Abstract
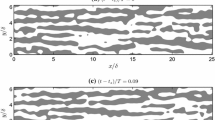
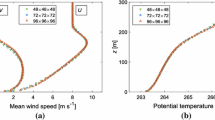
Large-eddy simulation has become an important tool for the study of the atmospheric boundary layer. However, since large-eddy simulation does not simulate small scales, which do interact to some degree with large scales, and does not explicitly resolve the viscous sublayer, it is reasonable to ask if these limitations affect significantly the ability of large-eddy simulation to simulate large-scale coherent structures. This issue is investigated here through the analysis of simulated coherent structures with the proper orthogonal decomposition technique. We compare large-eddy simulation of the atmospheric boundary layer with direct numerical simulation of channel flow. Despite the differences of the two flow types it is expected that the atmospheric boundary layer should exhibit similar structures as those in the channel flow, since these large-scale coherent structures arise from the same primary instability generated by the interaction of the mean flow with the wall surface in both flows. It is shown here that several important similarities are present in the two simulations: (i) coherent structures in the spanwise-vertical plane consist of a strong ejection between a pair of counter-rotating vortices; (ii) each vortex in the pair is inclined from the wall in the spanwise direction with a tilt angle of approximately 45°; (iii) the vortex pair curves up in the streamwise direction. Overall, this comparison adds further confidence in the ability of large-eddy simulation to produce large-scale structures even when wall models are used. Truncated reconstruction of instantaneous turbulent fields is carried out, testing the ability of the proper orthogonal decomposition technique to approximate the original turbulent field with only a few of the most important eigenmodes. It is observed that the proper orthogonal decomposition reconstructs the turbulent kinetic energy more efficiently than the vorticity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albertson JD (1996) Large-eddy simulation of land-atmosphere interaction. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California Davis, 185 pp
Albertson JD, Parlange MB (1999a) Natural integration of scalar fluxes from complex terrain. Adv Water Resour 23: 239–252. doi:10.1016/S0309-1708(99)00011-1
Albertson JD, Parlange MB (1999b) Surface length scales and shear stress: implications for land-atmosphere interaction over complex terrain. Water Resour Res 35: 2121–2132. doi:10.1029/1999WR900094
Aubry N, Holmes P, Lumley JL, Stone E (1988) The dynamics of coherent structures in the wall region of a turbulent boundary layer. J Fluid Mech 192: 115–173. doi:10.1017/S0022112088001818
Bakewell HP, Lumley JL (1967) Viscous sublayer and adjacent wall region in turbulent pipe flow. Phys Fluids 10: 1880–1889. doi:10.1063/1.1762382
Berkooz G, Holmes P, Lumley JL (1993) The proper orthogonal decomposition in the analysis of turbulent flows. Ann Rev Fluid Mech 25: 539–575. doi:10.1146/annurev.fl.25.010193.002543
Canuto C, Hussaini MY, Quarteroni A, Zang TA (1988) Spectral methods in fluid dynamics. Springer, Berlin, 557 pp
Cassiani M, Katul GG, Albertson JD (2008) The effects of canopy leaf area index on airflow across forest edges: large-eddy simulation and analytical results. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 126: 433–460. doi:10.1007/s10546-007-9242-1
Davidson PA (2004) Turbulence: an introduction for scientists and engineers. Oxford University Press, New York, p 657
Deardorf JW (1970) A numerical study of three-dimensional turbulent channel flow at large Reynolds numbers. J Fluid Mech 41: 453–465. doi:10.1017/S0022112070000691
Deardorff JW (1972) Numerical investigations of neutral and unstable planetary boundary layers. J Atmos Sci 29: 91–115. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1972)029<0091:NIONAU>2.0.CO;2
Del Alamo JC, Jimenez J (2001) Direct numerical simulation of the very large anisotropic scales in a turbulent channel center for turbulence research annual research briefs, Stanford University, 2001
Del Alamo JC, Jimenez J (2003) Spectra of the very large anisotropic scales in turbulent channels. Phys Fluids 15: L41–L44. doi:10.1063/1.1570830
Delville J, Ukeiley L, Cordier L, Bonnet JP, Glauser M (1999) Examination of large-scale structures in a turbulent plane mixing layer. Part 1. Proper orthogonal decomposition. J Fluid Mech 391: 91–122. doi:10.1017/S0022112099005200
Etling D, Brown RA (1993) Roll vortices in the planetary boundary layer: a review. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 65: 215–248. doi:10.1007/BF00705527
Finnigan JJ, Shaw RH (2000) A wind-tunnel study of airflow in waving wheat: an EOF analysis of the structure of the large-eddy motion. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 96: 211–255. doi:10.1023/A:1002618621171
Head MR, Bandyopadhyay P (1981) New aspects of turbulent boundary layer structure. J Fluid Mech 107: 297–338. doi:10.1017/S0022112081001791
Herzog S (1986) The large scale structure in the near-wall region of turbulent pipe flow. Ph.D. Thesis, Cornell University, 161 pp
Holmes P, Lumley JL, Berkooz G (1996) Turbulence, coherent structures, dynamical systems, and symmetry. Cambridge University Press, New York, p 420
Kaimal JC, Finnigan JJ (1994) Atmospheric boundary layer flows: their structure and measurement. Oxford University Press, New York, p 289
Katul G, Poggi D, Cava D, Finnigan J (2006) The relative importance of ejections and sweeps to momentum transfer in the atmospheric boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 120: 367–375. doi:10.1007/s10546-006-9064-6
Khanna S, Brasseur JG (1997) Analysis of Monin-Obukhov similarity from large-eddy simulation. J Fluid Mech 345: 251–286. doi:10.1017/S0022112097006277
Kim J, Moin P, Moser R (1987) Turbulence statistics in fully developed channel flow at low Reynolds number. J Fluid Mech 177: 133–166. doi:10.1017/S0022112087000892
Kosovic B (1997) Subgrid-scale modelling for the large-eddy simulation of high-Reynolds-number boundary layers. J Fluid Mech 336: 151–182. doi:10.1017/S0022112096004697
Lesieur M, Métais O, Comte P (2005) Large-eddy simulations of turbulence. Cambridge University Press, New York, p 219
Lilly DK (1967) The representation of small-scale turbulence in numerical simulation experiments. In: Goldstine HH (ed) Proceedings of the IBM scientific computing symposium on environmental sciences, New York, 1967
Lin CL, McWilliams JC, Moeng CH, Sullivan PP (1996) Coherent structures and dynamics in a neutrally stratified planetary boundary layer flow. Phys Fluids 8: 2626–2639. doi:10.1063/1.869048
Lumley JL (1967) The structure of inhomogeneous turbulent flows. In: Yagolm AM, Tatarsky VI (eds) Atmospheric turbulence and radio wave propagation, Moscow, 1967
Lumley JL (1970) Stochastic tools in turbulence. Academic Press, New York, p 194
Lumley JL (1981) Coherent structures in turbulence. In: Meyer RE (eds) Transition and turbulence. Academic, New York, pp 215–241
Mason PJ, Thomson DJ (1992) Stochastic backscatter in large-eddy simulations of boundary layers. J Fluid Mech 242: 51–78. doi:10.1017/S0022112092002271
Moeng CH (1984) A large-eddy simulation model for the study of planetary boundary layer turbulence. J Atmos Sci 41: 2052–2062. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1984)041<2052:ALESMF>2.0.CO;2
Moeng CH, Dudhia J, Klemp J, Sullivan P (2007) Examining two-way grid nesting for large eddy simulation of the PBL using the WRF model. Mon Weather Rev 135: 2295–2311. doi:10.1175/MWR3406.1
Moin P, Moser RD (1989) Characteristic-eddy decomposition of turbulence in a channel. J Fluid Mech 200: 471–509. doi:10.1017/S0022112089000741
Moin P, Reynolds WC, Ferziger JH (1978) Large-eddy simulation of incompressible turbulent channel flow. Dept. Mech. Eng. Stanford Universiy Rep. TF-12
Orlandi P (2000) Fluid flow phenomena: a numerical toolkit. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, p 356
Orszag SA, Pao YH (1974) Numerical computation of turbulent shear flows. Adv Geophys 18: 225–236. doi:10.1016/S0065-2687(08)60463-X
Perry AE, Henbest S, Chong MS (1986) A theoretical and experimental study of wall turbulence. J Fluid Mech 165: 163–199. doi:10.1017/S002211208600304X
Piomelli U, Balaras E (2002) Wall-layer models for large-eddy simulations. Ann Rev Fluid Mech 34: 349–374. doi:10.1146/annurev.fluid.34.082901.144919
Porte-Agel F, Meneveau C, Parlange MB (2000) A scale-dependent dynamic model for large-eddy simulation: application to a neutral atmospheric boundary layer. J Fluid Mech 415: 261–284. doi:10.1017/S0022112000008776
Rempfer D, Fasel HF (1994) Dynamics of three-dimensional coherent structures in a flat-plate boundary layer. J Fluid Mech 275: 257–283. doi:10.1017/S0022112094002351
Robinson SK (1991) Coherent motions in the turbulent boundary-layer. Ann Rev Fluid Mech 23: 601–639. doi:10.1146/annurev.fl.23.010191.003125
Sadani LK, Kulkarni JR (2001) A study of coherent structures in the atmospheric surface layer over short and tall grass. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 99: 317–334. doi:10.1023/A:1018992529079
Sagaut P (2002) Large eddy simulation for incompressible flows: an introduction. Springer, Berlin, p 426
Sagaut P, Deck S, Terracol M (2006) Multiscale and multiresolution approaches in turbulence. Imperial College Press, London, p 340
Schmidt H, Schumann U (1989) Coherent structure of the convective boundary layer derived from large-eddy simulations. J Fluid Mech 200: 511–562. doi:10.1017/S0022112089000753
Scotti A, Meneveau C, Lilly DK (1993) Generalized Smagorinsky model for anisotropic grids. Phys Fluids 5: 2306–2308. doi:10.1063/1.858537
Sirovich L (1987a) Turbulence and the dynamics of coherent structures, part 1: coherent structures. Q Appl Math 45: 561–571
Sirovich L (1987b) Turbulence and the dynamics of coherent structures, part 2: symmetries and transformations. Q Appl Math 45: 573–582
Sirovich L (1987c) Turbulence and the dynamics of coherent structures, part 3: dynamics and scaling. Q Appl Math 45: 583–590
Smagorinsky J (1963) General circulation experiments with the primitive equations. Mon Weather Rev 91: 99–164. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1963)091<0099:GCEWTP>2.3.CO;2
Smith TR, Moehlis J, Holmes P (2005) Low-dimensional modelling of turbulence using the proper orthogonal decomposition: a tutorial. Nonlinear Dyn 41: 275–307. doi:10.1007/s11071-005-2823-y
Stoll R, Porte-Agel F (2006) Effect of roughness on surface boundary conditions for large-eddy simulation. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 118: 169–187. doi:10.1007/s10546-005-4735-2
Stull RB (1988) An introduction to boundary layer meteorology. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht/ Boston/London, p 666
Sullivan PP, McWilliams JC, Moeng CH (1996) A grid nesting method for large-eddy simulation of planetary boundary-layer flows. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 80: 167–202. doi:10.1007/BF00119016
Townsend AA (1976) The structure of turbulent shear flow. Cambridge University Press, New York, p 429
Waleffe F (1997) On a self-sustaining process in shear flows. Phys Fluids 9: 883–900. doi:10.1063/1.869185
Wallace JM, Brodkey RS, Eckelman H (1972) Wall region in turbulent shear flow. J Fluid Mech 54: 39–48. doi:10.1017/S0022112072000515
Wilson DK (1996) Empirical orthogonal function analysis of the weakly convective atmospheric boundary layer. Part I: eddy structures. J Atmos Sci 53: 801–823. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1996)053<0801:EOFAOT>2.0.CO;2
Wilson DK, Wyngaard JC (1996) Empirical orthogonal function analysis of the weakly convective atmospheric boundary layer. Part II: eddy energetics. J Atmos Sci 53: 824–841. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1996)053<0824:EOFAOT>2.0.CO;2
Xie ZT, Voke PR, Hayden P, Robins AG (2004) Large-eddy simulation of turbulent flow over a rough surface. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 111: 417–440. doi:10.1023/B:BOUN.0000016599.75196.17
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., Cassiani, M. & Albertson, J.D. Analysis of Coherent Structures Within the Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 131, 147–171 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-009-9357-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-009-9357-7