Abstract
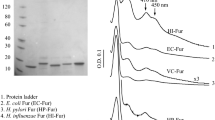
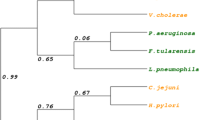
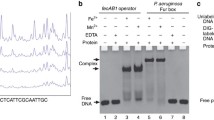
Escherichia coli ferric uptake regulator (Fur) binds a [2Fe–2S] cluster, not a mononuclear iron, when the intracellular free iron content is elevated in E. coli cells. Here we report that the C-terminal domain (residues 83–148) of E. coli Fur (Fur-CTD) is sufficient to bind the [2Fe–2S] cluster in response to elevation of the intracellular free iron content in E. coli cells. Deletion of gene fur in E. coli cells increases the intracellular free iron content and promotes the [2Fe–2S] cluster binding in the Fur-CTD in the cells grown in LB medium under aerobic growth conditions. When the Fur-CTD is expressed in wild type E. coli cells grown in M9 medium supplemented with increasing concentrations of iron, the Fur-CTD also progressively binds a [2Fe–2S] cluster with a maximum occupancy of about 36%. Like the E. coli Fur-CTD, the CTD of the Haemophilus influenzae Fur can also bind a [2Fe–2S] cluster in wild type E. coli cells grown in M9 medium supplemented with increasing concentrations of iron, indicating that binding of the [2Fe–2S] cluster in the C-terminal domain is highly conserved among Fur proteins. The results suggest that the Fur-CTD can be used as a physiological probe to assess the intracellular free iron content in bacteria.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated and analyzed in the present study are included in the manuscript. Raw data is available on request.
References
Abdul-Tehrani H, Hudson AJ, Chang YS, Timms AR, Hawkins C, Williams JM et al (1999) Ferritin mutants of Escherichia coli are iron deficient and growth impaired, and fur mutants are iron deficient. J Bacteriol 181:1415–1428
Bagg A, Neilands JB (1987) Ferric uptake regulation protein acts as a repressor, employing iron (II) as a cofactor to bind the operator of an iron transport operon in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 26:5471–5477
Baichoo N, Helmann JD (2002) Recognition of DNA by Fur: a reinterpretation of the Fur box consensus sequence. J Bacteriol 184:5826–5832. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.184.21.5826-5832.2002
Bohnke R, Matzanke BF (1995) The mobile ferrous iron pool in Escherichia coli is bound to a phosphorylated sugar derivative. Biometals 8:223–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00143380
Beauchene NA, Mettert EL, Moore LJ, Keles S, Willey ER, Kiley PJ (2017) O2 availability impacts iron homeostasis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:12261–12266. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1707189114
Brawley HN, Kreinbrink AC, Hierholzer JD, Vali SW, Lindahl PA (2023) Labile iron pool of isolated escherichia coli cytosol likely includes Fe-ATP and Fe-citrate but not Fe-glutathione or aqueous Fe. J Am Chem Soc 145:2104–2117. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.2c06625
Datsenko KA, Wanner BL (2000) One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6640–6645
de Lorenzo V, Wee S, Herrero M, Neilands JB (1987) Operator sequences of the aerobactin operon of plasmid ColV-K30 binding the ferric uptake regulation (fur) repressor. J Bacteriol 169:2624–2630. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.169.6.2624-2630.1987
Dian C, Vitale S, Leonard GA, Bahlawane C, Fauquant C, Leduc D et al (2011) The structure of the Helicobacter pylori ferric uptake regulator Fur reveals three functional metal binding sites. Mol Microbiol 79:1260–1275. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07517.x
Escolar L, Perez-Martin J, de Lorenzo V (1999) Opening the iron box: transcriptional metalloregulation by the Fur protein. J Bacteriol 181:6223–6229
Fillat MF (2014) The FUR (ferric uptake regulator) superfamily: diversity and versatility of key transcriptional regulators. Arch Biochem Biophys 546:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2014.01.029
Fischer DS (1967) A method for the rapid detection of acute iron toxicity. Clin Chem 13:6–11
Fontecave M, Pierre JL (1991) Iron metabolism: the low-molecular-mass iron. pool Biol Met 4:133–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01141302
Fontenot CR, Ding H (2022) Ferric uptake regulators (Fur) from Vibrio cholerae and Helicobacter pylori bind a [2Fe–2S] cluster in response to elevation of intracellular free iron content. Biometals. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-022-00390-9
Fontenot CR, Ding H (2023) Ferric uptake regulator (Fur) binds a [2Fe–2S] cluster to regulate intracellular iron homeostasis in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 299:104748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104748
Fontenot CR, Tasnim H, Valdes KA, Popescu CV, Ding H (2020) Ferric uptake regulator (Fur) reversibly binds a [2Fe–2S] cluster to sense intracellular iron homeostasis in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 295:15454–15463. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.014814
Hantke K (1981) Regulation of ferric iron transport in Escherichia coli K12: isolation of a constitutive mutant. Mol Gen Genet 182:288–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00269672
Hartmann A, Braun V (1981) Iron uptake and iron limited growth of Escherichia coli K-12. Arch Microbiol. 130:353–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00414599
Hamed MY, Neilands JB, Huynh V (1993) Binding of the ferric uptake regulation repressor protein (Fur) to mn(II), Fe(II), Co(II), and Cu(II) ions as co-repressors: electronic absorption, equilibrium, and 57Fe mossbauer studies. J Inorg Biochem 50:193–210
Jacques JF, Jang S, Prevost K, Desnoyers G, Desmarais M, Imlay J et al (2006) RyhB small RNA modulates the free intracellular iron pool and is essential for normal growth during iron limitation in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 62:1181–1190. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05439.x
Keyer K, Imlay JA (1996) Superoxide accelerates DNA damage by elevating free-iron levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:13635–13640
Lee JW, Helmann JD (2007) Functional specialization within the Fur family of metalloregulators. Biometals 20:485–499. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-006-9070-7
Mills SA, Marletta MA (2005) Metal binding characteristics and role of iron oxidation in the ferric uptake regulator from. Escherichia coli Biochemistry 44:13553–13559. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0507579
Moss ML, Mellon MG (1942) Colorimetric determination of Iron with 2,2′-bipyridyl and with 2,2′,2′-terpyridyl industrial. Eng Chem Anal Ed 14:862–865
Ma Z, Faulkner MJ, Helmann JD (2012) Origins of specificity and cross-talk in metal ion sensing by Bacillus subtilis. Fur Mol Microbiol 86:1144–1155. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.12049
Marcoleta AE, Gutiérrez-Cortez S, Hurtado F, Argandoña Y, Corsini G, Monasterio O et al (2018) The Ferric uptake regulator (Fur) and iron availability control the production and maturation of the antibacterial peptide microcin E492. PLoS One 13:e0200835. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0200835
McHugh JP, Rodríguez-Quiñones F, Abdul-Tehrani H, Svistunenko DA, Poole RK, Cooper CE et al (2003) Global iron-dependent gene regulation in Escherichia coli: a new mechanism for iron homeostasis. J Biol Chem 278:29478–29486. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M303381200
Nandal A, Huggins CC, Woodhall MR, McHugh J, Rodriguez-Quinones F, Quail MA et al (2010) Induction of the ferritin gene (ftnA) of Escherichia coli by Fe2+-Fur is mediated by reversal of H-NS silencing and is RyhB. Indep Mol Microbiol 75:637–657. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06977.x
Nunoshiba T, Obata F, Boss AC, Oikawa S, Mori T, Kawanishi S et al (1999) Role of iron and superoxide for generation of hydroxyl radical, oxidative DNA lesions, and mutagenesis in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 274:34832–34837. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.49.34832
Pi H, Helmann JD (2017) Sequential induction of Fur-regulated genes in response to iron limitation in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:12785–12790. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1713008114
Pecqueur L, D’Autreaux B, Dupuy J, Nicolet Y, Jacquamet L, Brutscher B et al (2006) Structural changes of Escherichia coli ferric uptake regulator during metal-dependent dimerization and activation explored by NMR and X-ray crystallography. J Biol Chem 281:21286–21295. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M601278200
Pinochet-Barros A, Helmann JD (2018) Redox sensing by Fe2+ bacterial Fur family metalloregulators. Antioxid Redox Signal 29:1858–1871. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2017.7359
Siegel LM (1965) A direct microdetermination of sulfide. Anal Biochem 11:126–132
Santos R, Batista BB, da Silva Neto JF (2020) Ferric uptake regulator fur coordinates siderophore production and defense against iron toxicity and oxidative stress and contributes to virulence in Chromobacterium violaceum. Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01620-20
Seo SW, Kim D, Latif H, O’Brien EJ, Szubin R, Palsson BO (2014) Deciphering Fur transcriptional regulatory network highlights its complex role beyond iron metabolism in Escherichia coli. Nat Commun 5:4910. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5910
Troxell B, Hassan HM (2013) Transcriptional regulation by ferric uptake regulator (Fur) in pathogenic bacteria. Front cell infect microbiol 3:59. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2013.00059
Tan G, Lu J, Bitoun JP, Huang H, Ding H (2009) IscA/SufA paralogues are required for the 4Fe-4S cluster assembly in enzymes of multiple physiological pathways in Escherichia coli under aerobic growth conditions. Biochem J 420:463–472. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20090206
Vitale S, Fauquant C, Lascoux D, Schauer K, Saint-Pierre C, Michaud-Soret I (2009) A ZnS(4) structural zinc site in the Helicobacter pylori ferric uptake regulator. Biochemistry. 48:5582–5591. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi9004396
Woodmansee AN, Imlay JA (2002) Quantitation of intracellular free iron by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Methods Enzymol 349:3–9
Wofford JD, Bolaji N, Dziuba N, Outten FW, Lindahl PA (2019) Evidence that a respiratory shield in Escherichia coli protects a low-molecular-mass Fe(II) pool from O(2)-dependent oxidation. J Biol Chem 294:50–62. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.005233
Funding
This work was supported by an NSF grant (MCB 2050032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CF and HD conceived and designed the study, performed the experiments, analyzed the date, and wrote the manuscript. HD reviewed and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fontenot, C.R., Ding, H. The C-terminal domain of the ferric uptake regulator (Fur) binds a [2Fe–2S] cluster to sense the intracellular free iron content in Escherichia coli. Biometals 36, 1285–1294 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-023-00517-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-023-00517-6