Abstract
Introduction
To assess treatment outcome and prognostic factors associated with prolonged survival in patients with brain metastases (BM) treated with stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) or hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (HFSRT).
Methods/Patients
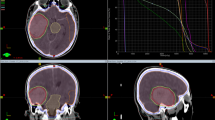
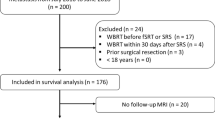
This study retrospectively reviewed 200 patients with 324 BM treated with one fraction (15–21 Gy) or 5–10 fractions (25–40 Gy) between January 2010 and August 2016. 26.5% of patients received whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) and 25% initial surgery. Demographics, prognostic scales, systemic and local controls, patterns of relapse and rescue, toxicity, and cause of death were analyzed. A stratified analysis by primary tumor was done.
Results
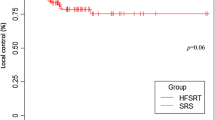
Median overall survival (OS) was 8 months from SRS/HFSRT. Breast cancer patients had a median OS of 17 months, followed by renal (11 months), lung (8 months), colorectal (5 months), and melanoma (4 months). The univariate analysis showed improved OS in females (p 0.004), RPA I–II (p < 0.001) initial surgery (p < 0.001), absence of extracranial disease (p 0.023), and good disease control (p 0.002). There were no differences in OS or local control between SRS and HFSRT or in patients receiving WBRT. Among 44% of brain recurrences, 11% were in field. 174 patients died, 10% from confirmed intracranial progression.
Conclusions
SRS and HSFRT are equally effective and safe for the treatment of BM, with no exceptions among different primary tumors. Disease control, surgery, age, and prognostic scales correlated with OS. However, the lack of survival benefit regarding WBRT might become logical evidence for its omission in a subset of patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soffietti R, Ruda R, Trevisan E. Brain metastases: current management and new developments. Curr Opin Oncol. 2008;20(6):676–84.
Abdel Razek AAK, Talaat M, El-Serougy L, Gaballa G, Abdelsalam M. Clinical applications of arterial spin labeling in brain tumors. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2019;43(4):525–32.
Abdel Razek AAK, Talaat M, El-Serougy L, Abdelsalam M, Gaballa G. Differentiating glioblastomas from solitary brain metastases using arterial spin labeling perfusion- and diffusion tensor imaging-derived metrics. World Neurosurg. 2019;127:e593–e598598.
Sperduto PW, Chao ST, Sneed PK, Luo X, Suh J, Roberge D, et al. Diagnosis specific prognostic factors, indexes, and treatment outcomes for patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases: a multi-institutional analysis of 4259 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;77(3):655–61.
Agboola O, Benoit B, Cross P, Da Silva V, Esche B, Lesiuk H, et al. Prognostic factors derived from recursive partition analysis (RPA) of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials applied to surgically resected and irradiated brain metastatic cases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998;42:155–9.
Gaspar LE, Scott C, Murray K, Curran W. Validation of the RTOG recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) classification for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;47:1001–6.
Sperduto PW, Berkey B, Gaspar LE, Mehta M, Curran W. A new prognostic index and comparison to three other indices for patients with brain metastases: an analysis of 1960 patients in the RTOG database. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70:510–4.
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, Xu Z, Shanley R, Luo X, et al. Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: an accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(4):419–25.
Sperduto PW, Yang TJ, Beal K, Pan H, Brown PD, Bangdiwala A, et al. Estimating survival in patients with lung cancer and brain metastases: an update of the graded prognostic assessment for lung cancer using molecular markers (lung-molGPA). JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(6):827–31.
Sperduto PW, Jiang W, Brown PD, Braunstein S, Sneed P, Wattson DA, et al. Estimating survival in melanoma patients with brain metastases: an update of the graded prognostic assessment for melanoma using molecular markers (melanoma-molGPA). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017;99(4):812–6.
Sperduto PW, Deegan BJ, Li J, Jethwa KR, Brown PD, Lockney N, et al. Estimating survival for renal cell carcinoma patients with brain metastases: an update of the renal graded prognostic assessment tool. Neuro Oncol. 2018;20(12):1652–60.
Nahed BV, Alvarez-Breckenridge C, Brestianos PK, Shih H, Sloan A, Ammirati M, et al. Congress of neurological surgeons systematic review and evidence-based guidelines on the role of surgery in the management of adults with metastatic brain tumors. Neurosurgery. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyy542.
Gaspar LE, Prabhu RS, Hdeib A, McCracken DJ, Lasker GF, McDermott MW, et al. Congress of neurological surgeons systematic review and evidence-based guidelines on the role of whole brain radiation therapy in adults with newly diagnosed metastatic brain tumors. Neurosurgery. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyy541.
Graber JJ, Cobbs CS, Olson JJ. Congress of neurological surgeons systematic review and evidence-based guidelines on the use of stereotactic radiosurgery in the treatment of adults with metastatic brain tumors. Neurosurgery. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyy543.
Han RH, Dunn GP, Chheda MG, Kim AH. The impact of systemic precision medicine and immunotherapy treatments on brain metastases. Oncotarget. 2019;10(62):6739–53.
Korytko T, Radivoyevitch T, Colussi V, Wessels BW, Pillai K, Maciunas RJ, et al. 12 Gy gamma knife radiosurgical volume is a predictor for radiation necrosis in non-AVM intracranial tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;64(2):419–24.
Fahrig A, Ganslandt O, Lambrecht U, Grabenbauer G, Kleinert G, Sauer R, et al. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases. Results from three different dose concepts. Strahlenther Onkol. 2007;183:625–30.
Ernst-Stecken A, Ganslandt O, Lanbrecht U, Sauer R, Grabenbauer G. Phase II trial of hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases: results and toxicity. Radiother Oncol. 2006;81:18–24.
Shaw E, Kline R, Gillin M, Souhami L, Hirschfeld A, Dinapoli R, et al. Radiation Therapy Oncology Group: radiosurgery quality assurance guidelines. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1993;27(5):1231–9.
Cox JD, Stetz J, Pajak TF. Toxicity criteria of the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;31(5):1341–6.
Kohutek ZA, Yamada Y, Chan TA, Brennan CW, Tabar V, Gutin PH, et al. Long-term risk of radionecrosis and imaging changes after stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases. J Neurooncol. 2015;125(1):149–56.
Razek AAKA, El-Serougy L, Abdelsalam M, Gaballa G, Talaat M. Differentiation of residual/recurrent gliomas from postradiation necrosis with arterial spin labeling and diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging-derived metrics. Neuroradiology. 2018;60(2):169–77.
Gorovents D, Rava P, Ebner DK, Tybor DJ, Cielo D, et al. Predictors for long-term survival free from whole brain radiation therapy in patients treated with radiosurgery for limited brain metastases. Front Oncol. 2015. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2015.00110.
Won YK, Lee JA, Kang YN, Jang JS, Kang JH, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer. Radiat Oncol J. 2015;33(3):207–16.
Sia J, Paul E, Dally M, Ruben J. Stereotactic radiosurgery for 318 brain metastases in a single Australian centre: the impact of histology and other factors. J Clin Neurosci. 2015;22(2):303–7.
Likhacheva A, Pinnix CC, Parikh NR, Allen PK, McAleer MF, Chiu MS, et al. Predictors of survival in contemporary practice after initial radiosurgery for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;85(3):656–61.
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M, Nakagawa K, Toyoda T, Hatano K, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2006;295(21):2483–91.
Akanda ZZ, Hong W, Nahavandi S, Haghighi N, Phillips C, Kok DL. Post-operative stereotactic radiosurgery following excision of brain metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinical article. Radiother Oncol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2019.08.024.
Sneed PK, Mendez J, den Vemer-van Hoek JG, Seymour ZA, Ma L, Molinaro AM, et al. Adverse radiation effect after stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: incidence, time course, and risk factors. J Neurosurg. 2015;123(2):373–86.
Funding
This research project has not been sponsored or received any financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Research was based on retrospective data form patients’ clinical chart. Our ethics committee board approved this project on February 5, 2018, with a record number 02.18.
Informed consent
Patients signed an informed consent before treatment with SRS/HFSRT.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sallabanda, M., García-Berrocal, M.I., Romero, J. et al. Brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy: outcomes and predictors of survival. Clin Transl Oncol 22, 1809–1817 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-020-02321-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-020-02321-x