Abstract
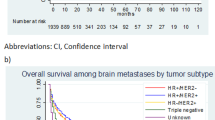
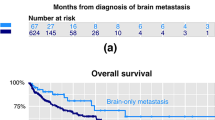
The improved survival following the diagnosis of breast cancer has potentially altered the characteristics and course of patients presenting with CNS involvement. We therefore sought to define our current cohort of breast cancer patients with metastatic disease to the CNS in regard to modern biomarkers and clinical outcome. Review of clinical and radiographic records of women presenting to a tertiary medical center with the new diagnosis of CNS metastatic disease from breast cancer. This was a retrospective review from patients identities obtained from two prospective databases. There were 88 women analyzed who were treated over the period of January 2003 to February 2010, average age 56.9 years. At the time of initial presentation of CNS disease, 68 % of patients had multiple brain metastases, 17 % had a solitary metastasis, and 15 % had only leptomeningeal disease (LMD). The median survival for all patients from the time of diagnosis of breast disease was 50.0 months, and 9.7 months from diagnosis of CNS involvement. The only factor related to overall survival was estrogen receptor-positive pathology (57.6 v. 38.2 months, p = .02 log-rank); those related to survival post CNS diagnosis were presentation with LMD (p = .004, HR = 3.1, Cox regression) and triple-negative hormonal/HER2 status (p = .02, HR = 2.3, Cox regression). Patients with either had a median survival of 3.1 months (no patients in common). Of the 75 patients who initially presented with metastatic brain lesions, 20 (26 %) subsequently developed LMD in the course of their disease (median 10.4 months), following which survival was grim (1.8 months median). Symptoms of LMD were most commonly lower extremity weakness (14/33), followed by cranial nerve deficits (11/33). The recently described Graded Prognostic Assessment (GPA) tumor index stratified median survival at 2.5, 5.9, 13.1, and 21.7 months, respectively, for indices of 1–4 (p = .004, log-rank), which contrasted with the nonsignificant survival difference between Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Recursive Partitioning Analysis classes one and two. (13.1 v. 13.2, p = .8, log-rank). Treatment of patients with metastatic brain disease from breast cancer should be tailored to the patient’s hormonal status and GPA index. Practitioners must be vigilant for the development of LMD, especially as it often presents with nondescript complaints such as back pain.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altundag K, Bondy ML, Mirza NQ, Shu-Wan K, Brogilo K, Hortobagyl GN, Rivera E (2007) Clinicopathologic characteristics and prognostic factors in 420 metastatic breast cancer patients with central nervous system metastasis. Cancer 110:2640–2647
Bindal AK, Bindal RK, Hess KR, Shiu A, Hassenbusch SJ, Shi WM, Sawaya R (1996) Surgery versus radiosurgery in the treatment of brain metastasis. J Neurosurg 84:748–754
Carey LA, Perou CM, Livasy CA, Dressler LG, Cowan D, Conway K, Karaca G, Troester MA, Tse CK, Edmiston S, Deming SL, Geradts J, Cheang MC, Nielsen TO, Moorman PG, Earp HS, Millikan RC (2006) Race, breast cancer subtypes and survival in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study. JAMA 295(295):2492–2502
Chamberlain MC (2010) Leptomeningeal metastasis. Semin Neurol 30:236–244
Cho SY, Choi HY (1980) Causes of death and metastatic patterns in patients with mammary cancer. Am J Clin Pathol 73:232–234
Clarke JL, Perez HR, Jacks LM, Panageas KS, DeAngelis LM (2010) Leptomeningeal metastases in the MRI era. Neurology 74:1449–1454
Dawood S, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Alabarracin C, Yu TK, Hortobagyl GN, Buchholz TA, Woodward WA (2010) Prognostic factors of survival in the trastuzumab era among women with breast cancer and brain metastases who receive whole brain radiotherapy. Cancer 116:3084–3092
Dowsett M, Dubier AK (2008) Emerging biomarkers and new understanding of traditional markers in personalized therapy for breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14:8019–8026
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (2005) Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomized trials. Lancet 365:1687–1717
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D, Verweij J (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228–247
Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M, Asbell S, Phillips T, Wasserman T, McKenna WG, Byhardt R (1997) Recursive partitioning (RPA) of prognostic factors in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 37:745–751
Gauthier H, Guilhaume MN, Bidard FC, Pierga JY, Girre V, Cottu PH, Laurence V, Livartowski A, Mignot L, Diéras V (2010) Survival of breast cancer patients with meningeal carcinomatosis. Ann Oncol 21:2183–2187
Harputluoglu H, Dizdar O, Aksoy S, Kilickap S, Dede DS, Ozisik Y, Guler N, Barista I, Gullu I, Hayran M, Selek U, Cengiz M, Zorlu F, Tekuzman G, Altundag K (2008) Characteristics of breast cancer patients with central nervous system metastases: a single center experience. J Nat Med Assoc 100:521–526
Hicks DG, Short SM, Prescott NL, Tarr SM, Coleman KA, Yoder BJ, Crowe JP, Choueiri TK, Dawson AE, Budd GT, Tubbs RR, Casey G, Weil RJ (2006) Breast cancers with brain metastases are more likely to be estrogen receptor negative, express the basal cytokeratin CK5/6, and overexpress HER2 or EGFR. Am J Surg Pathol 30:1097–1104
Kaplan IW, Meier R (1959) Submucous lipoma of the colon. Am J Gastroenterol 31:673–683
Karlovits BJ, Quigley MR, Karlovits SM, Miller L, Johnson M, Gayou O, Fuhrer R (2009) Stereotactic radiosurgery boost to the resection bed for oligometastatic brain disease: challenging the tradition of adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy. Neurosurg Focus 27(6):E7
Kim HJ, Im SA, Keam B, Kim YJ, Han SW, Kim TM, Oh DY, Kim JH, Lee SH, Chie EK, Han W, Kim DW, Kim TY, Noh DY, Heo DS, Park IA, Bang YJ, Ha SW (2012) Clinical outcome of central nervous system metastases from breast cancer: differences in survival depending on systemic treatment. J Neuro-Onc 106:303–313
Lee SS, Ahn J, Kim MK, Sym SJ, Gong G, Ahn AD, Kim S, Kim WK (2008) Brain metastases in breast cancer: prognostic factors and management. Breast Cancer Res Treat 111:523–530
Lee Y (1983) Breast carcinoma: pattern of metastasis at autopsy. J Surg Oncol 23:175–180
Lin NU, Bellon JR, Winer EP (2004) CNS metastases in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 22:3609–3617
Lin NU, Claus E, Sohl J, Razzak AR, Arnaout A, Winer EP (2008) Sites of distant relapse and clinical outcomes in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: high incidence of central nervous system metastases. Cancer 113:2638–2645
Nam B, Kim S, Han H, Kwon Y, Lee KS, Kim TH, Ro J (2008) Breast cancer subtypes and survival in patients with brain metastases. Breast Cancer Res 10:R20
Oakman C, Viale G, DiLeo A (2010) Management of triple negative breast cancer. Breast 19:312–321
Patanaphan V, Salazar OM, Risco R (1988) Breast cancer: metastatic patterns and their prognosis. South Med J 81:1109–1112
Paek SH, Audu PB, Sperling MR, Cho J, Andrews DW (2005) Reevaluation of surgery for the treatment of brain metastases: review of 208 patients with single or multiple brain metastases treated at one institution with modern neurosurgical techniques. Neurosurgery 56:1021–1034
Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA, Fluge O, Pergamenschikov A, Williams C, Zhu SX, Lønning PE, Børresen-Dale AL, Brown PO, Botstein D (2000) Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 406:747–752
Peto R, Boreham J, Clarke M, Davies C, Beral V (2000) UK and USA breast cancer deaths down 25 % in year 2000 at ages 20–69 years. Lancet 355:1822
Quigley MR, Fuhrer R, Karlovits S, Karlovits B, Johnson M (2008) Single session stereotactic radiosurgery boost to the post-operative site in lieu of whole brain radiation in metastatic brain disease. J Neurooncol 87:327–332
Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Thorsen T, Quist H, Matese JC, Brown PO, Botstein D, Eystein Lønning P, Børresen-Dale AL (2001) Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. PNAS 98:10869–10874
Sorlie T, Tibshirani R, Parker J, Hastie T, Marron JS, Nobel A, Deng S, Johnsen H, Pesich R, Geisler S, Demeter J, Perou CM, Lønning PE, Brown PO, Børresen-Dale AL, Botstein D (2003) Repeated observation of breast tumor subtypes in independent gene expression data sets. PNAS 100:8418–8423
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, Xu Z, Shanley R, Luo X, Sneed PK, Chao ST, Weil RJ, Suh J, Bhatt A, Jensen AW, Brown PD, Shih HA, Kirkpatrick J, Gaspar LE, Fiveash JB, Chiang V, Knisely JP, Sperduto CM, Lin N, Mehta M (2011) Effect of tumor subtype on survival and the graded prognostic assessment for patients with breast cancer and brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82(5):2111–2117
Tsukada Y, Fouad A, Pickeren JW, Lane WW (1983) Central nervous system metastasis from breast carcinoma. Cancer 52:2349–2354
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Comments
Moshe Hadani, Zvi R Cohen, Tel Aviv, Israel
In this article, Quigley et al. present a retrospective review of 88 patients with CNS involvement of breast cancer. The authors conclude that the treatment should be tailored to the patient hormonal status and GPA index. Their conclusion support previous publications. Their findings of the increased likelihood of active metastatic disease elsewhere in the body as well as frequent development of LMD in triple-negative disease are novel. The finding that there was no increase in LMD in patients that underwent SRS with or without surgery for oligometastases when WBXRT was initially withheld is of significant importance.
Andreas M. Stark, Kiel, Germany
Survival of breast cancer patients has significantly improved during the past decades. As a consequence, it is appropriate to evaluate a current cohort of patients with breast cancer brain metastases in the light of actual classifications, biomarkers, and clinical characteristics. Quigley and colleagues have reviewed the clinical data of 88 female patients with breast cancer brain metastases treated between 2003 and 2010. They included hormonal markers/HER2 status and presented survival data according to the LUMINAL classification [Geyer et al. 2012]. They found prognostic impact of estrogen receptor status on overall survival as well as prognostic impact of triple-negative hormonal/HER2 status on survival post central nervous system affection. Additionally, they evaluated their data based on the recently described Graded Prognostic Assessment Tumor Index [Sperduto et al. 2012]. This retrospective study is a solid basis for further prospective trials concerning patients with breast cancer brain lesions including endocrine and molecular data.
References
Geyer FC, Rodrigues DN, Weigelt B, Reis-Filho JS. Molecular classification of estrogen receptor-positive/luminal breast cancers. Adv Anat Pathol. 2012 Jan;19(1):39–53
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, Xu Z, Shanley R, Luo X, Sneed PK, Chao ST, Weil RJ, Suh J, Bhatt A, Jensen AW, Brown PD, Shih HA, Kirkpatrick J, Gaspar LE, Fiveash JB, Chiang V, Knisely JP, Sperduto CM, Lin N, Mehta M. Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: an accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2012 Feb 1;30(4):419–25. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.38.0527
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quigley, M.R., Fukui, O., Chew, B. et al. The shifting landscape of metastatic breast cancer to the CNS. Neurosurg Rev 36, 377–382 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-012-0446-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-012-0446-6