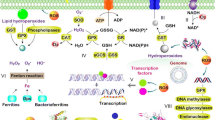
Abstract
The ferric uptake regulator (Fur) protein, as originally described in Escherichia coli, is an iron-sensing repressor that controls the expression of genes for siderophore biosynthesis and iron transport. Although Fur is commonly thought of as a metal-dependent repressor, Fur also activates the expression of many genes by either indirect or direct mechanisms. In the best studied model systems, Fur functions as a global regulator of iron homeostasis controlling both the induction of iron uptake functions (under iron limitation) and the expression of iron storage proteins and iron-utilizing enzymes (under iron sufficiency). We now appreciate that there is a tremendous diversity in metal selectivity and biological function within the Fur family which includes sensors of iron (Fur), zinc (Zur), manganese (Mur), and nickel (Nur). Despite numerous studies, the mechanism of metal ion sensing by Fur family proteins is still controversial. Other family members use metal catalyzed oxidation reactions to sense peroxide-stress (PerR) or the availability of heme (Irr).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Tehrani H, Hudson AJ, Chang YS et al (1999) Ferritin mutants of Escherichia coli are iron deficient and growth impaired, and fur mutants are iron deficient. J Bacteriol 181:1415–1428
Ahn BE, Cha J, Lee EJ, Han AR, Thompson CJ, Roe JH (2006) Nur, a nickel-responsive regulator of the Fur family, regulates superoxide dismutases and nickel transport in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 59:1848–1858
Akanuma G, Nanamiya H, Natori Y, Nomura N, Kawamura F (2006) Liberation of zinc-containing L31 (RpmE) from ribosomes by its paralogous gene product, YtiA, in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 188:2715–2720
Alamuri P, Mehta N, Burk A, Maier RJ (2006) Regulation of the Helicobacter pylori Fe-S cluster synthesis protein NifS by iron, oxidative stress conditions, and Fur. J Bacteriol 188:5325–5330
Althaus EW, Outten CE, Olson KE, Cao H, O’Halloran TV (1999) The ferric uptake regulation (Fur) repressor is a zinc metalloprotein. Biochemistry 38:6559–6569
Bagg A, Neilands JB (1987a) Ferric uptake regulation protein acts as a repressor, employing iron (II) as a cofactor to bind the operator of an iron transport operon in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 26:5471–5477
Bagg A, Neilands JB (1987b) Molecular mechanism of regulation of siderophore-mediated iron assimilation. Microbiol Rev 51:509–518
Baichoo N, Helmann JD (2002) Recognition of DNA by Fur: a reinterpretation of the Fur box consensus sequence. J Bacteriol 184:5826–5832
Baichoo N, Wang T, Ye R, Helmann JD (2002) Global analysis of the Bacillus subtilis Fur regulon and the iron starvation stimulon. Mol Microbiol 45:1613–1629
Bellini P, Hemmings AM (2006) In vitro characterization of a bacterial manganese uptake regulator of the fur superfamily. Biochemistry 45:2686–2698
Braun V (2003) Iron uptake by Escherichia coli. Front Biosci 8:s1409–s1421
Brenot A, King KY, Caparon MG (2005) The PerR regulon in peroxide resistance and virulence of Streptococcus pyogenes. Mol Microbiol 55:221–234
Bsat N, Chen L, Helmann JD (1996) Mutation of the Bacillus subtilis alkyl hydroperoxide reductase (ahpCF) operon reveals compensatory interactions among hydrogen peroxide stress genes. J Bacteriol 178:6579–6586
Bsat N, Helmann JD (1999) Interaction of Bacillus subtilis Fur (ferric uptake repressor) with the dhb operator in vitro and in vivo. J Bacteriol 181:4299–4307
Bsat N, Herbig A, Casillas-Martinez L, Setlow P, Helmann JD (1998) Bacillus subtilis contains multiple Fur homologues:identification of the iron uptake (Fur) and peroxide regulon (PerR) repressors. Mol Microbiol 29:189–198
Chen L, Helmann JD (1995) Bacillus subtilis MrgA is a Dps(PexB) homologue: evidence for metalloregulation of an oxidative-stress gene. Mol Microbiol 18:295–300
Chen L, James LP, Helmann JD (1993) Metalloregulation in Bacillus subtilis: isolation and characterization of two genes differentially repressed by metal ions. J Bacteriol 175:5428–5437
Chen L, Keramati L, Helmann JD (1995) Coordinate regulation of Bacillus subtilis peroxide stress genes by hydrogen peroxide and metal ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:8190–8204
Coy M, Doyle C, Besser J, Neilands JB (1994) Site-directed mutagenesis of the ferric uptake regulation gene of Escherichia coli. Biometals 7:292–298
D’Autreaux B, Touati D, Bersch B, Latour JM, Michaud-Soret I (2002) Direct inhibition by nitric oxide of the transcriptional ferric uptake regulation protein via nitrosylation of the iron. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:16619–16624
Delany I, Rappuoli R, Scarlato V (2004) Fur functions as an activator and as a repressor of putative virulence genes in Neisseria meningitidis. Mol Microbiol 52:1081–1090
Delany I, Spohn G, Rappuoli R, Scarlato V (2001) The Fur repressor controls transcription of iron-activated and -repressed genes in Helicobacter pylori. Mol Microbiol 42:1297–1309
Delany I, Spohn G, Rappuoli R, Scarlato V (2003) An anti-repression Fur operator upstream of the promoter is required for iron-mediated transcriptional autoregulation in Helicobacter pylori. Mol Microbiol 50:1329–1338
Diaz-Mireles E, Wexler M, Sawers G, Bellini D, Todd JD, Johnston AW (2004) The Fur-like protein Mur of Rhizobium leguminosarum is a Mn(2+)-responsive transcriptional regulator. Microbiology 150:1447–1456
Diaz-Mireles E, Wexler M, Todd JD, Bellini D, Johnston AW, Sawers RG (2005) The manganese-responsive repressor Mur of Rhizobium leguminosarum is a member of the Fur-superfamily that recognizes an unusual operator sequence. Microbiology 151:4071–4078
Ernst FD, Bereswill S, Waidner B et al (2005) Transcriptional profiling of Helicobacter pylori Fur- and iron-regulated gene expression. Microbiology 151:533–546
Ernst FD, Homuth G, Stoof J et al (2005) Iron-responsive regulation of the Helicobacter pylori iron-cofactored superoxide dismutase SodB is mediated by Fur. J Bacteriol 187:3687–3692
Escolar L, Perez-Martin J, de Lorenzo V (1998) Binding of the fur (ferric uptake regulator) repressor of Escherichia coli to arrays of the GATAAT sequence. J Mol Biol 283:537–547
Escolar L, Perez-Martin J, de Lorenzo V (1999) Opening the iron box: transcriptional metalloregulation by the Fur protein. J Bacteriol 181:6223–6229
Foster JW, Hall HK (1992) Effect of Salmonella typhimurium ferric uptake regulator (fur) mutations on iron- and pH-regulated protein synthesis. J Bacteriol 174:4317–4323
Friedman YE, O’Brian MR (2004) The ferric uptake regulator (Fur) protein from Bradyrhizobium japonicum is an iron-responsive transcriptional repressor in vitro. J Biol Chem 279:32100–32105
Fuangthong M, Helmann JD (2003) Recognition of DNA by three ferric uptake regulator (Fur) homologs in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 185:6348–6357
Fuangthong M, Herbig AF, Bsat N, Helmann JD (2002) Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis fur and perR genes by PerR: not all members of the PerR regulon are peroxide inducible. J Bacteriol 184:3276”3286
Gaballa A, Helmann JD (1998) Identification of a zinc-specific metalloregulatory protein, Zur, controlling zinc transport operons in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 180:5815–5821
Gaballa A, Helmann JD (2002) A peroxide-induced zinc uptake system plays an important role in protection against oxidative stress in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 45:997–1005
Gaballa A, Wang T, Ye RW, Helmann JD (2002) Functional analysis of the Bacillus subtilis Zur regulon. J Bacteriol 184:6508–6514
Gonzalez de Peredo A, Saint-Pierre C, Adrait A et al (1999) Identification of the two zinc-bound cysteines in the ferric uptake regulation protein from Escherichia coli:chemical modification and mass spectrometry analysis. Biochemistry 38:8582–8589
Grifantini R, Sebastian S, Frigimelica E et al (2003) Identification of iron-activated and -repressed Fur-dependent genes by transcriptome analysis of Neisseria meningitidis group B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:9542–9547
Guedon E, Helmann JD (2003) Origins of metal ion selectivity in the DtxR/MntR family of metalloregulators. Mol Microbiol 48:495–506
Hahn JS, Oh SY, Chater KF, Cho YH, Roe JH (2000) H2O2-sensitive fur-like repressor CatR regulating the major catalase gene in Streptomyces coelicolor. J Biol Chem 275:38254–38260
Hall HK, Foster JW (1996) The role of fur in the acid tolerance response of Salmonella typhimurium is physiologically and genetically separable from its role in iron acquisition. J Bacteriol 178:5683–5691
Hamza I, Chauhan S, Hassett R, O’Brian MR (1998) The bacterial Irr protein is required for coordination of heme biosynthesis with iron availability. J Biol Chem 273:21669–21674
Hamza I, Hassett R, O’Brian MR (1999) Identification of a functional fur gene in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol 181:5843–5846
Hantke K (1981) Regulation of ferric iron transport in Escherichia coli K12: isolation of a constitutive mutant. Mol Gen Genet 182:288–292
Hantke K (1987) Selection Procedure for deregulated iron transport mutants (fur) in Escherichia coli K (12): fur not only affects iron metabolism. Mol Gen Genet 210:135–139
Hantke K (2001) Iron and metal regulation in bacteria. Curr Opin Microbiol 4:172–177
Hayashi K, Ohsawa T, Kobayashi K, Ogasawara N, Ogura M (2005) The H2O2 stress-responsive regulator PerR positively regulates srfA expression in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 187:6659–6667
Helmann JD, Wu MF, Gaballa A et al (2003) The global transcriptional response of Bacillus subtilis to peroxide stress is coordinated by three transcription factors. J Bacteriol 185:243–253
Herbig AF, Helmann JD (2001) Roles of metal ions and hydrogen peroxide in modulating the interaction of the Bacillus subtilis PerR peroxide regulon repressor with operator DNA. Mol Microbiol 41:849–859
Hoffmann T, Schutz A, Brosius M, Volker A, Volker U, Bremer E (2002) High-salinity-induced iron limitation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 184:718–727
Horsburgh MJ, Clements MO, Crossley H, Ingham E, Foster SJ (2001) PerR controls oxidative stress resistance and iron storage proteins and is required for virulence in Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun 69:3744–3754
Horsburgh MJ, Wharton SJ, Cox AG, Ingham E, Peacock S, Foster SJ (2002) MntR modulates expression of the PerR regulon and superoxide resistance in Staphylococcus aureus through control of manganese uptake. Mol Microbiol 44:1269–1286
Jacquamet L, Aberdam D, Adrait A, Hazemann JL, Latour JM, Michaud-Soret I (1998) X-ray absorption spectroscopy of a new zinc site in the Fur protein from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 37:2564–2571
Keyer K, Imlay JA (1996) Superoxide accelerates DNA damage by elevating free-iron levels Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:13635–13640
Kiley PJ, Storz G (2004) Exploiting thiol modifications. PLoS Biol 2:e400
King KY, Horenstein JA, Caparon MG (2000) Aerotolerance and peroxide resistance in peroxidase and PerR mutants of Streptococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol 182:5290–5299
Lam MS, Litwin CM, Carroll PA, Calderwood SB (1994) Vibrio cholerae fur mutations associated with loss of repressor activity:implications for the structural–functional relationships of fur. J Bacteriol 176:5108–5115
Lavrrar JL, Christoffersen CA, McIntosh MA (2002) Fur-DNA interactions at the bidirectional fepDGC-entS promoter region in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 322:983–995
Lavrrar JL, McIntosh MA (2003) Architecture of a fur binding site: a comparative analysis. J Bacteriol 185:2194–2202
Le Cam E, Frechon D, Barray M, Fourcade A, Delain E (1994) Observation of binding and polymerization of Fur repressor onto operator-containing DNA with electron and atomic force microscopes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:11816–11820
Lee JW, Helmann JD (2006a) Biochemical characterization of the structural Zn2+ site in the Bacillus subtilis peroxide sensor PerR. J Biol Chem 281:23567–23578
Lee JW, Helmann JD (2006b) The PerR transcription factor senses H2O2 by metal-catalysed histidine oxidation. Nature 440:363–367
Lewin AC, Doughty PA, Flegg L, Moore GR, Spiro S (2002) The ferric uptake regulator of Pseudomonas aeruginosa has no essential cysteine residues and does not contain a structural zinc ion. Microbiology 148:2449–2456
Litwin CM, Calderwood SB (1994) Analysis of the complexity of gene regulation by fur in Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol 176:240–248
Masse E, Arguin M (2005) Ironing out the problem: new mechanisms of iron homeostasis. Trends Biochem Sci 30:462–468
Masse E, Gottesman S (2002) A small RNA regulates the expression of genes involved in iron metabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:4620–4625
Masse E, Vanderpool CK, Gottesman S (2005) Effect of RyhB small RNA on global iron use in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 187:6962–6971
McHugh JP, Rodriguez-Quinones F, Abdul-Tehrani H et al (2003) Global iron-dependent gene regulation in Escherichia coli. A new mechanism for iron homeostasis. J Biol Chem 278:29478–29486
Mey AR, Craig SA, Payne SM (2005) Characterization of Vibrio cholerae RyhB: the RyhB regulon and role of ryhB in biofilm formation. Infect Immun 73:5706–5719
Mills SA, Marletta MA (2005) Metal binding characteristics and role of iron oxidation in the ferric uptake regulator from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 44:13553–13559
Mongkolsuk S, Helmann JD (2002) Regulation of inducible peroxide stress responses. Mol Microbiol 45:9–15
Moore CM, Nakano MM, Wang T, Ye RW, Helmann JD (2004) Response of Bacillus subtilis to nitric oxide and the nitrosating agent sodium nitroprusside. J Bacteriol 186:4655–4664
Morrissey JA, Cockayne A, Brummell K, Williams P (2004) The staphylococcal ferritins are differentially regulated in response to iron and manganese and via PerR and Fur. Infect Immun 72:972–979
Mostertz J, Scharf C, Hecker M, Homuth G (2004) Transcriptome and proteome analysis of Bacillus subtilis gene expression in response to superoxide and peroxide stress. Microbiology 150:497–512
Outten CE, O’Halloran TV (2001) Femtomolar sensitivity of metalloregulatory proteins controlling zinc homeostasis. Science 292:2488–2492
Outten CE, Tobin DA, Penner-Hahn JE, O’Halloran TV (2001) Characterization of the metal receptor sites in Escherichia coli Zur, an ultrasensitive zinc(II) metalloregulatory protein. Biochemistry 40:10417–10423
Paget MS, Buttner MJ (2003) Thiol-based regulatory switches. Annu Rev Genet 37:91–121
Panina EM, Mironov AA, Gelfand MS (2001) Comparative analysis of FUR regulons in gamma-proteobacteria. Nucleic Acids Res 29:5195–5206
Panina EM, Mironov AA, Gelfand MS (2003) Comparative genomics of bacterial zinc regulons: enhanced ion transport, pathogenesis, and rearrangement of ribosomal proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:9912–9917
Patzer SI, Hantke K (1998) The ZnuABC high-affinity zinc uptake system and its regulator Zur in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 28:1199–1210
Patzer SI, Hantke K (2000) The zinc-responsive regulator Zur and its control of the znu gene cluster encoding the ZnuABC zinc uptake system in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 275:24321–24332
Payne SM, Wyckoff EE, Murphy ER, Oglesby AG, Boulette ML, Davies NM (2006) Iron and pathogenesis of Shigella: iron acquisition in the intracellular environment. Biometals 19:173-180
Pohl E, Haller JC, Mijovilovich A, Meyer-Klaucke W, Garman E, Vasil ML (2003) Architecture of a protein central to iron homeostasis: crystal structure and spectroscopic analysis of the ferric uptake regulator. Mol Microbiol 47:903–915
Puig S, Askeland E, Thiele DJ (2005) Coordinated remodeling of cellular metabolism during iron deficiency through targeted mRNA degradation. Cell 120:99–110
Qi Z, Hamza I, O’Brian MR (1999) Heme is an effector molecule for iron-dependent degradation of the bacterial iron response regulator (Irr) protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13056–13061
Qi Z, O’Brian MR (2002) Interaction between the bacterial iron response regulator and ferrochelatase mediates genetic control of heme biosynthesis. Mol Cell 9:155–162
Rea R, Hill C, Gahan CG (2005) Listeria monocytogenes perR mutants display a small-colony phenotype, increased sensitivity to hydrogen peroxide, and significantly reduced murine virulence. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8314”8322
Rea RB, Gahan CG, Hill C (2004) Disruption of putative regulatory loci in Listeria monocytogenes demonstrates a significant role for Fur and PerR in virulence. Infect Immun 72:717–727
Richardson AR, Dunman PM, Fang FC (2006) The nitrosative stress response of Staphylococcus aureus is required for resistance to innate immunity. Mol Microbiol 61:927–939
Rodionov DA, Dubchak I, Arkin A, Alm E, Gelfand MS (2004) Reconstruction of regulatory and metabolic pathways in metal-reducing delta-proteobacteria. Genome Biol 5:R90
Rudolph G, Hennecke H, Fischer HM (2006a) Beyond the Fur paradigm: iron-controlled gene expression in rhizobia. FEMS Microbiol Rev 30:631–648
Rudolph G, Semini G, Hauser F et al (2006b) The Iron control element, acting in positive and negative control of iron-regulated Bradyrhizobium japonicum genes, is a target for the Irr protein. J Bacteriol 188:733–744
Tottey S, Harvie DR, Robinson NJ (2005) Understanding how cells allocate metals using metal sensors and metallochaperones. Acc Chem Res 38:775–783
Traore DAK, El Gahzouani A, Ilango S et al (2006) Crystal structure of the apo-PerR-Zn protein from Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 61:1211–1219
van Vliet AH, Baillon ML, Penn CW, Ketley JM (1999) Campylobacter jejuni contains two fur homologs: characterization of iron-responsive regulation of peroxide stress defense genes by the PerR repressor. J Bacteriol 181:6371–6376
Wennerhold J, Krug A, Bott M (2005) The AraC-type regulator RipA represses aconitase and other iron proteins from Corynebacterium under iron limitation and is itself repressed by DtxR. J Biol Chem 280:40500–40508
White A, Ding X, vanderSpek JC, Murphy JR, Ringe D (1998) Structure of the metal-ion-activated diphtheria toxin repressor/tox operator complex. Nature 394:502–506
Wilderman PJ, Sowa NA, FitzGerald DJ et al (2004) Identification of tandem duplicate regulatory small RNAs in Pseudomonas aeruginosa involved in iron homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9792–9797
Yang J, Ishimori K, O’Brian MR (2005) Two heme binding sites are involved in the regulated degradation of the bacterial iron response regulator (Irr) protein. J Biol Chem 280:7671–7676
Yang J, Panek HR, O’Brian MR (2006a) Oxidative stress promotes degradation of the Irr protein to regulate haem biosynthesis in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Mol Microbiol 60:209–218
Yang J, Sangwan I, Lindemann A et al (2006b) Bradyrhizobium japonicum senses iron through the status of haem to regulate iron homeostasis and metabolism. Mol Microbiol 60:427–437
Acknowledgements
We thank M. O’Brian and A. van Vliet for helpful comments. Work in our laboratory on metalloregulation is supported by NIH (GM059323) and work on oxidative stress sensors is supported by the NSF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JW., Helmann, J.D. Functional specialization within the Fur family of metalloregulators. Biometals 20, 485–499 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-006-9070-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-006-9070-7