Abstract
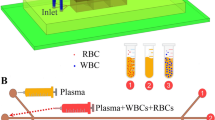
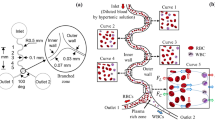
This paper is focused on the development of a six-stage cascade paramagnetic mode magnetophoretic separation (PMMS) system for separating suspended cells in blood based on their native magnetic properties. The design and fabrication of a PMMS system are presented and the microfluidic separation system is characterized experimentally using human whole blood as the case study. The PMMS system can separate blood cells types continuously using the magnetophoretic force produced from a high magnetic field gradient without magnetic or fluorescent tagging. Experimental results demonstrated that red blood cell separation in the PMMS system at a volumetric flow rate of 28.8 μL / hr, resulting in a separation time of 10.4 min for a 5.0 μL blood sample with a separation efficiency of 89.5 ± 0.20%. The PMMS system was tested at higher volumetric flow rates of 50.4 μL / hr and 72.0 μL / hr. The measured separation efficiencies were 86.2 ± 1.60% and 59.9 ± 6.06% respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.D. Adams, U. Kim, H.T. Soh, Multitarget magnetic activated cell sorter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 18165–18170 (2008)
R.W. Applegate, J. Squier, T. Vestad, J. Oakey, D.W.M. Marr, Optical trapping, manipulation, and sorting of cells and colloids in microfluidic systems with diode laser bars. Opt. Express 12, 4390–4398 (2004)
F.F. Becker, X.B. Wang, Y. Huang, R. Pethig, J. Vykoukal, P.R.C. Gascoyne, Separation of human breast-cancer cells from blood by differential dielectric affinity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92, 860–864 (1995)
H.T. Chen, A.D. Ebner, A.J. Rosengart, M.D. Kaminski, J.A. Ritter, Analysis of magnetic drug carrier particle capture by a magnetizable intravascular stent: 1. Parametric study with single wire correlation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 284, 181–194 (2004)
X. Chen, D.F. Cui, C.C. Liu, H. Li, Microfluidic chip for blood cell separation and collection based on crossflow filtration. Sens. Actuators, B, Chem. 130, 216–221 (2008)
I.F. Cheng, H.C. Chang, D. Hou, H.C. Chang, An integrated dielectrophoretic chip for continuous bioparticle filtering, focusing, sorting, trapping, and detecting. Biomicrofluidics 1, 15 (2007)
S. Choi, J.K. Park, Continuous hydrophoretic separation and sizing of microparticles using slanted obstacles in a microchannel. Lab Chip 7, 890–897 (2007)
D.A. Colling, Intrinsic magnetization of Fe-Ni-Mn alloys. J. Appl. Physi. 40, 1379–1381 (1969)
K. Dholakia, M.P. MacDonald, P. Zemanek, T. Cizmar, Cellular and colloidal separation using optical forces. Laser Manipulation of Cells and Tissues 82, 467–495 (2007)
A. Ditsch, J. Yin, P.E. Laibinis, D.I.C. Wang, T.A. Hatton, Ion-exchange purification of proteins using magnetic nanoclusters. Biotechnol. Prog. 22, 1153–1162 (2006)
A.D. Ebner, J.A. Ritter, L. Nunez, High-gradient magnetic separation for the treatment of high-level radioactive wastes. Sep. Sci. Technol. 34, 1333–1350 (1999)
A.B. Frazier, Metallic microstructures fabricated using photosensitive polyimide electroplating molds. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2, 87–94 (1993)
P.R.C. Gascoyne, J. Vykoukal, Particle separation by dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 23, 1973–1983 (2002)
K.H. Han, A.B. Frazier, Continuous magnetophoretic separation of blood cells in microdevice format. J. Appl. Physi. 96, 5797–5802 (2004)
K.H. Han, A.B. Frazier, Diamagnetic capture mode magnetophoretic microseparator for blood cells. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 14, 1422–1431 (2005a)
K.H. Han, A.B. Frazier, Reliability aspects of packaging and integration technology for microfluidic systems. IEEE Transactions on Device and Materials Reliability 5, 452–457 (2005b)
K.H. Han, A.B. Frazier, Paramagnetic capture mode magnetophoretic microseparator for blood cells. IEE Proc. Nanobiotechnol. 153, 67–73 (2006a)
K.H. Han, A.B. Frazier, Paramagnetic capture mode magnetophoretic microseparator for high efficiency blood cell separations. Lab Chip 6, 265–273 (2006b)
K.H. Han, A.B. Frazier, Lateral-driven continuous dielectrophoretic microseparators for blood cells suspended in a highly conductive medium. Lab Chip 8, 1079–1086 (2008)
L.A. Herzenberg, D. Parks, B. Sahaf, O. Perez, M. Roederer, L.A. Herzenberg, The history and future of the fluorescence activated cell sorter and flow cytometry: A view from Stanford. Clin. Chem. 48, 1819–1827 (2002)
Y. Kakihara, T. Fukunishi, S. Takeda, S. Nishijima, A. Nakahira, Superconducting high gradient magnetic separation for purification of wastewater from paper factory. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 14, 1565–1567 (2004)
M.P. MacDonald, G.C. Spalding, K. Dholakia, Microfluidic sorting in an optical lattice. Nature 426, 421–424 (2003)
M.P. MacDonald, S. Neale, L. Paterson, A. Richies, K. Dholakia, G.C. Spalding, Cell cytometry with a light touch: Sorting microscopic matter with an optical lattice. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 18, 200–205 (2004)
H. Maenaka, M. Yamada, M. Yasuda, M. Seki, Continuous and size-dependent sorting of emulsion droplets using hydrodynamics in pinched microchannels. Langmuir 24, 4405–4410 (2008)
D. Melville, F. Paul, S. Roath, High gradient magnetic separation of red-cells from whole-blood. IEEE Trans. Magn. 11, 1701–1704 (1975)
S. Miltenyi, W. Muller, W. Weichel, A. Radbruch, High-gradient magnetic cell-separation with MACS. Cytometry 11, 231–238 (1990)
G.D. Moeser, K.A. Roach, W.H. Green, P.E. Laibinis, T.A. Hatton, Water-based magnetic fluids as extractants for synthetic organic compounds. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 41, 4739–4749 (2002)
A.F. Ngomsik, A. Bee, M. Draye, G. Cote, V. Cabuil, Magnetic nano- and microparticles for metal removal and environmental applications: a review. Comptes Rendus Chimie 8, 963–970 (2005)
M. Ozkan, M. Wang, C. Ozkan, R. Flynn, A. Birkbeck, S. Esener, Optical manipulation of objects and biological cells in microfluidic devices. Biomed. Microdevices 5, 61–67 (2003)
N. Pamme, C. Wilhelm, Continuous sorting of magnetic cells via on-chip free-flow magnetophoresis. Lab Chip 6, 974–980 (2006)
N. Pamme, J.C.T. Eijkel, A. Manz, On-chip free-flow magnetophoresis: Separation and detection of mixtures of magnetic particles in continuous flow. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 307, 237–244 (2006)
M.S. Pommer, Y.T. Zhang, N. Keerthi, D. Chen, J.A. Thomson, C.D. Meinhart, H.T. Soh, Dielectrophoretic separation of platelets from diluted whole blood in microfluidic channels. Electrophoresis 29, 1213–1218 (2008)
A.J. Richards, O.S. Roath, R.J.S. Smith, J.H.P. Watson, The mechanisms of high gradient magnetic separation of human blood and bone marrow. IEEE Trans. Magn. 32, 459–470 (1996)
J.A. Ritter, A.D. Ebner, K.D. Daniel, K.L. Stewart, Application of high gradient magnetic separation principles to magnetic drug targeting. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 280, 184–201 (2004)
M. Sarikaya, T. Abbasov, M. Erdemoglu, Some aspects of magnetic filtration theory for removal of fine particles from aqueous suspensions. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 27, 193–198 (2006)
T. Schneider, L.R. Moore, Y. Jing, S. Haam, P.S. Williams, A.J. Fleischman, S. Roy, J.J. Chalmers, M. Zborowski, Continuous flow magnetic cell fractionation based on antigen expression level. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 68, 1–21 (2006)
Y.Y. Sun, X.C. Yuan, L.S. Ong, J. Bu, S.W. Zhu, R. Liu, Large-scale optical traps on a chip for optical sorting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, (2007)
M. Takayasu, D.R. Kelland, J.V. Minervini, Continuous magnetic separation of blood components from whole blood. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 10, 927–930 (2000)
A. Thiel, A. Scheffold, A. Radbruch, Immunomagnetic cell sorting—pushing the limits. Immunotechnology 4, 89–96 (1998)
T.E. Thomas, S.J.R. Abraham, A.J. Otter, E.W. Blackmore, P.M. Lansdorp, High-gradient magnetic separation of cells on the basis of expression levels of cell-surface antigens. J. Immunol. Methods 154, 245–252 (1992)
M. Toner, D. Irimia, Blood-on-a-chip. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 7, 77–103 (2005)
S. Vankrunkelsven, D. Clicq, K. Pappaert, W. Ranson, C. De Tandt, H. Ottevaere, H. Thienpont, G.V. Baron, G. Desmet, A novel microstep device for the size separation of cells. Electrophoresis 25, 1714–1722 (2004)
M.M. Wang, E. Tu, D.E. Raymond, J.M. Yang, H.C. Zhang, N. Hagen, B. Dees, E.M. Mercer, A.H. Forster, I. Kariv, P.J. Marchand, W.F. Butler, Microfluidic sorting of mammalian cells by optical force switching. Nat. Biotechnol. 23, 83–87 (2005)
N. Xia, T.P. Hunt, B.T. Mayers, E. Alsberg, G.M. Whitesides, R.M. Westervelt, D.E. Ingber, Combined microfluidic-micromagnetic separation of living cells in continuous flow. Biomed. Microdevices 8, 299–308 (2006)
M. Yamada, M. Seki, Microfluidic particle sorter employing flow splitting and recombining. Anal. Chem. 78, 1357–1362 (2006)
B.B. Yellen, Z.G. Forbes, D.S. Halverson, G. Fridman, K.A. Barbee, M. Chorny, R. Levy, G. Friedman, Targeted drug delivery to magnetic implants for therapeutic applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 293, 647–654 (2005)
M. Zborowski, G.R. Ostera, L.R. Moore, S. Milliron, J.J. Chalmers, A.N. Schechter, Red blood cell magnetophoresis. Biophys. J. 84, 2638–2645 (2003)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) under Grant Number ES10846.
Authorships
Contributions: Youngdo Jung designed the research, carried out fabrication and experiments, analyzed data, and wrote the paper. Yoonsu Choi carried out fabrication. Ki-Ho Han provided theoretical background for the research. A. Bruno Frazier managed overall research and edited the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, Y., Choi, Y., Han, KH. et al. Six-stage cascade paramagnetic mode magnetophoretic separation system for human blood samples. Biomed Microdevices 12, 637–645 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-010-9416-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-010-9416-3