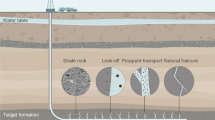
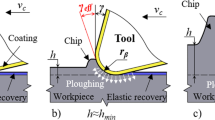
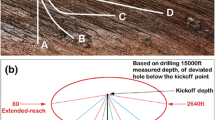
Drilling speed-increasing tools are essential in increasing penetration rate in deep and hard-to-drill formations. This paper delves into the characteristics, application scopes, and performance advantages of commonly used tools, such as torsional impact tools, friction reduction by impact tools, positive displacement motors (PDMs), turbodrills, and Gyro Stable Drilling tools. The suitability and effectiveness of these drilling speed-increasing tools for different types of hard-to-drill lithologies are also examined. This paper serves as a reference for selecting the appropriate drilling tools in challenging drilling conditions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang J., Liu S., Shi L. et al, Research on prediction model for formation pressure in compression structure. J . Acta Petrol Sinica, 30.5(2009):764-768.
Yang J. Relationship model between rock drilling strength and formation pressure and its application. J. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 25.2(2001):3.
Yang J., Gao D.L. Study on monitoring and prediction technology of formation pressure while drilling. J. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 23.001(1999):35-37.
Pan L., Cui Y.D., Xu J.F. Rock Breaking Mechanism and Experimental Study of Axe-shaped PDC Cutter. J. petroleum machinery, 50.01(2022):34-40.
Liu W.J., Yang F.L., Zhu X.H. Research on Mechanism of Rock Breaking and Speed Increase in Cutting with Abnormal PDC Cutter. J. China Mechanical Engineering, 33.17(2022):2133-2141.
Teodoriu, Catalin. Use of Downhole Mud-Driven Hammer for Geothermal Applicationsc.
Nguyen T. C., Al-Safran E., Nguyen V. Theoretical modeling of Positive Displacement Motors performance. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering , (2018):S0920410518302353.
He, Yuguang, et al. Optimization design for turbodrill blades based on a twisting method - ScienceDirect. J. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, (2021).
Su J., Yuan Z.M., He P.F. et al. Application of HPG Hybrid Percussion Generator speed-increasing tool in Bohai Oilfield. J. Ocean Engineering Equipment and Technology, 6.01(2019):457-464.
Zhu H. Application analysis of TorkBuster in the continental strata of Northeast Sichuan. J. Petrochemical Industry Technology, 27.04(2020):21-22.
Wang Z. J. Application of TorkBuster in drilling acceleration of extra-deep well A. J. Petrochemical Industry Technology, 25.04(2018):158.
Chen F.J. Test and application of TorkBuster in speed-increasing in hard formation. J. Chemical Enterprise Management, 17(2014).
Zhang L., Huo H.B., Li Z.H. et al. Application Evaluation of Two Kinds of Speed Increasing Tools in a Deep Well of Bohai Oilfield. J. Technology Supervision in Petroleum Industry, 36.04(2020):1-3.
Kang J., Hao W.W., Liu D.Z., et al. Analysis of drilling speed increasing by using high torque PDM and high efficiency PDC bit in high steep gravel formation. J. West-china Exploration Engineering, (2021).
Yu Y., Nan Y.M., Li S.G., et al. Technology for increasing drilling speed of Paleozoic stratum in Shunbei Oilfield. J. Fault-Block Oil AND Gas Field, (2019).
Han L.X., Yao J.L., Li W.C. Speed-increasing technology of drilling with impregnated diamond bit for turbine drill tools in Xujiahe formation in Sichuan and Chongqing areas. J. Drilling & Production Technology , 41.3(2018):4.
Wu H.X., Shen L.N., Li C. et al. Research and application of a new model bit with surface impregnated diamond in Bozi block. J. Drilling Engineering, (2021).
Zhang C., Zhang W.T., Liang Z.Y., et al. Application of turbine+impregnated speed-increasing technology in Gao 103 well in the southern margin of Junggar. J. Xinjiang Oil&Gas, 17.2(2021):6.
Hu Q.F. Discussion on theory and technology of fast drilling with turbodrill against deviation. J. Petrochemical Industry Technology, 35.3(2007):3.
Zhang Z.X., Liu D.F. Application of directional drilling with turbine and impregnated diamond bit in Yuanba area. J. China Chemical Trade, 000.013(2018):106.
Cheng F.S., Huang Y.Q., Cheng S.P., et al. Gyro stable drilling tool speed increasing principle analysis and application research. J. Natural Gas Technology and Economy, 9.05(2015):38-40+79.
Huaidong Luo, et al. Application of Gyro Shock-damping Tool Combining with PDC Bit in Granite Buried Hill Formation. J. China Petroleum Machinery.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel, No. 4, pp. 136–140, July – August, 2023.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, G., Xu, J., Zhang, L. et al. Increasing Drilling Speed in Hard-to-Drill Formations with Various Types of Tools. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 59, 841–849 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-023-01589-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-023-01589-3