Abstract
Purpose
We aimed to compare the initial and salvage brain-directed treatment and overall survival (OS) between patients with 1–4 brain metastases (BMs) and those with 5–10 from breast cancer (BC). We also organized a decision tree to select the initial whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT) for these patients.
Methods
Between 2008 and 2014, 471 patients were diagnosed with 1–10 BMs. They were divided into two groups based on the number of BM: 1–4 BMs (n = 337) and 5–10 BMs (n = 134). Median follow-up duration was 14.0 months.
Results
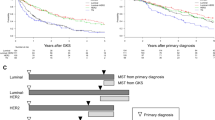
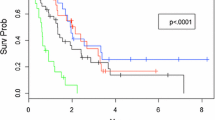
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS)/fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (FSRT) was the most common treatment modality (n = 120, 36%) in the 1–4 BMs group. In contrast, 80% (n = 107) of patients with 5–10 BMs were treated with WBRT. The median OS of the entire cohort, 1–4 BMs, and 5–10 BMs was 18.0, 20.9, and 13.9 months, respectively. In the multivariate analysis, the number of BM and WBRT were not associated with OS, whereas triple-negative BC and extracranial metastasis decreased OS. Physicians determined the initial WBRT based on four variables in the following order: number and location of BM, primary tumor control, and performance status. Salvage brain-directed treatment (n = 184), mainly SRS/FSRT (n = 109, 59%), prolonged OS by a median of 14.3 months.
Conclusion
The initial brain-directed treatment differed notably according to the number of BM, which was chosen based on four clinical factors. In patients with ≤ 10 BMs, the number of BM and WBRT did not affect OS. The major salvage brain-directed treatment modality was SRS/FSRT and increased OS.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Jeon W, Jang BS, Jeon SH et al (2018) Analysis of survival outcomes based on molecular subtypes in breast cancer brain metastases: a single institutional cohort. Breast J 24:920–926. https://doi.org/10.1111/tbj.13111
Kim JS, Kim IA (2020) Evolving treatment strategies of brain metastases from breast cancer: current status and future direction. Ther Adv Med Oncol 12:175883592093611. https://doi.org/10.1177/1758835920936117
Quigley MR, Fukui O, Chew B et al (2013) The shifting landscape of metastatic breast cancer to the CNS. Neurosurg Rev 36:377–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-012-0446-6
Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR et al (2009) Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10:1037–1044. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70263-3
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M et al (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Med Assoc 295:2483–2491. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.295.21.2483
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U et al (2011) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952–26001 study. J Clin Oncol 29:134–141. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2010.30.1655
Brown PD, Jaeckle K, Ballman KV et al (2016) Effect of radiosurgery alone vs radiosurgery with whole brain radiation therapy on cognitive function in patients with 1 to 3 brain metastases a randomized clinical trial. JAMA - J Am Med Assoc 316:401–409. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.9839
Chaung KV, Sloan AE, Choi S (2021) Limited brain metastases: a narrative review. Ann Palliat Med 10:6016–6027. https://doi.org/10.21037/apm-21-363
Gondi V, Bauman G, Bradfield L et al (2022) Radiation therapy for brain metastases: an ASTRO clinical practice guideline. Pract Radiat Oncol 12:265–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prro.2022.02.003
Kim JS, Kim K, Jung W et al (2022) The pattern of care for brain metastasis from breast cancer over the past 10 years in Korea: a multicenter retrospective study (KROG 16–12). Cancer Res Treat 54:1121–1129. https://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2021.1083
Kim JS, Kim K, Jung W et al (2020) Survival outcomes of breast cancer patients with brain metastases: a multicenter retrospective study in Korea (KROG 16–12). The Breast 49:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.breast.2019.10.007
Kim JS, Kim K, Jung W et al (2021) New brain metastases after whole-brain radiotherapy of initial brain metastases in breast cancer patients: the significance of molecular subtypes (KROG 16–12). Breast Cancer Res Treat 186:453–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-020-06043-0
Kim JS, Kim K, Jung W et al (2021) Novel prognostic classification predicts overall survival of patients receiving salvage whole-brain radiotherapy for recurrent brain metastasis from breast cancer: a recursive partitioning analysis (KROG 16–12). The Breast 60:272–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.breast.2021.11.005
Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Shuto T et al (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): a multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol 15:387–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70061-0
Rogers S, Baumert B, Blanck O et al (2022) Stereotactic radiosurgery and radiotherapy for resected brain metastases: current pattern of care in the radiosurgery and stereotactic radiotherapy working group of the German association for radiation oncology (DEGRO). Strahlentherapie und Onkol 198:919–925. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-022-01991-6
Khan M, Lin J, Liao G et al (2017) Comparison of WBRT alone, SRS alone, and their combination in the treatment of one or more brain metastases: review and meta-analysis. Tumor Biol 39:101042831770290. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010428317702903
Yan H, Li X, Peng Y et al (2020) Apatinib and fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for the treatment of limited brain metastases from primary lung mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Medicine (Baltimore) 99:e22925. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000022925
Hendriks LEL, Schoenmaekers J, Zindler JD et al (2015) Safety of cranial radiotherapy concurrent with tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer patients: a systematic review. Cancer Treat Rev 41:634–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2015.05.005
Funding
This work was supported by grants from Korean Ministry of Science and Information & Communication Technology (NRF#2023R1A2C3003782) to In Ah Kim.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JSK contributed to formal analysis, methodology, visualization, writing of the original draft, and writing, reviewing, and editing of the manuscript. KK contributed to formal analysis, methodology, supervision, writing of the original draft, and writing, reviewing, and editing of the manuscript. WJ, KHS, SAI, HJK, YBK, JSC, JHK, DHC, YHP, DYK, THK, BOC, SWL, SK, JK, KMK, WKC, KSK, WSY, JHK, JC, and YKO contributed to investigation and writing, reviewing, and editing of the manuscript. IAK contributed to conceptualization, supervision, and writing, reviewing, and editing of the manuscript. All the authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
The Institutional Review Board of each institution approved this study. This study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to participate
The requirement for informed consent was waived because of the retrospective design.
Consent to publish
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Jae Sik Kim currently working at the Department of Radiation Oncology in Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.S., Kim, K., Jung, W. et al. Comparison of initial and sequential salvage brain-directed treatment in patients with 1–4 vs. 5–10 brain metastases from breast cancer (KROG 16–12). Breast Cancer Res Treat 200, 37–45 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-023-06936-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-023-06936-w