Abstract
Objectives
This work aimed to construct a versatile, effective, and food-grade Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation (ATMT) system for recombinant expression in the filamentous fungus Penicillium rubens (also known as Pencillium chrysogenum).
Results
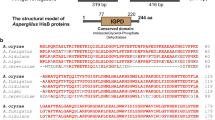
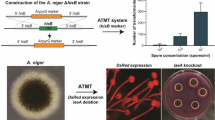
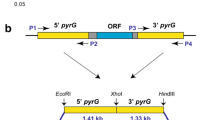
In this study, the wild-type P. chrysogenum VTCC 31172 strain was re-classified as P. rubens by a multilocus sequencing analysis. Further, the pyrG gene required for uridine/uracil biosynthesis was successfully deleted in the VTCC 31172 strain by homologous recombination to generate a stable uridine/uracil auxotrophic mutant (ΔpyrG). The growth of the P. rubens ΔpyrG strain could be restored by uridine/uracil supplementation, and a new ATMT system based on the uridine/uracil auxotrophic mechanism was established for this strain. The optimal ATMT efficiency could reach 1750 transformants for 106 spores (equivalent to 0.18%). In addition, supplementation of uridine/uracil at the concentrations of 0.005–0.02% during the co-cultivation process significantly promoted transformation efficiency. Especially, we demonstrated that the pyrG marker and the amyB promoter from the koji mold Aspergillus oryzae were fully functional in P. rubens ΔpyrG. Expression of the DsRed reporter gene under the regulation of the A. oryzae amyB promoter lighted up the mycelium of P. rubens with a robust red signal under fluorescence microscopy. Furthermore, genomic integration of multiple copies of the Aspergillus fumigatus phyA gene under the control of the amyB promoter significantly enhanced phytase activity in P. rubens.
Conclusions
The ATMT system developed in our work provides a safe genetic platform for producing recombinant products in P. rubens without using drug resistance markers.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Arnau J, Yaver D, Hjort CM (2020) Strategies and challenges for the development of industrial enzymes using fungal cell factories. In: Nevalainen H (ed) Grand challenges in fungal biotechnology. Springer Nature, pp 179–210
Binh CT, Thai HD, Ha BTV, Tran VT (2021) Establishment of a new and efficient Agrobacterium-mediated transformation system in the nematicidal fungus Purpureocillium lilacinum. Microbiol Res 249:126773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2021.126773
Campuzano V, del Valle P, de Vicente JI, Eslava AP, Alvarez MI (1993) Isolation, characterization and mapping of pyrimidine auxotrophs of Phycomyces blakesleeanus. Curr Genet 24:515–519. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00351715
Covert SF, Kapoor P, Lee M-h, Briley A, Nairn CJ (2001) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Fusarium circinatum. Mycol Res 105:259–264. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0953756201003872
de Boer P, Bronkhof J, Dukiќ K, Kerkman R, Touw H, van den Berg M, Offringa R (2013) Efficient gene targeting in Penicillium chrysogenum using novel Agrobacterium-mediated transformation approaches. Fungal Genet Biol 61:9–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2013.08.012
de Groot MJ, Bundock P, Hooykaas PJ, Beijersbergen AG (1998) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of filamentous fungi. Nat Biotechnol 16:839–842. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0998-839
Fierro F, Vaca I, Castillo NI, García-Rico RO, Chávez R (2022) Penicillium chrysogenum, a vintage model with a cutting-edge profile in biotechnology. Microorganisms 10:573. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030573
Glass NL, Donaldson GC (1995) Development of primer sets designed for use with the PCR to amplify conserved genes from filamentous ascomycetes. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:1323–1330. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.61.4.1323-1330.1995
Gouka RJ, Gerk C, Hooykaas PJJ, Bundock P, Musters W, Verrips CT, de Groot MJA (1999) Transformation of Aspergillus awamori by Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated homologous recombination. Nat Biotechnol 17:598–601. https://doi.org/10.1038/9915
Guzmán-Chávez F, Zwahlen RD, Bovenberg RAL, Driessen AJM (2018) Engineering of the filamentous fungus Penicillium chrysogenum as cell factory for natural products. Front Microbiol 9:2768. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02768
Hong SB, Go SJ, Shin HD, Frisvad JC, Samson RA (2005) Polyphasic taxonomy of Aspergillus fumigatus and related species. Mycologia 97:1316–1329. https://doi.org/10.3852/mycologia.97.6.1316
Houbraken J, Frisvad JC, Samson RA (2011) Fleming’s penicillin producing strain is not Penicillium chrysogenum but P. rubens. IMA Fungus 2:87–95. https://doi.org/10.5598/imafungus.2011.02.01.12
Houbraken J, Visagie CM, Frisvad JC, Rokas A (2021) Recommendations to prevent taxonomic misidentification of genome-sequenced fungal strains. Microbiol Resource Announcements 10:e01074–e01020. https://doi.org/10.1128/mra.01074-20
Lazo G, Stein P, Ludwig R (1991) A DNA transformation–competent Arabidopsis genomic library in Agrobacterium. Nat Biotechnol 9:963–967. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1091-963
Michielse CB, Hooykaas PJJ, van den Hondel CAMJJ, Ram AFJ (2005) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation as a tool for functional genomics in fungi. Curr Genet 48:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-005-0578-0
Mózsik L, Hoekzema M, de Kok NAW, Bovenberg RAL, Nygård Y, Driessen AJM (2021) CRISPR-based transcriptional activation tool for silent genes in filamentous fungi. Sci Rep 11:1118. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-80864-3
Nguyen KT, Ho QN, Pham TH, Phan TN, Tran VT (2016) The construction and use of versatile binary vectors carrying pyrG auxotrophic marker and fluorescent reporter genes for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Aspergillus oryzae. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 32:204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-016-2168-3
Nguyen KT, Ho QN, Do LTBX, Mai LTD, Pham DN, Tran HTT, Le DH, Nguyen HQ, Tran VT (2017) A new and efficient approach for construction of uridine/uracil auxotrophic mutants in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus oryzae using Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33:107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2275-9
Pathak A, Nowell RW, Wilson CG, Ryan MJ, Barraclough TG (2020) Comparative genomics of Alexander Fleming’s original Penicillium isolate (IMI 15378) reveals sequence divergence of penicillin synthesis genes. Sci Rep 10:15705. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-72584-5
Pohl C, Kiel JAKW, Driessen AJM, Bovenberg RAL, Nygård Y (2016) CRISPR/Cas9 based genome editing of Penicillium chrysogenum. ACS Synth Biol 5:754–764. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.6b00082
Pohl C, Polli F, Schütze T, Viggiano A, Mózsik L, Jung S, de Vries M, Bovenberg RAL, Meyer V, Driessen AJM (2020) A Penicillium rubens platform strain for secondary metabolite production. Sci Rep 10:7630. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64893-6
Polli F, Meijrink B, Bovenberg RAL, Driessen AJM (2016) New promoters for strain engineering of Penicillium chrysogenum. Fungal Genet Biol 89:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2015.12.003
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.73
Sonderegger C, Galgóczy L, Garrigues S, Fizil Á, Borics A, Manzanares P, Hegedüs N, Huber A, Marcos JF, Batta G, Marx F (2016) A Penicillium chrysogenum-based expression system for the production of small, cysteine-rich antifungal proteins for structural and functional analyses. Microb Cell Fact 15:192. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-016-0586-4
Sun CB, Kong QL, Xu WS (2002) Efficient transformation of Penicillium chrysogenum mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens LBA4404 for cloning of Vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene. Electron J Biotechnol 5:9–10. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-34582002000100009
Thai HD, Tran VT (2020) Heterologous phytase expression in the food filamentous fungus Aspergillus oryzae using the added rice husk cultivation model. Acad J Biology 42:75–84. https://doi.org/10.15625/2615-9023/v42n2.14985
Tran VT, Thai HD, Vu TX (2022) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation systems for genetic manipulation in agriculturally important fungi. In: Jeschke P, Starikov EB (eds) Agricultural biocatalysis: biological and chemical applications. Jenny Stanford Publishing, New York, pp 283–311
Tsuchiya K, Tada S, Gomi K, Kitamoto k, Kumagai C, Jigami Y, Tamura G (1992) High level expression of the synthetic human lysozyme gene in Aspergillus oryzae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38:109–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00169428
van den Berg MA, Albang R, Albermann K, Badger JH, Daran J-M, Driessen M, Garcia-Estrada AJ, Fedorova C, Harris ND, Heijne DM, Joardar WHM, Kiel VW, Kovalchuk JAK, Martín A, Nierman JF, Nijland WC, Pronk JG, Roubos JT, van der Klei JA, van Peij IJ, Veenhuis NNME, von Döhren M, Wagner H, Wortman C, Bovenberg J RAL (2008) Genome sequencing and analysis of the filamentous fungus Penicillium chrysogenum. Nat Biotechnol 26:1161–1168. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1498
van Hartingsveldt W, Mattern IE, van Zeijl CMJ, Pouwels PH, van den Hondel CAMJJ (1987) Development of a homologous transformation system for Aspergillus niger based on the pyrG gene. Mol Gen Genet 206:71–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00326538
Villarino M, De Cal A, Melgarejo P, Larena I, Espeso EA (2015) The development of genetic and molecular markers to register and commercialize Penicillium rubens (formerly Penicillium oxalicum) strain 212 as a biocontrol agent. Microb Biotechnol 9:89–99. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12325
Villarino M, Espeso EA, Melgarejo P, Larena I (2018) Transformation of Penicillium rubens 212 and expression of GFP and DsRED coding genes for visualization of plant-biocontrol agent interaction. Front Microbiol 9:1653. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01653
Visagie CM, Houbraken J, Frisvad JC, Hong SB, Klaassen CHW, Perrone G, Seifert KA, Varga J, Yaguchi T, Samson RA (2014) Identification and nomenclature of the genus Penicillium. Stud Mycol 78:343–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.simyco.2014.09.001
Vohra A, Satyanarayana T (2003) Phytases: microbial sources, production, purification, and potential biotechnological applications. Crit Rev Biotechnol 23:29–60. https://doi.org/10.1080/713609297
Vu TX, Vu HH, Nguyen GT, Vu HT, Mai LTD, Pham DN, Le DH, Nguyen HQ, Tran VT (2019) A newly constructed Agrobacterium-mediated transformation system revealed the influence of nitrogen sources on the function of the LaeA regulator in Penicillium chrysogenum. Fungal Biology 123:830–842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funbio.2019.08.010
Wyss M, Pasamontes L, Rémy R, Kohler J, Kusznir E, Gadient M, Müller F, van Loon APGM (1998) Comparison of the thermostability properties of three acid phosphatases from molds: Aspergillus fumigatus phytase, A. niger phytase, and A. niger pH 2.5 acid phosphatase. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4446–4451. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.64.11.4446-4451.1998
Xu N, Li L, Chen F (2022) Construction of gene modification system with highly efficient and markerless for Monascus ruber M7. Front Microbiol 13:952323. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.952323
Zhong Y, Yu H, Wang X, Lu Y, Wang T (2010) Towards a novel efficient T-DNA-based mutagenesis and screening system using green fluorescent protein as a vital reporter in the industrially important fungus Trichoderma reesei. Mol Biol Rep 38:4145–4151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0534-z
Acknowledgements
The authors thank members of the National Key Laboratory of Enzyme and Protein Technology (KLEPT) for technical assistance and helpful discussion.
Funding
This work was supported by Vietnam National University, Hanoi (VNU) through grant number TXTCN.21.29.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by HDT, TXV, HHV, GTN, MTT, HTTT, HTTP, NTHL, and VTT. The first draft of the manuscript was written by VTT, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any study with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tran, VT., Thai, HD., Vu, T.X. et al. An efficient Agrobacterium-mediated system based on the pyrG auxotrophic marker for recombinant expression in the filamentous fungus Penicillium rubens. Biotechnol Lett 45, 689–702 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-023-03374-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-023-03374-y