690. doi:10.1063/1.448118
Bergenstråhle-Wohlert M, Berglund LA, Brady JW et al (2012) Concentration enrichment of urea at cellulose surfaces: results from molecular dynamics simulations and NMR spectroscopy. Cellulose 19:1–12. doi:10.1007/s10570-011-9616-x
Bialik E, Stenqvist B, Fang Y et al (2016) Ionization of cellobiose in aqueous alkali and the mechanism of cellulose dissolution. J Phys Chem Lett 7:5044–5048. doi:10.1021/acs.jpclett.6b02346
Brendler E, Fischer S, Leipner H (2001) 7Li NMR as probe for solvent–cellulose interactions in cellulose dissolution. Cellulose 8:283–288. doi:10.1023/A:1015120107514
Brown W, Wikström R (1965) A viscosity-molecular weight relationship for cellulose in cadoxen and a hydrodynamic interpretation. Eur Polym J 1:1–10. doi:10.1016/0014-3057(65)90041-8
Cai J, Zhang L (2005) Rapid dissolution of cellulose in LiOH/Urea and NaOH/Urea aqueous solutions. Macromol Biosci 5:539–548. doi:10.1002/mabi.200400222
Cai J, Zhang L, Liu S et al (2008) Dynamic self-assembly induced rapid dissolution of cellulose at low temperatures. Macromolecules 41:9345–9351
Cai L, Liu Y, Liang H (2012) Impact of hydrogen bonding on inclusion layer of urea to cellulose: study of molecular dynamics simulation. Polymer 53:1124–1130. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2012.01.008
Chen P, Nishiyama Y, Wohlert J et al (2017) Translational entropy and dispersion energy jointly drive the adsorption of urea to cellulose. J Phys Chem B 121:2244–2251. doi:10.1021/acs.jpcb.6b11914
Chrapava S, Touraud D, Rosenau T et al (2003) The investigation of the influence of water and temperature on the LiCl/DMAc/cellulose system. Phys Chem Chem Phys 5:1842–1847. doi:10.1039/B212665F
Esaki K, Yokota S, Egusa S et al (2009) Preparation of lactose-modified cellulose films by a nonaqueous enzymatic reaction and their biofunctional characteristics as a scaffold for cell culture. Biomacromol 10:1265–1269
Fink HP, Weigel P, Purz HJ, Ganster J (2001) Structure formation of regenerated cellulose materials from NMMO-solutions. Prog Polym Sci 26:1473–1524
Glasser WG, Atalla RH, Blackwell J et al (2012) About the structure of cellulose: debating the Lindman hypothesis. Cellulose 19:589–598. doi:10.1007/s10570-012-9691-7
Hess B, Kutzner C, van der Spoel D, Lindahl E (2008) GROMACS 4: algorithms for highly efficient, load-balanced, and scalable molecular simulation. J Chem Theory Comput 4:435–447. doi:10.1021/ct700301q
Isobe N, Noguchi K, Nishiyama Y et al (2013) Role of urea in alkaline dissolution of cellulose. Cellulose 20:97–103. doi:10.1007/s10570-012-9800-7
Jorgensen WL, Chandrasekhar J, Madura JD et al (1983) Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J Chem Phys 79:926–935. doi:10.1063/1.445869
Kamide K, Kowsaka K, Okajima K (1985) Determination of intramolecular hydrogen bonds and selective coordination of sodium cation in alkalicellulose by CP/MASS 13C NMR. Polym J 17:707–711
Kielland J (1937) Individual activity coefficients of ions in aqueous solutions. J Am Chem Soc 59:1675–1678. doi:10.1021/ja01288a032
Kirschner KN, Yongye AB, Tschampel SM et al (2008) GLYCAM06: a generalizable biomolecular force field. Carbohydrates. J Comput Chem 29:622–655. doi:10.1002/jcc.20820
Klemm D, Heublein B, Fink H-P, Bohn A (2005) Cellulose: fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:3358–3393
Kosan B, Michels C, Meister F (2008) Dissolution and forming of cellulose with ionic liquids. Cellulose 15:59–66
Lamoureux G, Roux B (2006) Absolute hydration free energy scale for alkali and halide ions established from simulations with a polarizable force field. J Phys Chem B 110:3308–3322. doi:10.1021/jp056043p
Li P, Song LF, Merz KM (2015a) Systematic parameterization of monovalent ions employing the nonbonded model. J Chem Theory Comput 11:1645–1657. doi:10.1021/ct500918t
Li R, Wang S, Lu A, Zhang L (2015b) Dissolution of cellulose from different sources in an NaOH/urea aqueous system at low temperature. Cellulose 22:339–349. doi:10.1007/s10570-014-0542-6
Li Y, Liu X, Zhang S et al (2015c) Dissolving process of a cellulose bunch in ionic liquids: a molecular dynamics study. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:17894–17905. doi:10.1039/C5CP02009C
Liu Z, Zhang C, Liu R et al (2016) Dissolution of cellobiose in the aqueous solutions of chloride salts: hofmeister series consideration. Cellulose 23:295–305. doi:10.1007/s10570-015-0827-4
Luo N, Lv Y, Wang D et al (2012) Direct visualization of solution morphology of cellulose in ionic liquids by conventional TEM at room temperature. Chem Commun 48:6283–6285. doi:10.1039/C2CC31483E
Marcus Y (1983) Ionic radii in aqueous solutions. J Solut Chem 12:271–275. doi:10.1007/BF00646201
Matsumoto T, Tatsumi D, Tamai N, Takaki T (2001) Solution properties of celluloses from different biological origins in LiCl·DMAc. Cellulose 8:275–282. doi:10.1023/A:1015162027350
Netravali AN, Chabba S (2003) Composites get greener. Mater Today 6:22–29. doi:10.1016/S1369-7021(03)00427-9
Nishiyama Y, Langan P, Chanzy H (2002) Crystal structure and hydrogen-bonding system in cellulose Iβ from synchrotron X-ray and neutron fiber diffraction. J Am Chem Soc 124:9074–9082. doi:10.1021/ja0257319
Payal RS, Balasubramanian S (2014) Dissolution of cellulose in ionic liquids: an ab initio molecular dynamics simulation study. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:17458–17465. doi:10.1039/C4CP02219J
Pinkert A, Marsh KN, Pang S, Staiger MP (2009) Ionic liquids and their interaction with cellulose. Chem Rev 109:6712–6728
Rabideau BD, Ismail AE (2015) Mechanisms of hydrogen bond formation between ionic liquids and cellulose and the influence of water content. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:5767–5775. doi:10.1039/C4CP04060K
Rosenau T, Potthast A, Sixta H, Kosma P (2001) The chemistry of side reactions and byproduct formation in the system NMMO/cellulose (Lyocell process). Prog Polym Sci 26:1763–1837
Rosenau T, Potthast A, Adorjan I et al (2002) Cellulose solutions in N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide (NMMO)–degradation processes and stabilizers. Cellulose 9:283–291
Swatloski RP, Spear SK, Holbrey JD, Rogers Robin D (2002) Dissolution of cellulose with ionic liquids. J Am Chem Soc 124:4974–4975
Templeman GJ, Van Geet AL (1972) Sodium magnetic resonance of aqueous salt solutions. J Am Chem Soc 94:5578–5582. doi:10.1021/ja00771a008
Wang Y, Deng Y (2009) The kinetics of cellulose dissolution in sodium hydroxide solution at low temperatures. Biotechnol Bioeng 102:1398–1405. doi:10.1002/bit.22160
Wang S, Lu A, Zhang L (2016) Recent advances in regenerated cellulose materials. Prog Polym Sci 53:169–206. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2015.07.003
Wang S, Sun P, Liu M et al (2017a) Weak interactions and their impact on cellulose dissolution in an alkali/urea aqueous system. Phys Chem Chem Phys 19:17909–17917. doi:10.1039/C7CP02514A
Wang S, Sun P, Zhang R et al (2017b) Cation/macromolecule interaction in alkaline cellulose solution characterized with pulsed field-gradient spin-echo NMR spectroscopy. Phys Chem Chem Phys 19:7486–7490. doi:10.1039/C6CP08744B
Wolf MG, Grubmüller H, Groenhof G (2014) Anomalous surface diffusion of protons on lipid membranes. Biophys J 107:76–87. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2014.04.062
Wu DH, Chen AD, Johnson CS (1995) An improved diffusion-ordered spectroscopy experiment incorporating bipolar-gradient pulses. J Magn Reson A 115:260–264. doi:10.1006/jmra.1995.1176
Xiong B, Zhao P, Cai P et al (2013) NMR spectroscopic studies on the mechanism of cellulose dissolution in alkali solutions. Cellulose 20:613–621
Xiong B, Zhao P, Hu K et al (2014) Dissolution of cellulose in aqueous NaOH/urea solution: role of urea. Cellulose 21:1183–1192. doi:10.1007/s10570-014-0221-7
Yamashiki T, Kamide K, Okajima K et al (1988) Some characteristic features of dilute aqueous alkali solutions of specific alkali concentration (2.5 mol l-1) which possess maximum solubility power against cellulose. Polym J 20:447–457
Yuan X, Cheng G (2015) From cellulose fibrils to single chains: understanding cellulose dissolution in ionic liquids. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:31592–31607. doi:10.1039/C5CP05744B
Zhang L, Ruan D, Gao S (2002) Dissolution and regeneration of cellulose in NaOH/thiourea aqueous solution. J Polym Sci, Part B: Polym Phys 40:1521–1529. doi:10.1002/polb.10215
Zhang J, Zhang H, Wu J et al (2010) NMR spectroscopic studies of cellobiose solvation in EmimAc aimed to understand the dissolution mechanism of cellulose in ionic liquids. Phys Chem Chem Phys 12:1941–1947. doi:10.1039/B920446F
Zhou J, Zhang L (2000) Solubility of cellulose in NaOH/Urea aqueous solution. Polym J 32:866–870. doi:10.1295/polymj.32.866
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Major Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (21334005), the Major International (Regional) Joint Research Project (21620102004) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51573143, 51203122 and 21505153).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Lyu, K., Sun, P. et al. Influence of cation on the cellulose dissolution investigated by MD simulation and experiments. Cellulose 24, 4641–4651 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1456-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1456-x