Abstract
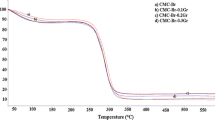
In this work, MCNT/MnO2 composite electrode actuators were fabricated by ultrasonic oscillating adsorption of MnO2 on both sides of the MCNT coated chitosan membrane. Elemental composition determined by an energy-dispersive spectrometer showed that the doping MnO2 was successfully adsorbed on the surface of MCNT. Surface morphologies of actuators under different doping MnO2 ratios (0, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 1) were characterized using scanning electron microscopy. The electromechanical properties of actuators were further given by the experimental test platform, and the electrochemical properties of actuators were analyzed using cyclic voltammetry (CV). CV results revealed that the changing trends of specific capacitance and output force density, specific capacitance and strain were basically the same. When the ratio of MnO2 was less than 0.5, the former performance increased rapidly, while higher than 0.5, the latter grew faster. The experimental results showed that the adsorption content of MnO2 particles was affected by changing the conductivity of the electrode layer, which affected the electromechanical properties of actuators.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21(2):885–896
French AD, Concha M, Dowd MK et al (2014) Electron (charge) density studies of cellulose models. Cellulose 21(2):1051–1063
Gu YQ, Mou JG, Dai DS (2015) Characteristics on drag reduction of bionic jet surface based on earthworm’s back orifice jet. Acta Phys Sin Chin Ed 64(2):024701
Hadden JA, French AD, Woods RJ (2014) Effect of microfibril twisting on theoretical powder diffraction patterns of cellulose Iβ. Cellulose 21(2):879–884
Ishii S, Kokubo H, Hashimoto K (2017) Tetra-PEG network containing ionic liquid synthesized via michael addition reaction and its application to polymer actuator. Macromolecules 50(7):2906–2915
Kim J, Jeon JH, Kim HJ (2014) Durable and water-floatable ionic polymer actuator with hydrophobic and asymmetrically laser-scribed reduced graphene oxide paper electrodes. ACS Nano 8(3):2986–2997
Kumar K, Knie C, Bléger D (2016) A chaotic self-oscillating sunlight-driven polymer actuator. Nat Commun 7:11975
Lee SW, Kim JW, Kim YH (2013) Actuation characteristics of all-organic polymer actuator with conducting polymer electrode. Macromol Res 21(6):699–703
Li C, Wang D, Liang T (2004) A study of activated carbon nanotubes as double-layer capacitors electrode materials. Mater Lett 58(29):3774–3777
Nam S, French AD, Condon BD (2016) Segal crystallinity index revisited by the simulation of X-ray diffraction patterns of cotton cellulose Iβ and cellulose II. Carbohyd Polym 135:1–9
Rogers GW, Liu JZ (2011) High-performance graphene oxide electromechanical actuators. J Am Chem Soc 134(2):1250–1255
Sait U, Muthuswamy S (2016) A study on the effect of surface topography on the actuation performance of stacked-rolled dielectric electro active polymer actuator. Funct Mater Lett 9(03):1650042
Shintake J, Rosset S, Schubert B (2016) Versatile soft grippers with intrinsic electroadhesion based on multifunctional polymer actuators. Adv Mater 28(2):231–238
Shoji E (2016) Fabrication of a diaphragm micropump system utilizing the ionomer-based polymer actuator. Sensor Actuat B Chem 237:660–665
Terasawa N, Asaka K (2016) High-performance PEDOT: PSS/single-walled carbon nanotube/ionic liquid actuators combining electrostatic double-layer and faradaic capacitors. Langmuir 32(28):7210–7218
Uh K, Yoon B, Lee CW (2016) An electrolyte-free conducting polymer actuator that displays electrothermal bending and flapping wing motions under a magnetic field. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(2):1289–1296
Xu X, Zhou J, Nagaraju DH (2015) Flexible, highly graphitized carbon aerogels based on bacterial cellulose/lignin: catalyst-free synthesis and its application in energy storage devices. Adv Funct Mater 25(21):3193–3202
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Science Foundation of China (No. 31470714) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2572017BB08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Z., Song, W., Zhao, G. et al. Chitosan-based polymer gel paper actuators coated with multi-wall carbon nanotubes and MnO2 composite electrode. Cellulose 24, 4383–4392 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1416-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1416-5