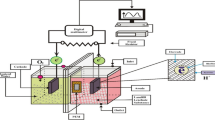
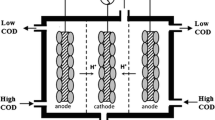
Abstract
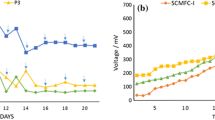
Anaerobic/aerobic conditions affected bacterial community composition and the subsequent chlorophenols (CPs) degradation in biocathode microbial fuel cells (MFCs). Bacterial communities acclimated with either 4-chlorophenol (4-CP) or 2,4-dichlorophenol (2,4-DCP) under anaerobiosis can degrade the respective substrates more efficiently than the facultative aerobic bacterial communities. The anaerobic bacterial communities well developed with 2,4-DCP were then adapted to 2,4,6-trichlorophenol (2,4,6-TCP) and successfully stimulated for enhanced 2,4,6-TCP degradation and power generation. A 2,4,6-TCP degradation rate of 0.10 mol/m3/d and a maximum power density of 2.6 W/m3 (11.7 A/m3) were achieved, 138 and 13 % improvements, respectively compared to the controls with no stimulation. Bacterial communities developed with the specific CPs under anaerobic/aerobic conditions as well as the stimulated biofilm shared some dominant genera and also exhibited great differences. These results provide the most convincing evidence to date that anaerobic/aerobic conditions affected CPs degradation with power generation from the biocathode systems, and using deliberate substrates can stimulate the microbial consortia and be potentially feasible for the selection of an appropriate microbial community for the target substrate (e.g. 2,4,6-TCP) degradation in the biocathode MFCs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abed RM, Safi NM, Koster J, de Beer D, El-Nahhal Y, Rullkotter J, Garcia-Pichel F (2002) Microbial diversity of a heavily polluted microbial mat and its community changes following degradation of petroleum compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1674–1683
Arnett CM, Rodriguez G, Maloney SW (2009) Analysis of bacterial community diversity in anaerobic fluidized bed bioreactors treating 2,4-dinitroanisole (DNAN) and n-methyl-4-nitroaniline (MNA) using 16S rRNA gene clone libraries. Microbes Environ 24:72–75
Aulenta F, Maio VD, Ferri T, Majone M (2010) The humic acid analogue anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate (AQDS) serves as an electron shuttle in the electricity-driven microbial dechlorination of trichloroethene to cis-dichloroethene. Bioresour Technol 101:9728–9733
Baek SH, Kim KH, Yin CR, Jeon CO, Im WT, Kim KK, Lee ST (2003) Isolation and characterization of bacteria capable of degrading phenol and reducing nitrate under low-oxygen conditions. Curr Microbiol 47:462–466
Butler CS, Clauwaert P, Green SJ, Verstraete W, Nerenberg R (2010) Bioelectrochemical perchlorate reduction in a microbial fuel cell. Environ Sci Technol 44:4685–4691
Cai PJ, Xiao X, He YR, Li WW, Zang GL, Sheng GP, Lam MHW, Yu L, Yu HQ (2013) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by cyanobacteria act as an electron acceptor in the biocathode of a bioelectrochemical system. Biosens Bioelectron 39:306–310
Cao F, Liu T, Wu C, Li F, Li X, Yu H, Tong H, Chen M (2012) Enhanced biotransformation of DDTs by an iron- and humic-reducing bacteria Aeromonas hydrophila HS01 upon addition of goethite and anthraquinone-2,6-disulphonic disodium salt (AQDS). J Agric Food Chem 60:11238–11244
Chandra R, Singh R, Yadav S (2012) Effect of bacterial inoculum ratio in mixed culture for decolourization and detoxification of pulp paper mill effluent. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 87:436–444
Chen Y, Lin CJ, Lan H, Fu S, Zhan H (2010) Changes in pentachlorophenol (PCP) metabolism and physicochemical characteristics by granules responding to different oxygen availability. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 29:307–312
Chen JL, Wang JY, Wu CC, Chiang KY (2011) Electro-catalytic degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol by granular graphite electrodes. Colloids Surf A 379:163–168
Chen M, Shih K, Hu M, Li F, Liu C, Wu W, Tong H (2012) Biostimulation of indigenous microbial communities for anaerobic transformation of pentachlorophenol in paddy soils of southern China. J Agric Food Chem 60:2967–2975
Chen JJ, Chen W, He H, Li DB, Li WW, Xiong L, Yu HQ (2013) Manipulation of microbial extracellular electron transfer by changing molecular structure of phenazine-type redox mediators. Environ Sci Technol 47:1033–1039
Cheng IF, Fernando Q, Korte N (1997) Electrochemical dechlorination of 4-chlorophenol to phenol. Environ Sci Technol 31:1074–1078
Cheng KY, Ginige MP, Kaksonen AH (2012) Ano-cathodophilic biofilm catalyzes both anodic carbon oxidation and cathodic denitrification. Environ Sci Technol 46:10372–10378
Chun CL, Payne RB, Sowers KR, May HD (2013) Electrical stimulation of microbial PCB degradation in sediment. Water Res 47:141–152
Cycon M, Zmijowska A, Piotrowska-Seget Z (2011) Biodegradation kinetics of 2,4-D by bacterial strains isolated from soil. Cent Eur J Biol 6:188–198
De Schamphelaire L, Cabezas A, Marzorati M, Friedrich MW, Boon N, Verstraete W (2010) Microbial community analysis of anodes from sediment microbial fuel cells powered by rhizodeposits of living rice plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:2002–2008
Desaint S, Hartmann A, Parekh NR, Fournier J (2000) Genetic diversity of carbofuran-degrading soil bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 34:173–180
Ehrenreich P, Behrends A, Harder J, Widdel F (2000) Anaerobic oxidation of alkanes by newly isolated denitrifying bacteria. Arch Microbiol 173:58–64
Field JA, Sierra-Alvarez R (2008) Microbial degradation of chlorinated phenols. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 7:211–241
Field EK, D’Imperio S, Miller AR, VanEngelen MR, Gerlach R, Lee BD, Apel WA, Peyton BM (2010) Application of molecular techniques to elucidate the influence of cellulosic waste on the bacterial community structure at a simulated low-level-radioactive-waste site. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:3106–3115
Friedrich U, Prior K, Altendorf K, Lipski A (2002) High bacterial diversity of a waste gas-degrading community in an industrial biofilter as shown by a 16S rDNA clone library. Environ Microbiol 4:721–734
Futamata H, Nagano Y, Watanabe K, Hiraishi A (2005) Unique kinetic properties of phenol-degrading variovorax strains responsible for efficient trichloroethylene degradation in a chemostat enrichment culture. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:904–911
Gu H, Zhang X, Li Z, Lei L (2007) Studies on treatment of chlorophenol-containing wastewater by microbial fuel cell. Chin Sci Bull 52:3448–3451
Hong X, Zhang X, Liu B, Mao Y, Liu Y, Zhao L (2010) Structural differentiation of bacterial communities in indole-degrading bioreactors under denitrifying and sulfate-reducing conditions. Res Microbiol 161:687–693
Huang LP, Cheng SA, Chen GH (2011a) Bioelectrochemical systems for efficient recalcitrant wastes treatment. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 86:481–491
Huang LP, Regan JM, Quan X (2011b) Electron transfer mechanisms, new applications, and performance of biocathode microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 102:316–323
Huang LP, Chai XL, Quan X, Logan BE, Chen GH (2012) Reductive dechlorination and mineralization of pentachlorophenol in biocathode microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol 111:167–174
Huang LP, Wang Q, Quan X, Liu YX, Chen GH (2013) Bioanodes/biocathodes formed in bioelectrochemical cells at optimal potentials enhance subsequent pentachlorophenol degradation and power generation from microbial fuel cells. Bioelectrochemistry 94:13–22
Ishii S, Suzuki S, Norden-Krichmar TM, Wanger G, Nealson KH, Sekiguchi Y, Gorby YA, Bretchger O (2012) Functionally stable and phylogenetically diverse microbial enrichments from microbial fuel cells during wastewater treatment. PLoS One 7:e30495
Jeremiasse AW, Hamelers HVM, Croese E, Buisman CJN (2012) Acetate enhances startup of a H2-producing microbial biocathode. Biotechnol Bioeng 109:657–664
Juteau P, Larocque R, Rho D, LeDuy A (1999) Analysis of the relative abundance of different types of bacteria capable of toluene degradation in a compost biofilter. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:863–868
Karn SK, Balda S (2013) Bioremediation 2,4,6-trichlorophenol (2,4,6-TCP) by Shigella sp. S2 isolated from industrial dumpsite. Bioremediat J 17:71–78
Karn SK, Reddy MS (2012) Degradation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol by bacteria isolated from secondary sludge of a pulp and paper mill. J Gen Appl Microbiol 58:413–420
Kiely PD, Call DF, Yates MD, Regan JM, Logan BE (2010) Anodic biofilms in microbial fuel cells harbor low numbers of higher-power-producing bacteria than abundant genera. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88:371–380
Kim D, Kim YS, Kim SK, Kim SW, Zylstra GJ, Kim YM, Kim E (2002) Monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation by Rhodococcus sp. strain DK17. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3270–3278
Kim GT, Webster G, Wimpenny JW, Kim BH, Kim HJ, Weightman AJ (2006) Bacterial community structure, compartmentalization and activity in a microbial fuel cell. J Appl Microbiol 101:698–710
Kraigher B, Kosjek T, Heath E, Kompare B, Mandic-Mulec I (2008) Influence of pharmaceutical residues on the structure of activated sludge bacterial communities in wastewater treatment bioreactors. Water Res 42:4578–4588
Krumins V, Park JW, Son EK, Rodenburg LA, Kerkhof LJ, Häggblom MM, Fennell DE (2009) PCB dechlorination enhancement in Anacostia river sediment microcosms. Water Res 43:4549–4558
Li WW, Yu HQ (2011) From wastewater to bioenergy and biochemicals via two-stage bioconversion processes: a future paradigm. Biotechnol Adv 29:972–982
Li D, Yang M, Hu J, Zhang J, Liu R, Gu X, Zhang Y, Wang Z (2009) Antibiotic-resistance profile in environmental bacteria isolated from penicillin production wastewater treatment plant and the receiving river. Environ Microbiol 11:1506–1517
Li Z, Yang S, Inoue Y, Yoshida N, Katayama A (2010) Complete anaerobic mineralization of pentachlorophenol (PCP) under continuous flow conditions by sequential combination of PCP-dechlorinating and phenol-degrading consortia. Biotechnol Bioeng 107:775–785
Logan BE (2009) Exoelectrogenic bacteria that power microbial fuel cells. Nat Rev Microbiol 7:375–381
Logan BE (2012) Essential data and techniques for conducting microbial fuel cell and other types of bioelectrochemical system experiments. ChemSusChem 15:988–994
Logan BE, Rabaey K (2012) Conversion of wastes into bioelectricity and chemicals by using microbial electrochemical technologies. Science 337:686–690
May HD, Miller GS, Kjellerup BV, Sowers KR (2008) Dehalorespiration with polychlorinated biphenyls by an anaerobic ultramicrobacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2089–2094
Milia S, Cappai G, De Gioannis G, Carucci A (2011) Effects of the cometabolite/growth substrate ratio on the aerobic degradation of 4-monochlorophenol. Water Sci Technol 63:311–317
Mun CH, Ng WJ, He J (2008) Acidogenic sequencing batch reactor start-up procedures for induction of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol dechlorination. Water Res 42:1675–1683
Murcia MD, Gomez M, Gomez E, Gomez JL, Sinada FA, Christofi N (2012) Testing a Pseudomonas putida strain for 4-chlorophenol degradation in the presence of glucose. Desalin Water Treat 40:33–37
Papazi A, Kotzabasis K (2013) “Rational” management of dichlorophenols biodegradation by the microalga Scenedesmus obliquus. PLoS One 8:e61682
Park JW, Krumins V, Kjellerup BV, Fennell DE, Rodenburg LA, Sowers KR, Kerkhof LJ, Häggblom MM (2011) The effect of co-substrate activation on indigenous and bioaugmented PCB dechlorinating bacterial communities in sediment microcosms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:2005–2017
Perkins SD, Scalfone NB, Angenent LT (2011) Comparative 16S rRNA gene surveys of granular sludge from three upflow anaerobic bioreactors treating purified terephthalic acid (PTA) wastewater. Water Sci Technol 64:1406–1412
Podmirseg SM, Schoen MA, Murthy S, Insam H, Wett B (2010) Quantitative and qualitative effects of bioaugmentation on ammonia oxidisers at a two-step WWTP. Water Sci Technol 61:1003–1009
Puyol D, Mohedano AF, Rodriguez JJ, Sanz JL (2011) Effect of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol on the microbial activity of adapted anaerobic granular sludge bioaugmented with Desulfitobacterium strains. New Biotechnol 29:79–89
Radjenovic J, Flexer V, Donose BC, Sedlak DL, Keller J (2013) Removal of the X-ray contrast media diatrizoate by electrochemical reduction and oxidation. Environ Sci Technol 47(23):13686–13694
Shehab N, Li D, Amy GL, Logan BE, Saikaly PE (2013) Characterization of bacterial and archaeal communities in air-cathode microbial fuel cells, open circuit and sealed-off reactors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:9885–9895
Singleton DR, Sangaiah R, Gold A, Ball LM, Aitken MD (2006) Identification and quantification of uncultivated Proteobacteria associated with pyrene degradation in a bioreactor treating PAH-contaminated soil. Environ Microbiol 8:1736–1745
Sponza DT, Ulukoy AE (2005) Treatment of 2,4-dichlorophenol (DCP) in a sequential anaerobic (upflow anaerobic sludge blanket) aerobic (completely stirred tank) reactor system. Process Biochem 40:3419–3428
Strycharz SM, Gannon SM, Boles AR, Nevin KP, Franks AE, Lovley DR (2010) Anaeromyxobacter dehalogens interacts with a poised graphite electrode for reductive dechlorination of 2-chlorophenol. Environ Microbiol Rep 2:289–294
Stuart SL, Woods SL, Lemmon TL, Ingle JD (1999) The effect of redox potential changes on reductive dechlorination of pentachlorophenol and the degradation of acetate by a mixed, methanogenic culture. Biotechnol Bioeng 63:69–78
Sun M, Yan F, Zhang R, Reible D, Lowry G, Gregory K (2010) Redox control and hydrogen production in sediment caps using carbon cloth electrodes. Environ Sci Technol 44:8209–8215
Sun YM, Wei JC, Liang P, Huang X (2012) Microbial community analysis in biocathode microbial fuel cells packed with different materials. AMB Express 2:21
Tandukar M, Huber SJ, Onodera T, Pavlostathis SG (2009) Biological chromium (VI) reduction in the cathode of a microbial fuel cell. Environ Sci Technol 43:8159–8165
Ter Heijne A, Liu F, Van der Weijden R, Weijma J, Buisman CJN, Hamelers HVM (2010) Copper recovery combined with electricity production in a microbial fuel cell. Environ Sci Technol 44:4376–4381
Thavamani P, Malik S, Beer M, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2012) Microbial activity and diversity in long-term mixed contaminated soils with respect to polyaromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals. J Environ Manage 99:10–17
Tyagi M, da Fonseca MMR, de Carvalho CCCR (2011) Bioaugmentation and biostimulation strategies to improve the effectiveness of bioremediation processes. Biodegradation 22:231–241
Udikovic-Kolic N, Devers-Lamrani M, Petric I, Hrsak D, Martin-Laurent F (2011) Evidence for taxonomic and functional drift of an atrazine-degrading culture in response to high atrazine input. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:1547–1554
van der Zaan BM, Saia FT, Stams AJM, Plugge CM, de Vos WM, Smidt H, Langenhoff AAM, Gerritse J (2012) Anaerobic benzene degradation under denitrifying conditions: peptococcaceae as dominant benzene degraders and evidence for a syntrophic process. Environ Microbiol 14:1171–1181
Verhagen P, De Gelder L, Hoefman S, De Vos P, Boon N (2011) Planktonic versus biofilm catabolic communities: importance of the biofilm for species selection and pesticide degradation. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:4728–4735
Wen Q, Yang T, Wang S, Chen Y, Cong L, Qu Y (2013) Dechlorination of 4-chlorophenol to phenol in bioelectrochemical systems. J Hazard Mater 244–245:743–749
Winfield J, Ieropoulos I, Rossiter J, Greenman J, Patton D (2013) Biodegradation and proton exchange using natural rubber in microbial fuel cells. Biodegradation. doi:10.1007/s10532-013-9621-x
Wrighton KC, Virdis B, Clauwaert P, Read ST, Daly RA, Boon N, Piceno Y, Andersen GL, Coates JD, Rabaey K (2010) Bacterial community structure corresponds to performance during cathodic nitrate reduction. ISME J 4:1443–1455
Xia X, Sun Y, Liang P, Huang X (2012) Long-term effect of set potential on biocathodes in microbial fuel cells: electrochemical and phylogenetic characterization. Bioresour Technol 120:26–33
Xia X, Tokash JC, Zhang F, Liang P, Huang X, Logan BE (2013) Oxygen-reducing biocathodes operating with passive oxygen transfer in microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 47:2085–2091
Yoshie S, Makino H, Hirosawa H, Shirotani K, Tsuneda S, Hirata A (2006) Molecular analysis of halophilic bacterial community for high-rate denitrification of saline industrial wastewater. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:182–189
Yuan SJ, He H, Sheng GP, Chen JJ, Tong ZH, Cheng YY, Li WW, Lin ZQ, Zhang F, Yu HQ (2013) A photometric high-throughput method for identification of electrochemically active bacteria using a WO3 nanocluster probe. Sci Rep 3:1315
Zhu X, Tokash JC, Hong Y, Logan BE (2013) Controlling the occurrence of power overshoot by adapting microbial fuel cells to high anode potentials. Bioelectrochemistry 90:30–35
Ziemer CJ, Kerr BJ, Trabue SL, Stein H, Stahl DA, Davidson SK (2009) Dietary protein and cellulose effects on chemical and microbial characteristics of swine feces and stored manure. J Environ Quality 38:2138–2146
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21077017 and 51178077) and Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education “SRFDP” (No. 20120041110026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, L., Shi, Y., Wang, N. et al. Anaerobic/aerobic conditions and biostimulation for enhanced chlorophenols degradation in biocathode microbial fuel cells. Biodegradation 25, 615–632 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-014-9686-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-014-9686-1