Abstract
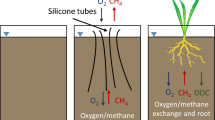
In the root zone of rice plants aerobic methanotrophic bacteria catalyze the oxidation of CH4 to CO2, thereby reducing CH4 emissions from paddy soils to the atmosphere. However, methods for in situ quantification of microbial processes in paddy soils are scarce. Here we adapted the push–pull tracer-test (PPT) method to quantify CH4 oxidation in the root zone of potted rice plants. During a PPT, a test solution containing CH4 ± O2 as reactant(s), Cl− and Ar as nonreactive tracers, and BES as an inhibitor of CH4 production was injected into the root zone at different times throughout the circadian cycle (daytime, early nighttime, late nighttime). After a 2-h incubation phase, the test solution/pore-water mixture was extracted from the same location and rates of CH4 oxidation were calculated from the ratio of measured reactant and nonreactive tracer concentrations. In separate rice pots, O2 concentrations in the vicinity of rice roots were measured throughout the circadian cycle using a fiber-optic sensor. Results indicated highly variable CH4 oxidation rates following a circadian pattern. Mean rates at daytime and early nighttime varied from 62 up to 451 μmol l−1 h−1, whereas at late nighttime CH4 oxidation rates were low, ranging from 13 to 37 μmol l−1 h−1. Similarly, daytime O2 concentration in the vicinity of rice roots increased to up to 250% air saturation, while nighttime O2 concentration dropped to below detection (<0.15% air saturation). Our results suggest a functional link between root-zone CH4 oxidation and photosynthetic O2 supply.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong W (1964) Oxygen diffusion from the roots of some british bog plants. Nature 204(4960):801–802
Bassein E, Jaffe PR (2009) Measuring in situ reaction rate constants in wetland sediments. Environ Monit and Assess 159(1–4):51–62
Bosse U, Frenzel P (1997) Activity and distribution of methane-oxidizing bacteria in flooded rice soil microcosms and in rice plants (oryza sativa). Appl Environ Microbiol 63(4):1199–1207
Butterbach-Bahl K, Papen H, Rennenberg H (1997) Impact of gas transport through rice cultivars on methane emission from rice paddy fields. Plant Cell Environ 20(9):1175–1183
Calhoun A, King GM (1997) Regulation of root-associated methanotrophy by oxygen availability in the rhizosphere of two aquatic macrophytes. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(8):3051–3058
Chanton JP, Whiting GJ, Blair NE, Lindau CW, Bollich PK (1997) Methane emission from rice: Stable isotopes, diurnal variations, and CO2 exchange. Global Biogeochem Cycles 11(1):15–27
Chen CC, Dixon JB, Turner FT (1980) Iron coatings on rice roots—mineralogy and quantity influencing factors. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44(3):635–639
Christensen PB, Revsbech NP, Sand-Jensen K (1994) Microsensor analysis of oxygen in the rhizosphere of the aquatic macrophyte Littorella uniflora (L.) ascherson. Plant Physiol 105(3):847–852
Colmer TD (2003) Long-distance transport of gases in plants: a perspective on internal aeration and radial oxygen loss from roots. Plant Cell Environ 26(1):17–36
Colmer TD, Pedersen O (2008) Oxygen dynamics in submerged rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol 178(2):326–334
Colmer TD, Gibberd MR, Wiengweera A, Tinh TK (1998) The barrier to radial oxygen loss from roots of rice (Oryza sativa L.) is induced by growth in stagnant solution. J Exp Bot 49(325):1431–1436
Conrad R, Rothfuss F (1991) Methane oxidation in the soil surface layer of a flooded rice field and the effect of ammonium. Biol Fertil Soils 12(1):28–32
Denman KL, Brasseur G, Chidthaisong A, Ciais P, Cox PM, Dickinson RE, Hauglustaine D, Heinze C, Holland E, Jacob D, Lohmann U, Ramachandran S, da Silva Dias PL, Wofsy SC, Zhang X (2007) Couplings between changes in the climate system and biogeochemistry. In: Solomon S, D. Qin, M. Manning, Z. Chen, M. Marquis, K.B. Averyt, M.Tignor and H.L. Miller (eds) Climate change 2007: The physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
Eller G, Frenzel P (2001) Changes in activity and community structure of methane-oxidizing bacteria over the growth period of rice. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(6):2395–2403
Eller G, Kruger M, Frenzel P (2005) Comparing field and microcosm experiments: a case study on methano- and methylo-trophic bacteria in paddy soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 51(2):279–291
Epp MA, Chanton JP (1993) Rhizospheric methane oxidation determined via the methyl fluoride inhibition technique. J Geophys Res Atm 98(D10):18413–18422
Ferrell RT, Himmelblau DM (1967) Diffusion coefficients of nitrogen and oxygen in water. J Chem Eng Data 12(1):111–115
Forster P, Ramaswamy V, Artaxo P, Berntsen T, Betts R, Fahey DW, Haywood J, Lean J, Lowe DC, Myhre G, Nganga J, Prinn R, Raga G, Schulz M, Van Dorland R (2007) Changes in atmospheric constituents and in radiative forcing. In: Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller HL (edS) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
Frenzel P, Rothfuss F, Conrad R (1992) Oxygen profiles and methane turnover in a flooded rice microcosm. Biol Fertil Soils 14(2):84–89
Fuller EN, Schettle Pd, Giddings JC (1966) A new method for prediction of binary gas-phase diffusion coefficients. Ind Eng Chem 58(5):19–27
Gerard G, Chanton J (1993) Quantification of methane oxidation in the rhizosphere of emergent aquatic macrophytes—defining upper limits. Biogeochemistry 23(2):79–97
Gilbert B, Frenzel P (1995) Methanotrophic bacteria in the rhizosphere of rice microcosms and their effect on porewater methane concentration and methane emission. Biol Fertil Soils 20(2):93–100
Gilbert B, Frenzel P (1998) Rice roots and CH4 oxidation: the activity of bacteria, their distribution and the microenvironment. Soil Biol Biochem 30(14):1903–1916
Gomez KE, Gonzalez-Gil G, Lazzaro A, Schroth MH (2009) Quantifying methane oxidation in a landfill-cover soil by gas push–pull tests. Waste Manag 29(9):2518–2526
Gonzalez-Gil G, Schroth MH, Zeyer J (2007) Transport of methane and noble gases during gas push-pull tests in dry porous media. Environ Sci Technol 41(9):3262–3268
Groot TT, van Bodegom PM, Harren FJM, Meijer HAJ (2003) Quantification of methane oxidation in the rice rhizosphere using 13c-labelled methane. Biogeochemistry 64(3):355–372
Hageman KJ, Field JA, Istok JD, Semprini L (2004) Quantifying the effects of fumarate on in situ reductive dechlorination rates. J Contam Hydrol 75(3–4):281–296
Haggerty R, Schroth MH, Istok JD (1998) Simplified method of “push–pull” test data analysis for determining in situ reaction rate coefficients. Ground Water 36(2):314–324
Hanson RS, Hanson TE (1996) Methanotrophic bacteria. Microbiol Rev 60(2):439–471
Henckel T, Roslev P, Conrad R (2000) Effects of O2 and CH4 on presence and activity of the indigenous methanotrophic community in rice field soil. Environ Microbiol 2(6):666–679
Holzapfel-Pschorn A, Seiler W (1986) Methane emission during a cultivation period from an Italian rice paddy. J Geophys Res 91(D11):11803–11814
Holzapfel-Pschorn A, Conrad R, Seiler W (1985) Production, oxidation and emission of methane in rice paddies. FEMS Microbiol Lett 31(6):343–351
Istok JD, Humphrey MD, Schroth MH, Hyman MR, Oreilly KT (1997) Single-well, “push–pull”‘ test for in situ determination of microbial activities. Ground Water 35(4):619–631
Kampbell DH, Vandegrift SA (1998) Analysis of dissolved methane, ethane, and ethylene in ground water by a standard gas chromatographic technique. J Chromatogr Sci 36(5):253–256
Kim Y, Istok JD, Semprini L (2006) Push-pull tests evaluating in situ aerobic cometabolism of ethylene, propylene, and cis-1,2-dichloroethylene. J Contam Hydrol 82(1–2):165–181
King G (1996) In situ analyses of methane oxidation associated with the roots and rhizomes of a bur reed, Sparganium eurycarpum, in a maine wetland. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(12):4548–4555
Kleikemper J, Schroth MH, Sigler WV, Schmucki M, Bernasconi SM, Zeyer J (2002) Activity and diversity of sulfate-reducing bacteria in a petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated aquifer. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(4):1516–1523
Koop-Jakobsen K, Giblin AE (2009) New approach for measuring denitrification in the rhizosphere of vegetated marsh sediments. Limnol Oceanogr Methods 7:626–637
Krüger M, Frenzel P, Conrad R (2001) Microbial processes influencing methane emission from rice fields. Glob Change Biol 7(1):49–63
Krüger M, Eller G, Conrad R, Frenzel P (2002) Seasonal variation in pathways of CH4 production and in CH4 oxidation in rice fields determined by stable carbon isotopes and specific inhibitors. Glob Change Biol 8(3):265–280
Kumaraswamy S, Rath AK, Ramakrishnan B, Sethunathan N (2000) Wetland rice soils as sources and sinks of methane: a review and prospects for research. Biol Fertil Soils 31(6):449–461
Liesack W, Schnell S, Revsbech NP (2000) Microbiology of flooded rice paddies. FEMS Microbiol Rev 24(5):625–645
Lobo VMM, Ribeiro ACF, Verissimo LMP (1998) Diffusion coefficients in aqueous solutions of potassium chloride at high and low concentrations. J Mol Liq 78(1–2):139–149
Macfie SM, Crowder AA (1987) Soil factors influencing ferric hydroxide plaque-formation on roots of Typha latifolia L. Plant Soil 102(2):177–184
Massman WJ (1998) A review of the molecular diffusivities of H2o, CO2, CH4, Co, O−3, SO2, NH3, N2O, NO, and NO2 in air, O−2 and N−2 near STP. Atmos Environ 32(6):1111–1127
Nauer PA, Schroth MH (2010) In situ quantification of atmospheric methane oxidation in near-surface soils. Vadose Zone J 9(4):1052–1062
Nouchi I, Mariko S, Aoki K (1990) Mechanism of methane transport from the rhizosphere to the atmosphere through rice plants. Plant Physiol 94(1):59–66
Oremland RS, Taylor BF (1977) Diurnal fluctuations of O2, N2, and CH4 in rhizosphere of Thalassia testudinum. Limnol Oceanogr 22(3):566–570
Rao DK, Bhattacharya SK, Jani RA (2008) Seasonal variations of carbon isotopic composition of methane from Indian paddy fields. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 22(1):GB1004
Revsbech NP, Pedersen O, Reichardt W, Briones A (1999) Microsensor analysis of oxygen and pH in the rice rhizosphere under field and laboratory conditions. Biol Fertil Soils 29(4):379–385
Sander R (1999) Compilation of Henry’s law constants for inorganic and organic species of potential importance in environmental chemistry (version 3) http://www.Henrys-law.org
Sanders IA, Trimmer M (2006) In situ application of the 15NO3 isotope pairing technique to measure denitrification in sediments at the surface water–groundwater interface. Limnol Oceanogr Methods 4:142–152
Schroth MH, Istok JD (2006) Models to determine first-order rate coefficients from single-well push–pull tests. Ground Water 44(2):275–283
Schütz H, Seiler W, Conrad R (1989) Processes involved in formation and emission of methane in rice paddies. Biogeochemistry 7(1):33–53
Seiler W, Holzapfel-Pschorn A, Conrad R, Scharffe D (1983) Methane emission from rice paddies. J Atmos Chem 1(3):241–268
Urmann K, Gonzalez-Gil G, Schroth MH, Hofer M, Zeyer J (2005) New field method: gas push-pull tests for the in situ quantification of microbial activities in the vadose zone. Environ Sci Technol 39(1):304–310
van Bodegom P, Stams F, Mollema L, Boeke S, Leffelaar P (2001) Methane oxidation and the competition for oxygen in the rice rhizosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(8):3586–3597
van der Gon HACD, Neue H-U (1996) Oxidation of methane in the rhizosphere of rice plants. Biol Fertil Soils 22(4):359–366
van der Gon HACD, van Breemen N (1993) Diffusion-controlled transport of methane from soil to atmosphere as mediated by rice plants. Biogeochemistry 21(3):177–190
van der Nat F-FWA, Middelburg JJ, Van Meteren D, Wielemakers A (1998) Diel methane emission patterns from Scirpus lacustris and Phragmites australis. Biogeochemistry 41(1):1–22
Wang ZP, Zeng D, Patrick WH (1997) Characteristics of methane oxidation in a flooded rice soil profile. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 49(1):97–103
Wassmann R, Papen H, Rennenberg H (1993) Methane emission from rice paddies and possible mitigation strategies. Chemosphere 26(1–4):201–217
Waters I, Armstrong W, Thompson CJ, Setter TL, Adkins S, Gibbs J, Greenway H (1989) Diurnal changes in radial oxygen loss and ethanol-metabolism in roots of submerged and non-submerged rice seedlings. New Phytol 113(4):439–451
Witherspoon P, Saraf DN (1965) Diffusion of methane, ethane, propane and n-butane in water from 25 to 43 degrees. J Phys Chem 69(11):3752–3755
Yagi K, Tsuruta H, Minami K (1997) Possible options for mitigating methane emission from rice cultivation. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 49(1):213–220
Yaws CL (2010) Yaws’ transport properties of chemicals and hydrocarbons (electronic edition). Knovel, Norwich. http://knovel.com/web/portal/browse/display?_EXT_KNOVEL_DISPLAY_bookid=2905&VerticalID=0
Yoshinari T, Knowles R (1976) Acetylene inhibition of nitrous oxide reduction by denitrifying bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 69(3):705–710
Acknowledgments
We thank Christof Sautter and his team for the cultivation of the rice plants, and Ruben Kretzschmar (all at ETH Zurich) for providing the climate chamber. Funding for this project was provided by ETH Zurich through grant no. TH-20 06-3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, R., Schroth, M.H. & Zeyer, J. Circadian methane oxidation in the root zone of rice plants. Biogeochemistry 111, 317–330 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-011-9651-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-011-9651-6