Abstract
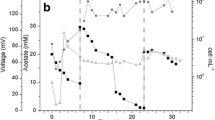
We report the electrochemical characterization and microbial community analysis of closed circuit microbial fuel cells (CC-MFCs) and open circuit (OC) cells continuously fed with propionate as substrate. Differences in power output between MFCs correlated with their polarization behavior, which is related to the maturation of the anodophilic communities. The microbial communities residing in the biofilm growing on the electrode, biofouled cation-exchange membrane and anodic chamber liquor of OC-and CC-MFCs were characterized by restriction fragment length polymorphism screening of 16S rRNA gene clone libraries. The results show that the CC-MFC anode was enriched in several microorganisms related to known electrochemically active and dissimilatory Fe(III) reducing bacteria, mostly from the Geobacter spp., to the detriment of Bacteroidetes abundant in the OC-MFC anode. The results also evidenced the lack of a specific pelagic community in the liquor sample. The biofilm growing on the cation-exchange membrane of the CC-MFC was found to be composed of a low-diversity community dominated by two microaerophilic species of the Achromobacter and Azovibrio genus.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aelterman P, Rabaey K, Pham HT, Boon N, Verstraete W (2006) Continuous electricity generation at high voltages and currents using stacked microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 71(1):63–66
Aldrovandi A, Marsili E, Stante L, Paganin P, Tabacchioni S, Giordano A (2009) Sustainable power production in a membrane-less and mediator-less synthetic wastewater microbial fuel cell. Bioresour Technol 100(13):3252–3260
Bond DR, Holmes DE, Tender LM, Lovley DR (2002) Electrode-reducing microorganisms that harvest energy from marine sediments. Science 295(5554):483–485
Brown DG, Komlos J, Jaffe PR (2005) Simultaneous utilization of acetate and hydrogen by Geobacter sulfurreducens and implications for use of hydrogen as an indicator of redox conditions. Environ Sci Tech 39(9):3069–3076
Chang IS, Moon H, Bretschger O, Jang JK, Park HI, Nealson KH, Kim BH (2006) Electrochemically active bacteria (EAB) and mediator-less microbial fuel cells. J Microbiol Biotechnol 16(2):163–177
Cheng S, Liu H, Logan BE (2006) Increased power generation in a continuous flow MFC with advective flow through the porous anode and reduced electrode spacing. Environ Sci Technol 40(7):2426–2432
Cole JR, Chai B, Farris RJ, Wang Q, Kulam SA, McGarrell DM, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2005) The ribosomal database project (RDP-II): Sequences and tools for high-throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 33:D294–D296
Diaz EE, Stams AJM, Amils R, Sanz JL (2006) Phenotypic properties and microbial diversity of methanogenic granules from a full-scale upflow anaerobic sludge bed reactor treating brewery wastewater. Appl Environ Microbol 72(7):4942–4949
Ghangrekar MM, Shinde VB (2008) Simultaneous sewage treatment and electricity generation in membrane-less microbial fuel cell. Water Sci Technol 58(1):37–43
Gregory KB, Bond DR, Lovley DR (2004) Graphite electrodes as electron donors for anaerobic respiration. Environ Microbiol 6(6):596–604
Hall TA (1999) Bioedit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for windows 95/98/nt. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Holmes DE, Bond DR, O’Neil RA, Reimers CE, Tender LR, Lovley DR (2004) Microbial communities associated with electrodes harvesting electricity from a variety of aquatic sediments. Microb Ecol 48(2):178–190
Holzman DC (2005) Microbe power! Environ Health Perspect 113(11):A754–A757
Huber T, Faulkner G, Hugenholtz P (2004) Bellerophon: a program to detect chimeric sequences in multiple sequence alignments. Bioinformatics 20(14):2317–2319
Jang JK, Chang IS, Hwang HW, Choo Y, Lee J, Cho KS, Kim BH, Nealson KH (2010) Electricity generation coupled to oxidation of propionate in a microbial fuel cell. Biotechnol Lett 32(1):79–85
Jung S, Regan J (2007) Comparison of anode bacterial communities and performance in microbial fuel cells with different electron donors. Appl Microbiol Biot 77(2):393–402
Kim BH, Park HS, Kim HJ, Kim GT, Chang IS, Lee J, Phung NT (2004) Enrichment of microbial community generating electricity using a fuel cell type electrochemical cell. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63(6):672–681
Kim JR, Min B, Logan BE (2005) Evaluation of procedures to acclimate a microbial fuel cell for electricity production. Appl Microbiol Biot 68(1):23–30
Kim BH, Chang IS, Gadd GM (2007) Challenges in microbial fuel cell development and operation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76(3):485–494
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16(2):111–120
Koch M, Dolfing J, Wuhrmann K, Zehnder AJB (1983) Pathways of propionate degradation by enriched methanogenic cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 45(4):1411–1414
Kostka JE, Dalton DD, Skelton H, Dollhopf S, Stucki JW (2002) Growth of iron(III)-reducing bacteria on clay minerals as the sole electron acceptor and comparison of growth yields on a variety of oxidized iron forms. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(12):6256–6262
Lee J, Phung NT, Chang IS, Kim BH, Sung HC (2003) Use of acetate for enrichment of electrochemically active microorganisms and their 16S rDNA analyses. FEMS Microbiol Lett 223(2):185–191
Lin B, Hyacinthe C, Bonneville S, Braster M, Van Cappellen P, Roling WFM (2007) Phylogenetic and physiological diversity of dissimilatory ferric iron reducers in sediments of the polluted Scheldt estuary, northwest Europe. Environ Microbiol 9(8):1956–1968
Liu H, Ramnarayanan R, Logan BE (2004) Production of electricity during wastewater treatment using a single chamber microbial fuel cell. Environ Sci Technol 38(7):2281–2285
Lovley DR, Giovannoni SJ, White DC, Champine JE, Phillips EJ, Gorby YA, Goodwin S (1993) Geobacter metallireducens gen. nov. sp. nov., a microorganism capable of coupling the complete oxidation of organic compounds to the reduction of iron and other metals. Arch Microbiol 159:336–344
Marsili E, Rollefson JB, Baron DB, Hozalski RM, Bond DR (2008) Microbial biofilm voltammetry: direct electrochemical characterization of catalytic electrode-attached biofilms. App Environ Microbiol 74(23):7329–7337
Min B, Kim J, Oh S, Regan JM, Logan BE (2005) Electricity generation from swine wastewater using microbial fuel cells. Water Res 39(20):4961–4968
Moon H, Chang IS, Jang JK, Kim BH (2005) Residence time distribution in microbial fuel cell and its influence on cod removal with electricity generation. Biochem Eng J 27(1):59–65
O’Hayre R, Colella W, Prinz FB (2006) Fuel cell fundamentals. Wiley, New York
Oh SE, Logan BE (2005) Hydrogen and electricity production from a food processing wastewater using fermentation and microbial fuel cell technologies. Water Res 39(19):4673–4682
Paradis E, Claude J, Strimmer K (2004) Ape: analyses of phylogenetics and evolution in R language. Bioinformatics 20(2):289–290
Picioreanu C, Katuri KP, Head IM, van Loosdrecht MCM, Scott K (2008) Mathematical model for microbial fuel cells with anodic biofilms and anaerobic digestion. Water Sci Technol 57(7):965–971
Rabaey K, Verstraete W (2005) Microbial fuel cells: novel biotechnology for energy generation. Trends Biotechnol 23(6):291–298
Rabaey K, Lissens G, Siciliano SD, Verstraete W (2003) A microbial fuel cell capable of converting glucose to electricity at high rate and efficiency. Biotechnol Lett 25(18):1531–1535
Ramasamy RP, Ren ZY, Mench MM, Regan JM (2008) Impact of initial biofilm growth on the anode impedance of microbial fuel cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 101(1):101–108
Roller SD, Bennetto HP, Delaney GM, Mason JR, Stirling JL, Thurston CF (1984) Electron-transfer coupling in microbial fuel cells: 1. Comparison of redox-mediator reduction rates and respiratory rates of bacteria. J Chem Technol Biot 34(1):3–12
Schink B (1997) Energetics of syntrophic cooperation in methanogenic degradation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61(2):262–280
Shigematsu T, Era S, Mizuno Y, Ninomiya K, Kamegawa Y, Morimura S, Kida K (2006) Microbial community of a mesophilic propionate-degrading methanogenic consortium in chemostat cultivation analyzed based on 16S rRNA and acetate kinase genes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72(2):401–415
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173(2):697–703
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from Doyak (previously, the NRL Program, R0A-2008-000-20088-0) funded by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of the Korean government (MEST), and the United Nations University and Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology Joint Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Cárcer, D.A., Ha, P.T., Jang, J.K. et al. Microbial community differences between propionate-fed microbial fuel cell systems under open and closed circuit conditions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89, 605–612 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2903-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2903-x