Abstract
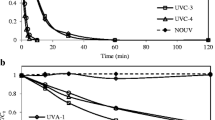
Sulfoxaflor (SUL, [N-[methyloxido[1-[6-(trifluoromethyl)-3-pyridinyl] ethyl]-λ4-sulfanylidene] cyanamide]) is a widely used systemic insecticide, and its residue has frequently been detected in the environment, posing a potential threat to the environment. In this study, Pseudaminobacter salicylatoxidans CGMCC 1.17248 rapidly converted SUL into X11719474 via a hydration pathway mediated by two nitrile hydratases (AnhA and AnhB). Extensive (96.4%) degradation of 0.83 mmol/L SUL was achieved by P. salicylatoxidans CGMCC 1.17248 resting cells within 30 min (half-life of SUL 6.4 min). Cell immobilization by entrapment into calcium alginate remediated 82.8% of the SUL in 90 min, and almost no SUL was observed in surface water after incubation for 3 h. P. salicylatoxidans NHases AnhA and AnhB both hydrolyzed SUL to X11719474, although AnhA exhibited much better catalytic performance. The genome sequence of P. salicylatoxidans CGMCC 1.17248 revealed that this strain could efficiently eliminate nitrile-containing insecticides and adapt to harsh environments. We firstly found that UV irradiation transforms SUL to the derivatives X11719474 and X11721061, and the potential reaction pathways were proposed. These results further deepen our understanding of the mechanisms of SUL degradation as well as the environmental fate of SUL.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Naggar Y, Paxton RJ (2021) The novel insecticides flupyradifurone and sulfoxaflor do not act synergistically with viral pathogens in reducing honey bee (Apis mellifera) survival but sulfoxaflor modulates host immunocompetence. Microb Biotechnol 14(1):227–240. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.13673
Bouabidi ZB, El-Naas MH, Zhang Z (2019) Immobilization of microbial cells for the biotreatment of wastewater: a review. Environ Chem Lett 17(1):241–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0795-7
Cao DT, He SH, Li X, Shi LH, Wang FY, Yu SM, Xu SJ, Ju C, Fang H, Yu YL (2021) Characterization, genome functional analysis, and detoxification of atrazine by Arthrobacter sp. C2. Chemosphere 264:128514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128514
Chen XW, Ma KS, Li F, Liang PZ, Liu Y, Guo TF, Song DL, Desneux N, Gao XW (2016) Sublethal and transgenerational effects of sulfoxaflor on the biological traits of the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii Glover (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Ecotoxicology 25(10):1841–1848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1732-9
Conde-Avila V, Ortega-Martínez LD, Loera O, El Kassis EG, Dávila JG, Valenzuela CM, Armendáriz BP (2021) Pesticides degradation by immobilised microorganisms. Int J Environ Anal Chem 101(15):2975–3005. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1715375
Cutler P, Slater R, Edmunds AJ, Maienfisch P, Hall RG, Earley FG, Pitterna T, Pal S, Paul VL, Goodchild J, Blacker M, Hagmann L, Crossthwaite AJ (2013) Investigating the mode of action of sulfoxaflor: a fourth-generation neonicotinoid. Pest Manag Sci 69(5):607–619. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.3413
Dáder B, Viñuela E, Moreno A, Plaza M, Garzo E, del Estal P, Fereres A (2019) Sulfoxaflor and natural pyrethrin with piperonyl butoxide are effective alternatives to neonicotinoids against juveniles of Philaenus spumarius, the European vector of Xylella fastidiosa. InSects 10(8):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10080225
Dáder B, Colomer I, Adán Á, Medina P, Viñuela E (2020) Compatibility of early natural enemy introductions in commercial pepper and tomato greenhouses with repeated pesticide applications. Insect Sci 27(5):1111–1124. https://doi.org/10.1111/1744-7917.12723
Dai ZL, Yang WL, Fan ZX, Guo L, Liu ZH, Dai YJ (2021) Actinomycetes Rhodococcus ruber CGMCC 17550 degrades neonicotinoid insecticide nitenpyram via a novel hydroxylation pathway and remediates nitenpyram in surface water. Chemosphere 270:128670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128670
Ellis-Hutchings RG, Rasoulpour RJ, Terry C, Carney EW, Billington R (2014) Human relevance framework evaluation of a novel rat developmental toxicity mode of action induced by sulfoxaflor. Crit Rev Toxicol 44:45–62. https://doi.org/10.3109/10408444.2014.910752
Fang S, Zhang YZ, You XW, Sun P, Qiu J, Kong FY (2018) Lethal toxicity and sublethal metabolic interference effects of sulfoxaflor on the earthworm (Eisenia fetida). J Agric Food Chem 66(45):11902–11908. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b04633
Guo LL, Yang WL, Cheng X, Fan ZX, Chen XM, Ge F, Dai YJ (2021) Degradation of neonicotinoid insecticide acetamiprid by two different nitrile hydratases of Pseudaminobacter salicylatoxidans CGMCC 1.17248. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 157:105141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2020.105141
Huang X, He J, Yan X, Hong Q, Chen K, He Q, Zhang L, Liu XW, Chuang SC, Li SP, Jiang JD (2017) Microbial catabolism of chemical herbicides: microbial resources, metabolic pathways and catabolic genes. Pestic Biochem Physiol 143:272–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2016.11.010
Jones OAH, Voulvoulis N, Lester JN (2001) Human pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment a review. Environ Technol 22(12):1383–1394. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593332208618186
Jun LY, Yon LS, Mubarak NM, Bing CH, Pan S, Danquah MK, Abdullah EC, Khalid M (2019) An overview of immobilized enzyme technologies for dye and phenolic removal from wastewater. J Environ Chem Eng 7(2):102961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.102961
Kim H, Kim DU, Lee H, Yun J, Ka JO (2017a) Syntrophic biodegradation of propoxur by Pseudaminobacter sp. SP1a and Nocardioides sp. SP1b isolated from agricultural soil. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 118:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.01.024
Kim SW, Rahman MM, Abd El-Aty AM, Kabir MH, Na TW, Choi JH, Shin HC, Shim JH (2017b) Simultaneous detection of sulfoxaflor and its metabolites, X11719474 and X11721061, in lettuce using a modified QuEChERS extraction method and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed Chromatogr 31(6):e3885. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.3885
Kobayashi M, Shimizu S (1998) Metalloenzyme nitrile hydratase: structure, regulation, and application to biotechnology. Nat Biotechnol 16(8):733–736. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0898-733
Lebaron MJ, Gollapudi BB, Terry C, Billington R, Rasoulpour RJ (2014) Human relevance framework for rodent liver tumors induced by the insecticide sulfoxaflor. Crit Rev Toxicol 44:15–24. https://doi.org/10.3109/10408444.2014.910751
Lin HY, Chen ZL, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2013) Biodegradation of TNT using Bacillus mycoides immobilized in PVA-sodium alginate-kaolin. Appl Clay Sci 83–84:336–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2013.08.004
Lin AYC, Lin YC, Lee WN (2014) Prevalence and sunlight photolysis of controlled and chemotherapeutic drugs in aqueous environments. Environ Pollut 187:170–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.01.005
Papagiannaki D, Medana C, Binetti R, Calza P, Roslev P (2020) Effect of UV-A, UV-B and UV-C irradiation of glyphosate on photolysis and mitigation of aquatic toxicity. Sci Rep 10(1):20247. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76241-9
Qu J, Miao LL, Liu Y, Liu ZP (2015) Complete genome sequence of Rhodococcus sp. strain IcdP1 shows diverse catabolic potential. Genome Announc 3(4):e00711–e00715. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00711-15
Remucal CK (2014) The role of indirect photochemical degradation in the environmental fate of pesticides: a review. Environ Sci Process Impacts 16(4):628–653. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3EM00549F
Siviter H, Brown MJF, Leadbeater E (2018) Sulfoxaflor exposure reduces bumblebee reproductive success. Nature 561(7721):109–112. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0430-6
Sodhi KK, Kumar M, Balan B, Dhaulaniya AS, Shree P, Sharma N, Singh DK (2021) Perspectives on the antibiotic contamination, resistance, metabolomics, and systemic remediation. SN Appl Sci 3(2):269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-04003-3
Sparks TC, Watson GB, Loso MR, Geng CX, Babcock JM, Thomas JD (2013) Sulfoxaflor and the sulfoximine insecticides: chemistry, mode of action and basis for efficacy on resistant insects. Pestic Biochem Physiol 107(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2013.05.014
Suchail S, Debrauwer L, Belzunces LP (2004) Metabolism of imidacloprid in Apis mellifera. Pest Manag Sci 60(3):291–296. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.772
Sun SL, Lu TQ, Yang WL, Guo JJ, Rui X, Mao SY, Zhou LY, Dai YJ (2016) Characterization of a versatile nitrile hydratase of the neonicotinoid thiacloprid-degrading bacterium Ensifer meliloti CGMCC 7333. RSC Adv 6(19):15501–15508. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA27966F
Sun SL, Yang WL, Guo JJ, Zhou YN, Rui X, Ge F, Dai YJ (2017) Biodegradation of the neonicotinoid insecticide acetamiprid in surface water by the bacterium Variovorax boronicumulans CGMCC 4969 and its enzymatic mechanism. RSC Adv 7(41):25387–25397. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA01501A
Sun SL, Fan ZX, Zhao YX, Guo L, Dai YJ (2019) A novel nutrient deprivation-induced neonicotinoid insecticide acetamiprid degradation by Ensifer adhaerens CGMCC 6315. J Agric Food Chem 67(1):63–71. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b06154
Sun YF, Chen YT, Wei JJ, Zhang XX, Zhang L, Yang Z, Huang Y (2021) Ultraviolet-B radiation stress alters the competitive outcome of algae: based on analyzing population dynamics and photosynthesis. Chemosphere 272:129645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129645
Supreetha K, Rao SN, Srividya D, Anil HS, Kiran S (2019) Advances in cloning, structural and bioremediation aspects of nitrile hydratases. Mol Biol Rep 46(4):4661–4673. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-04811-w
Terry C, Rasoulpour RJ, Knowles S, Billington R (2015) Utilizing relative potency factors (RPF) and threshold of toxicological concern (TTC) concepts to assess hazard and human risk assessment profiles of environmental metabolites: a case study. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 71(2):301–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2014.12.010
Wang JL, Quan XC, Han LP, Qian Y, Hegemann W (2002) Microbial degradation of quinoline by immobilized cells of Burkholderia pickettii. Water Res 36(9):2288–2296. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00457-2
Wang SX, Li XJ, Liu W, Li PJ, Kong LX, Ren WJ, Wu HY, Tu Y (2012) Degradation of pyrene by immobilized microorganisms in saline-alkaline soil. J Environ Sci 24(9):1662–1669. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(11)60963-7
Watson GB, Loso MR, Babcock JM, Hasler JM, Letherer TJ, Young CD, Zhu YM, Casida JE, Sparks TC (2011) Novel nicotinic action of the sulfoximine insecticide sulfoxaflor. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 41(7):432–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2011.01.009
Wiezorek S, Lamers P, Bolm C (2019) Conversion and degradation pathways of sulfoximines. Chem Soc Rev 48(21):5408–5423. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CS00483A
Xu L, Zhao CQ, Zhang YN, Liu Y, Gu ZY (2016) Lethal and sublethal effects of sulfoxaflor on the small brown planthopper Laodelphax striatellus. J Asia-Pac Entomol 19(3):683–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aspen.2016.06.013
Xu LW, Guo LL, Wang ZX, Xu XX, Zhang S, Wu XL, Kuang H, Xu CL (2020) Profiling and identification of biocatalyzed transformation of sulfoxaflor in vivo. Angew Chem Int Ed 59(37):16218–16224. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202007079
Yamada H, Kobayashi M (1996) Nitrile hydratase and its application to industrial production of acrylamide. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 60(9):1391–1400. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.60.1391
Yang WL, Guo LL, Dai ZL, Qin RC, Zhao YX, Dai YJ (2019) Biodegradation of the insecticide flonicamid by Alcaligenes faecalis CGMCC 17553 via hydrolysis and hydration pathways mediated by nitrilase. J Agric Food Chem 67(36):10032–10041. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b04245
Yang WL, Dai ZL, Cheng X, Guo L, Fan ZX, Ge F, Dai YJ (2020) Sulfoxaflor degraded by Aminobacter sp. CGMCC 1.17253 through hydration pathway mediated by nitrile hydratase. J Agric Food Chem 68(16):4579–4587. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b06668
Yang WL, Fan ZX, Jiang HY, Zhao YX, Guo L, Dai YJ (2021) Biotransformation of flonicamid and sulfoxaflor by multifunctional bacterium Ensifer meliloti CGMCC 7333. J Environ Sci Health Part B 56(2):122–131. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2020.1852854
Zhang XL, Wang XG, Liu YL, Fang K, Liu T (2020) The toxic effects of sulfoxaflor induced in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) under effective concentrations. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(5):1740. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051740
Zhao YX, Jiang HY, Cheng X, Zhu YX, Fan ZX, Dai ZL, Guo L, Liu ZH, Dai YJ (2019) Neonicotinoid thiacloprid transformation by the N2-fixing bacterium Microvirga flocculans CGMCC 1.16731 and toxicity of the amide metabolite. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 145:104806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2019.104806
Zhao YX, Yang WL, Guo L, Jiang HY, Cheng X, Dai YJ (2020) Bioinformatics of a novel nitrile hydratase gene cluster of the N2-fixing bacterium Microvirga flocculans CGMCC 1.16731 and characterization of the enzyme. J Agric Food Chem 68(35):9299–9307. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c03702
Zhao YX, Guo L, Wang L, Jiang ND, Chen KX, Dai YJ (2021a) Biodegradation of the pyridinecarboxamide insecticide flonicamid by Microvirga flocculans and characterization of two novel amidases involved. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 220:112384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112384
Zhao YX, Wang L, Chen KX, Jiang ND, Sun SL, Ge F, Dai YJ (2021b) Biodegradation of flonicamid by Ensifer adhaerens CGMCC 6315 and enzymatic characterization of the nitrile hydratases involved. Microb Cell Fact 20(1):133. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-021-01620-4
Acknowledgements
We thank James Allen, DPhil, from Liwen Bianji, Edanz Group China, for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31970094) and the Program for Jiangsu Excellent Scientific and Technological Innovation Team (17CXTD00014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y-XZ and Y-JD contributed to the design and implementation of the research, to the analysis of the results and to the writing of the manuscript. K-XC prepared Figs.1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and revised the manuscript. LW and P-PY prepared Tables 1 and Table 2. Y-JD provided the funding and directed the project. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
All authors gave their consent for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, YX., Chen, KX., Wang, L. et al. Biodegradation of sulfoxaflor and photolysis of sulfoxaflor by ultraviolet radiation. Biodegradation 34, 341–355 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-023-10020-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-023-10020-x