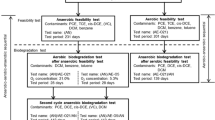
Abstract
Thermally-enhanced bioremediation is a promising treatment approach for petroleum contamination; however, studies examining temperature effects on anaerobic biodegradation in zones containing light non-aqueous phase liquids (LNAPLs) are lacking. Herein, laboratory microcosm studies were conducted for a former refinery to evaluate LNAPL transformation, sulfate reduction, and methane generation over a one-year period for temperatures ranging from 4 to 40 °C, and microbial community shifts were characterized. Temperatures of 22 and 30 °C significantly increased total biogas generation compared to lower (4 and 9 °C) and higher temperatures (35 and 40 °C; p < 0.1). Additionally, at 22 and 30 °C methane generation commenced ~6 months earlier than for 35 and 40 °C. Statistically significant biodegradation of benzene, toluene and xylenes was observed at elevated temperatures but not at lower temperatures (p < 0.1). Additionally, a novel differential chromatogram approach was developed to overcome challenges associated with resolving losses in complex mixtures of hydrocarbons, and application of this method revealed greater losses of hydrocarbons at 22 and 30 °C as compared to lower and higher temperatures. Finally, molecular biology assays revealed that the composition and activity of microbial communities shifted in a temperature-dependent manner. Collectively, results demonstrated that anaerobic biodegradation processes can be enhanced by increasing the temperature of LNAPL-containing soils, but biodegradation does not simply increase as temperature increases likely due to a lack of microorganisms that thrive at temperatures well above the historical high temperatures for a site. Rather, optimal degradation is achieved by holding soils at the high end of, or slightly higher than, their natural range.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- BTEX:
-
Benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and the xylenes
- DRO:
-
Diesel range organics
- GRO:
-
Gasoline range organics
- LNAPL:
-
Light non-aqueous phase liquid
References
Aburto A, Peimbert M (2011) Degradation of a benzene-toluene mixture by hydrocarbon-adapted bacterial communities. Ann Microbiol 61(3):553–562. doi:10.1007/s13213-010-0173-6
Akhbari D (2013) Thermal aspects of sustainable thermally enhanced LNAPL attenuation (STELA). M.S. thesis, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO
Alawi M, Lipski A, Sanders T, Eva Maria P, Spieck E (2007) Cultivation of a novel cold-adapted nitrite oxidizing betaproteobacterium from the Siberian Arctic. ISME J 1(3):256–264. doi:10.1038/ismej.2007.34
Balk M, van Gelder T, Weelink SA, Stams AJA (2008) (Per)chlorate reduction by the thermophilic bacterium Moorella perchloratireducens sp. nov., isolated from underground gas storage. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:403–409. doi:10.1128/aem.01743-07
Boonchayaanant B, Kitanidis PK, Criddle CS (2008) Growth and cometabolic reduction kinetics of a uranium- and sulfate-reducing Desulfovibrio Clostridia mixed culture: temperature effects. Biotechnol Bioeng 99(5):1107–1119. doi:10.1002/bit.21670
Bossert I, Bartha R (1984) The fate of petroleum in soil ecosystems. In: Atlas RM (ed) Petroleum microbiology. MacMillan Publishing Co, New York, pp 434–476
Clark MM (1996) Arrhenius’ law and the effect of temperature on reaction rate, transport modeling for environmental engineers and scientists. Wiley, New York
Clarke KR (1993) Nonparametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust J Ecol 18(1):117–143
Coulon F, Pelletier E, Gourhant L, Delille D (2005) Effects of nutrient and temperature on degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in contaminated sub-Antarctic soil. Chemosphere 58(10):1439–1448. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.10.007
Coulon F, McKew BA, Osborn AM, McGenity TJ, Timmis KN (2007) Effects of temperature and biostimulation on oil-degrading microbial communities in temperate estuarine waters. Environ Microbiol 9(1):177–186. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.01126.x
Cross KM, Biggar KW, Semple K, Foght J, Guigard SE, Armstrong JE (2006) Intrinsic bioremediation of diesel-contaminated cold groundwater in bedrock. J Environ Eng Sci 5(1):13–27. doi:10.1139/s05-014
Cupples AM (2011) The use of nucleic acid based stable isotope probing to identify the microorganisms responsible for anaerobic benzene and toluene biodegradation. J Microbiol Methods 85(2):83–91. doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2011.02.011
de Carcer DA, Phuc TH, Jang JK, Chang IS (2011) Microbial community differences between propionate-fed microbial fuel cell systems under open and closed circuit conditions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89(3):605–612. doi:10.1007/s00253-010-2903-x
Deeb RA, Alvarez-Cohen L (1999) Temperature effects and substrate interactions during the aerobic biotransformation of BTEX mixtures by toluene-enriched consortia and Rhodococcus rhodochrous. Biotechnol Bioeng 62(5):526–536
Edwards EA, Grbicgalic D (1992) Complete mineralization of benzene by aquifer microorganisms under strickly anaerobic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 58(8):2663–2666
Edwards EA, Grbicgalic D (1994) Anaerobic degradation of toluene and o-xylene by a methanogenic consortium. Appl Environ Microbiol 60(1):313–322
Edwards EA, Wills LE, Reinhard M, Grbicgalic D (1992) Anaerobic degradation of toluene and xylene by aquifer microorganisms under sulfate-reducing conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 58(3):794–800
Eggen T, Majcherczyk A (2006) Effects of zero-valent iron (Fe-0) and temperature on the transformation of DDT and its metabolites in lake sediment. Chemosphere 62(7):1116–1125. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.05.044
Ferguson SH, Franzmann PD, Snape I, Revill AT, Trefry MG, Zappia LR (2003) Effects of temperature on mineralisation of petroleum in contaminated Antarctic terrestrial sediments. Chemosphere 52(6):975–987. doi:10.1016/s0045-6535(03)00265-0
Filler DA, Lindstrom JE, Braddock JF, Johnson RA, Nickalaski R (2001) Integral biopile components for successful bioremediation in the Arctic. Cold Regions Sci Technol 32(2–3):143–156. doi:10.1016/s0165-232x(01)00020-9
Galagan JE, Nusbaum C, Roy A, Endrizzi MG, Macdonald P, FitzHugh W, Calvo S, Engels R, Smirnov S, Atnoor D, Brown A, Allen N, Naylor J, Stange-Thomann N, DeArellano K, Johnson R, Linton L, McEwan P, McKernan K, Talamas J, Tirrell A, Ye WJ, Zimmer A, Barber RD, Cann I, Graham DE, Grahame DA, Guss AM, Hedderich R, Ingram-Smith C, Kuettner HC, Krzycki JA, Leigh JA, Li WX, Liu JF, Mukhopadhyay B, Reeve JN, Smith K, Springer TA, Umayam LA, White O, White RH, de Macario EC, Ferry JG, Jarrell KF, Jing H, Macario AJL, Paulsen I, Pritchett M, Sowers KR, Swanson RV, Zinder SH, Lander E, Metcalf WW, Birren B (2002) The genome of M. acetivorans reveals extensive metabolic and physiological diversity. Genome Res 12(4):532–542. doi:10.1101/gr.223902
Golby S, Ceri H, Gieg LM, Chatterjee I, Marques LLR, Turner RJ (2012) Evaluation of microbial biofilm communities from an Alberta oil sands tailings pond. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 79(1):240–250. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01212.x
Higashioka Y, Kojima H, Fukui M (2011) Temperature-dependent differences in community structure of bacteria involved in degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons under sulfate-reducing conditions. J Appl Microbiol 110(1):314–322. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2010.04886.x
Hiraishi A, Hoshino Y, Satoh T (1991) Rhodoferax fermentans gen. nov., sp. nov., a phototrophic purple nonsulfur bacterium previously referred to as the “Rhodocyclus gelatinosus-like” group. Arch Microbiol 155(4):330–336
Horel A, Schiewer S (2011) Influence of constant and fluctuating temperature on biodegradation rates of fish biodiesel blends contaminating Alaskan sand. Chemosphere 83(5):652–660. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.02.027
Hurek T, Wagner B, ReinholdHurek B (1997) Identification of N-2-fixing plant- and fungus-associated Azoarcus species by PCR-based genomic fingerprints. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(11):4331–4339
Hutchins SR, Sewell GW, Kovacs DA, Smith GA (1991) Biodegradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by aquifer microorganisms under denitrifying conditions. Environ Sci Technol 25(1):68–76
Iqbal J, Metosh-Dickey C, Portier RJ (2007) Temperature effects on bioremediation of PAHs and PCP contaminated South Louisiana soils: a laboratory mesocosm study. J Soils Sediments 7(3):153–158. doi:10.1065/jss2007.01.204
Irianni Renno M (2013) Biogeochemical characterization of a LNAPL body in support of STELA. M.S. thesis, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO
Johnson P, Lundegard P, Liu Z (2006) Source zone natural attenuations at petroleum hydrocarbon spill sites-I: site-specific assessment approach. Groundwater Monit Remediat 26(4):82–92
JRB (1984) Summary report: remedial response at hazardous waste sites, prepared for municipal environment research laboratory. EPA report no. 625/6-82-006
Kettunen RH, Rintala JA (1997) The effect of low temperature (5–29 °C) and adaptation on the methanogenic activity of biomass. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 48(4):570–576
Kleikemper J, Pombo SA, Schroth MH, Sigler WV, Pesaro M, Zeyer J (2005) Activity and diversity of methanogens in a petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated aquifer. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(1):149–158. doi:10.1016/aem.71.1.149-158.2005
Ku HH (1966) Notes on use of propagation of error formulas. J Res Natl Bur Stand 70:263–273
Li W, Wang LY, Duan RY, Liu JF, Gu JD, Mu BZ (2012) Microbial community characteristics of petroleum reservoir production water amended with n-alkanes and incubated under nitrate-, sulfate-reducing and methanogenic conditions. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 69:87–96. doi:10.1016/j.ibiod.2012.01.005
Lin CY, Noike T, Sato K, Matsumoto J (1987) Temperature characteristics of the methanogenesis process in anaerobic digestion. Water Sci Technol 19(1–2):299–310
Liu RY, Zhang Y, Ding R, Li D, Gao YX, Yang M (2009) Comparison of archaeal and bacterial community structures in heavily oil-contaminated and pristine soils. J Biosci Bioeng 108(5):400–407. doi:10.1016/j.jbiosc.2009.05.010
Lokshina LY, Vavilin VA (1999) Kinetic analysis of the key stages of low temperature methanogenesis. Ecol Model 117(2–3):285–303. doi:10.1016/s0304-3800(99)00008-3
Lovley DR (1997) Potential for anaerobic bioremediation of BTEX in petroleum-contaminated aquifers. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 18(2–3):75–81
Madigan MT, Jung DO, Woese CR, Achenbach LA (2000) Rhodoferax antarcticus sp. nov., a moderately psychrophilic purple nonsulfur bacterium isolated from an Antarctic microbial mat. Arch Microbiol 173(4):269–277. doi:10.1007/s002030000140
Martin F, Torelli S, Le Paslier D, Barbance A, Martin-Laurent F, Bru D, Geremia R, Blake G, Jouanneau Y (2012) Betaproteobacteria dominance and diversity shifts in the bacterial community of a PAH-contaminated soil exposed to phenanthrene. Environ Pollut 162:345–353. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2011.11.032
Mbadinga SM, Wang LY, Zhou L, Liu JF, Gu JD, Mu BZ (2011) Microbial communities involved in anaerobic degradation of alkanes. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 65(1):1–13. doi:10.1016/j.ibiod.2010.11.009
Mohn WW, Stewart GR (2000) Limiting factors for hydrocarbon biodegradation at low temperature in Arctic soils. Soil Biol Biochem 32(8–9):1161–1172. doi:10.1016/s0038-0717(00)00032-8
Mulkinsphillips GJ, Stewart JE (1974) Effect of environmental parameters on bacterial degradation of bunker C oil, crude oils, and hydrocarbons. Appl Microbiol 28(6):915–922
Penner TJ, Foght JM (2010) Mature fine tailings from oil sands processing harbour diverse methanogenic communities. Can J Microbiol 56(6):459–470. doi:10.1139/w10-029
Perfumo A, Banat IM, Marchant R, Vezzulli L (2007) Thermally enhanced approaches for bioremediation of hydrocarbon-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 66(1):179–184. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.05.006
Rastegarzadeh L, Nelson Y (2006) Biotreatment of synthetic drill-cutting waste in soil. In: Proceedings of the fifth international conference on remediation of chlorinated and recalcitrant compounds, Monterey, CA, May 2006
Reimer KJ, Colden M, Francis P, Mauchan JJ, Mohn WW, Poland JS (2003) Cold climate bioremediation: a comparison of various approaches. In: Proceedings of the third biennial workshop on assessment and remediation of contaminated sites in arctic and cold climates, Edmonton, AB, pp 290–298
Reinhold-Hurek B, Hurek T (2000) Reassessment of the taxonomic structure of the diazotrophic genus Azoarcus sensu lato and description of three new genera and new species, Azovibrio restrictus gen. nov., sp. nov., Azospira oryzae gen. nov., sp. nov. and Azonexus fungiphilus gen. nov., sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:649–659
SAS Institute Inc. (2011) SAS 9.3 help and documentation. SAS Institute Inc., Cary
Speight JG, Arjoon KK (2012) Bioremediation of petroleum and petroleum products. Wiley, Hoboken
Sun WM, Cupples AM (2012) Diversity of five anaerobic toluene-degrading microbial communities investigated using stable isotope probing. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(4):972–980. doi:10.1128/aem.06770-11
USEPA (2013) Frequent questions regarding petroleum brownfields. http://www.epa.gov/oust/petroleumbrownfields/pbfaqs.htm. Accessed 14 May 2013
Valo R, Apajalahti J, Salkinojasalonen M (1985) Studies of the physiology of microbial degradation of pentachlorophenol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 21(5):313–319
Walworth J, Woolard C, Acomb L, Chaobal V, Wallace M (1999) Nutrient and temperature interactions in bioremediation of petroleum-contaminated cryic soil. In: Allerman B (ed) In situ bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon and other organic compounds. Battelle Pr, pp 506–510
Winderl C, Penning H, von Netzer F, Meckenstock RU, Lueders T (2010) DNA-SIP identifies sulfate-reducing Clostridia as important toluene degraders in tar-oil-contaminated aquifer sediment. ISME J 4(10):1314–1325. doi:10.1038/ismej.2010.54
Wolcott RD, Gontcharova V, Sun Y, Dowd SE (2009) Evaluation of the bacterial diversity among and within individual venous leg ulcers using bacterial tag-encoded FLX and titanium amplicon pyrosequencing and metagenomic approaches. BMC Microbiol 9:226
Wu QZ, Bedard DL, Wiegel J (1997) Temperature determines the pattern of anaerobic microbial dechlorination of Aroclor 1260 primed by 2,3,4,6-tetrachlorobiphenylin Woods Pond sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(12):4818–4825
Xiao KK, Guo CH, Zhou Y, Maspolim Y, Wany JY, Ng WJ (2013) Acetic acid inhibition on methanogens in a two-phase anaerobic process. Biochem Eng J 75:1–7
Yadav BK, Shrestha SR, Hassanizadeh SM (2012) Biodegradation of toluene under seasonal and diurnal fluctuations of soil-water temperature. Water Air Soil Pollut 223(7):3579–3588. doi:10.1007/s11270-011-1052-x
Zhuang K, Izallalen M, Mouser P, Richter H, Risso C, Mahadevan R, Lovley DR (2011) Genome-scale dynamic modeling of the competition between Rhodoferax and Geobacter in anoxic subsurface environments. ISME J 5(2):305–316. doi:10.1038/ismej.2010.117
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Chevron and the University Consortium for Field-Focused Groundwater Contamination Research. Additionally, support during field sampling activities was provided by Trihydro Corporation. The authors would like to thank Julio Zimbron for providing assistance with analytical methods, Emilie Lefèvre for providing assistance with microbial methods, Gary Dick for support with experimental design and set up, and Phillip Chapman for guidance with statistical analysis and for running ANOVA tests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeman, N.R., Irianni Renno, M., Olson, M.R. et al. Temperature impacts on anaerobic biotransformation of LNAPL and concurrent shifts in microbial community structure. Biodegradation 25, 569–585 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-014-9682-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-014-9682-5