Abstract
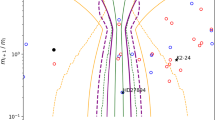
The dynamics of the two Jupiter triangular libration points perturbed by Saturn is studied in this paper. Unlike some previous works that studied the same problem via the pure numerical approach, this study is done in a semianalytic way. Using a literal solution, we are able to explain the asymmetry of two orbits around the two libration points with symmetric initial conditions. The literal solution consists of many frequencies. The amplitudes of each frequency are the same for both libration points, but the initial phase angles are different. This difference causes a temporary spatial asymmetry in the motions around the two points, but this asymmetry gradually disappears when the time goes to infinity. The results show that the two Jupiter triangular libration points should have symmetric spatial stable regions in the present status of Jupiter and Saturn. As a test of the literal solution, we study the resonances that have been extensively studied in Robutel and Gabern (Mon Not R Astron Soc 372:1463–1482, 2006). The resonance structures predicted by our analytic theory agree well with those found in Robutel and Gabern (Mon Not R Astron Soc 372:1463–1482, 2006) via a numerical approach. Two kinds of chaotic orbits are discussed. They have different behaviors in the frequency map. The first kind of chaotic orbits (inner chaotic orbits) is of small to moderate amplitudes, while the second kind of chaotic orbits (outer chaotic orbits) is of relatively larger amplitudes. Using analytical theory, we qualitatively explain the transition process from the inner chaotic orbits to the outer chaotic orbits with increasing amplitudes. A critical value of the diffusion rate is given to separate them in the frequency map. In a forthcoming paper, we will study the same problem but keep the planets in migration. The time asymmetry, which is unimportant in this paper, may cause an observable difference in the two Jupiter Trojan groups during a very fast planet migration process.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandersen, M., Gladman, B., Greenstreet, S., et al.: A uranian Trojan and the frequency of temporary giant-planet co-orbitals. Science 341, 994 (2013)
Beaugé, C., Roig, F.: A semi-analytical model for the motion of the Trojan asteroids: proper elements and families. Icarus 153, 391–415 (2001)
Biasco, L., Chierchia, L., Valdinoci, E.: Elliptic two-dimensional invariant tori for the planetary three-body problem. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 170, 91–135 (2003)
Biasco, L., Chierchia, L., Valdinoci, E.: N-dimensional elliptic invariant tori for the planar (N+1)-body problem. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 37, 1560–1588 (2006)
Brasser, R., Mikkola, S., Huang, T.-Y., et al.: Long-term evolution of the Neptune Trojan 2001 QR322. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 347, 833–836 (2004)
Brasser, R., Morbidelli, A., Gomes, R., et al.: Constructing the secular architecture of the Solar system II: the terrestrial planets. Astron. Astrophys. 507, 1053–1065 (2009)
Celletti, A., Giorgilli, A.: On the stability of Lagrangian points in the spatial restricted problem of three bodies. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 50, 31–58 (1991)
Connors, M., Wiegert, P., Veillet, C.: Earth’s Trojan asteroid. Nature 475, 481–483 (2011)
Couetdic, J., Laskar, J., Correia, A.C.M., et al.: Dynamical stability analysis of the HD202206 system and constraints to the planetary orbits. Astron. Astrophys. 519, A10 (2010)
Díez, C., Jorba, À., Simó, C.: A dynamical equivalent to the equilateral libration points of the earth-moon system. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 50, 13–29 (1991)
Dufey, J., Noyelles, B., Rambaux, N., Lamaitre, A.: Latitudinal librations of Mercury with a fluid core. Icarus 203, 1–12 (2009)
Dvorak, R., Schwarz, R.: On the stability regions of the Trojan asteroids. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 92, 19–28 (2005)
Érdi, B.: Long periodic perturbations of Trojan asteroids. Celest. Mech. 43, 303–308 (1988)
Érdi, B., Forgács-Dajka, E., Süli, Á.: On some long time dynamical features of the Trojan asteroids of Jupiter. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 117, 3–16 (2013)
Freistetter, F.: The size of the stability regions of Jupiter Trojans. Astron. Astrophys. 453, 353–361 (2006)
Gabern, F., Jorba, À.: A restricted four-body model for the dynamics near the Lagrangian points of the Jun-Jupiter system. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. 1, 143–182 (2001)
Gabern, F., Jorba, À., Robutel, P.: On the accuracy of restricted three-body models for the Trojan motion. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. 11, 843–854 (2004)
Gabern, F., Jorba, À., Locatelli, U.: On the construction of the Kolmogorov normal form for the Trojan asteroids. Nonlinearility 18, 1705–1734 (2005)
Giorgilli, A., Delshams, A., Fontich, E., et al.: Effective stability for a Hamiltonian system near an elliptic equilibrium point, with an application to the restricted three-body problem. J. Differ. Equ. 77, 167–198 (1989)
Giorgilli, A., Skokos, C.: On the stability of the Trojan asteroids. A&A 317, 254–261 (1997)
Gómez, G., Llibre, J., Martínez, R., Simó, C.: Dynamics and Mission Design near Libration Point Orbits, Vol. I, Fundamentals. The Case of Collinear Libration Points. World Scientific, Singapore (2001)
Guzzo, M., Benettin, G.: On the stability of the Trojan asteroids. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser B 1, 1–28 (2001)
Hou, X.Y., Liu, L.: On quasi-periodic motions around the triangular libration points of the real Earth-Moon system. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 108, 301–313 (2010)
Hou, X.Y., Liu, L.: On quasi-periodic motions around the collinear libration points in the real Earth-Moon system. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 110, 71–98 (2011)
Hou, X.Y., Scheeres, D.J., Liu, L.: Saturn Trojans: a dynamical point of view. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 437, 1420–1433 (2014)
Jorba, À., Simó, C.: On quasi-periodic perturbations of elliptic equilibrium points. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 27, 1704–1737 (1996)
Jorba, À., Ramírez, R., Villanueva, J.: Effective reducibility of quasi-periodic linear equations close to constant coefficients. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 28, 178–188 (1997)
Jorba, À., Villanueva, J.: On the persistence of lower dimensional invariant tori under quasi-periodic perturbations. J. Nonlinear Sci. 7, 427–473 (1997)
Laskar, J.: Introduction to frequency map analysis. In: Simó, C. (ed.) Hamiltonian Systems with Three or More Degrees of Freedom, pp. 131–147. Kluwer, Spain (1999)
Laskar, J.: Frequency map analysis and quasi periodic decompositions. In: Benest, et al. (eds.) Hamiltonian Systems and Fourier Analysis. Taylor and Francis, London (2005)
Laskar, J., Froeschlé, C., Celletti, A.: The measure of chaos by the numerical analysis of the fundamental frequencies. Application to the standard mapping. Physica D 56, 253–269 (1992)
Lei, H.-L., Xu, B.: High-order analytical solutions around the triangular libration points in CRTBP. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 434, 1376–1386 (2013)
Levison, H.F., Shoemaker, E.M., Shoemaker, C.S.: The dispersal of the Trojan asteroid swarm. Nature 385, 42–44 (1997)
Marzari, F., Scholl, H., Murray, C., Lagerkvist, C.: Origin and evolution of Trojan asteroids. Asteroids III, Tucson, pp. 725–738. University of Arizona Press, Arizona (2002)
Marzari, F., Scholl, H.: On the instability of Jupiter’s Trojans. Icarus 159, 328–338 (2002)
Marzari, F., Scholl, H.: Long term stability of Earth Trojans. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 117, 91–100 (2013)
Michtchenko, T.A., Beaugé, C., Roig, F.: Planetary migration and the effects of mean motion resonances on Jupiter’s Trojan asteroids. AJ 122, 3485–3491 (2001)
Mikkola, S., Innanen, K.A., Muinonen, K., et al.: A preliminary analysis of the orbit of the Mars Trojan asteroid (5261) EUREKA. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 58, 53–64 (1994)
Milani, A., Nobili, A.M.: An example of stable chaos in the solar system. Nature 357, 569–571 (1992)
Milani, A.: The Trojan asteroid belt: proper elements, stability, chaos and families. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 57, 59–94 (1993)
Morbidelli, A., Levison, H.F., Tsiganis, K., Gomes, R.: Chaotic capture of Jupiter’s Trojan asteroids in the earth solar system. Nature 435, 462–465 (2005)
Morbidelli, A., Brasser, R., Gomes, R., et al.: Evidence from the asteroid belt for a violent past evolution of Jupiter’s orbit. Astron. J. 140, 1391–1401 (2010)
Murray, C.D., Dermott, S.F.: Solar System Dynamics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1999)
Nesvorný, D., Dones, L.: How long-lived are the hypothetical Trojan populations of Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Icarus 160, 271–288 (2002)
Nesvorný, D., Morbidelli, A.: Statistical study of the early Solar system’s instability with four, five, and six giant planets. Astron. J. 144, 117–136 (2012)
Nesvorný, D., Vokrouhlický, D., Morbidelli, A.: Capture of Trojans by jumping Jupiter. Astrophys. J. 768, 45–52 (2013)
Noyelles, B., Dufey, J., Lemaitre, A.: Core-mantle interactions for Mercury. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 407, 479–496 (2010)
O’Brien, D.P.: A dynamical origin of the leading/trailing asymmetry in Jupiter’s Trojan swarms? AAS/Div. Planet. Sci. Meet. Abstr. 44(210), 10 (2012)
Porco, C.C., Baker, E., Barbara, J., et al.: Cassini imaging science: Initial results on Saturn’s rings and small satellites. Science 307, 1226–1236 (2005)
Quinlan, G.D., Tremaine, S.: Symmetric multistep methods for the numerical integration of planetary orbits. AJ 100, 1694–1700 (1990)
Rabe, E.: Third-order stability of the long-period Trojan librations. Astron. J. 72, 10–19 (1967)
Robutel, P., Gabern, F.: The resonant structure of Jupiter’s Trojan asteroids-I. Long-term stability and diffusion. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 372, 1463–1482 (2006)
Robutel, P., Bodossian, J.: The resonant structure of Jupiter’s Trojan asteroids-II. What happens for different configurations of the planetary system. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 339, 69–87 (2009)
Schwarz, R., Gyergyovits, M., Dvorak, R.: On the stability of high inclined L4 and L5 Trojans. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 90, 139–148 (2004)
Skokos, C., Dokoumetzidis, A.: Effective stability of the Trojan asteroids. Astron. Astrophys. 367, 729–736 (2001)
Szebehely, : Theory of Orbits. Academic Press, New York (1967)
Tsiganis, K., Varvoglis, H., Dvorak, R.: Chaotic diffusion and effective stability of Jupiter Trojans. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 92, 71–87 (2005)
Acknowledgments
This work was completed during the first author’s visit to the Colorado Center for Astrodynamics Research (CCAR). It was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11322330, 11078001), National Basic Research Program of China (2013CB834100), and National High Technology Research and Development Program 863 of China (2012AA 121602). The authors owe their thanks to Philippe Robutel and another anonymous referee for their critical and useful comments. The first author would also like to thank Prof. Liyong Zhou in his department for useful discussions on resonance mechanisms.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, X., Scheeres, D.J. & Liu, L. Dynamics of the Jupiter Trojans with Saturn’s perturbation in the present configuration of the two planets. Celest Mech Dyn Astr 119, 119–142 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-014-9544-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-014-9544-9