Abstract
Objectives
To develop a new vector for constitutive expression in Pichia pastoris based on the endogenous glycolytic PGK1 promoter.
Results
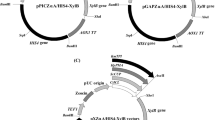
P. pastoris plasmids bearing at least 415 bp of PGK1 promoter sequences can be used to drive plasmid integration by addition at this locus without affecting cell growth. Based on this result, a new P. pastoris integrative vector, pPICK2, was constructed bearing some features that facilitate protein production in this yeast: a ~620 bp PGK1 promoter fragment with three options of restriction sites for plasmid linearization prior to yeast transformation: a codon-optimized α-factor secretion signal, a new polylinker, and the kan marker for vector propagation in bacteria and selection of yeast transformants.
Conclusions
A new constitutive vector for P. pastoris represents an alternative platform for recombinant protein production and metabolic engineering purposes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agaphonov M, Romanova N, Choi ES, Ter-Avanesyan M (2010) A novel kanamycin/G418 resistance marker for direct selection of transformants in Escherichia coli and different yeast species. Yeast 27:189–195
Çalık P, Ata O, Güneş H, Massahi A, Boy E, Keskin A, Öztürk S, Zerze GH, Özdamar TH (2015) Recombinant protein production in Pichia pastoris under glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter: from carbon source metabolism to bioreactor operation parameters. Biochem Eng J 95:20–36
Cereghino LGP, Cereghino JL, Sunga AJ, Johnson MA, Lim M, Gleeson MA, Cregg JM (2001) New selectable marker/auxotrophic host strain combinations for molecular genetic manipulation of Pichia pastoris. Gene 263:159–169
Daly R, Hearn MT (2005) Expression of heterologous proteins in Pichia pastoris: a useful experimental tool in protein engineering and production. J Mol Recognit 18:119–138
de Almeida JR, de Moraes LM, Torres FA (2005) Molecular characterization of the 3-phosphoglycerate kinase gene (PGK1) from the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Yeast 22:725–737
Fraenkel DG (1982) Carbohydrate metabolism. In: Strathern JN, Jones EW, Broach JR (eds) The molecular biology of the yeast Saccharomyces: metabolism and gene expression. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, NY, pp 1–37
Fuwa H (1954) A new method for microdetermination of amylase activity by the use of amylose as the substrate. J Biochem 41:583–603
Janner CR, Brito AL, Moraes LM, Reis VC, Torres FA (2013) pPCV, a versatile vector for cloning PCR products. Springerplus 2:441
Liu ZW, Yin HX, Yi XP, Zhang AL, Luo JX, Zhang TY, Fu CY, Zhang ZH, Shen JC, Chen LP (2012) Constitutive expression of barley alpha-amylase in Pichia pastoris by high-density cell culture. Mol Biol Rep 39:5805–5810
Macauley-Patrick S, Fazenda ML, McNeil B, Harvey LM (2005) Heterologous protein production using the Pichia pastoris expression system. Yeast 22:249–270
Menéndez C, Hernández L, Banguela A, País J (2004) Functional production and secretion of the Gluconoacetobacter diazatrophicus fructose-releasing exo-levanase (LsdB) in Pichia pastoris. Enz Microb Technol 34:446–452
Qin X, Qian J, Yao G, Zhuang Y, Zhang S, Chu J (2011) GAP promoter library for fine-tuning of gene expression in Pichia pastoris. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:3600–3608
Reis VC, Nicola AM, de Neto OSO, Batista VD, de Moraes LM, Torres FA (2012) Genetic characterization and construction of an auxotrophic strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae JP1, a Brazilian industrial yeast strain for bioethanol production. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39:1673–1683
Romanos MA, Scorer CA, Clare JJ (1992) Foreign gene expression in yeast: a review. Yeast 8:423–488
Scorer CA, Clare JJ, McCombie WR, Romanos MA, Sreekrishna K (1994) Rapid selection using G418 of high copy number transformants of Pichia pastoris for high-level foreign gene expression. Biotechnology 12:181–184
Stadlmayr G, Mecklenbrauker A, Rothmuller M, Maurer M, Sauer M, Mattanovich D, Gasser B (2010) Identification and characterisation of novel Pichia pastoris promoters for heterologous protein production. J Biotechnol 150:519–529
Sunga AJ, Tolstorukov I, Cregg JM (2008) Posttransformational vector amplification in the yeast Pichia pastoris. FEMS Yeast Res 8:870–876
Yang CH, Huang YC, Chen CY, Wen CY (2010) Expression of Thermobifida fusca thermostable raw starch digesting alpha-amylase in Pichia pastoris and its application in raw sago starch hydrolysis. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 37:401–406
Zhang AL, Luo JX, Zhang TY, Pan YW, Tan YH, Fu CY, Tu FZ (2009) Recent advances on the GAP promoter derived expression system of Pichia pastoris. Mol Biol Rep 36:1611–1619
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by FAPDF (Grant# 193.000.582/2009) and CNPq. The authors are thankful to Alexsandro Sobreira Galdino for his assistance in the zymogram methodology.
Supporting Information
Supplementary Fig. 1–Sequence of the 270-bp synthetic DNA fragment used to remove the PvuI and SmaI sites present in the kan coding sequence
Supplementary Fig. 2–Relevant sequences required for heterologous gene expression present on pPICK2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arruda, A., Reis, V.C.B., Batista, V.D.F. et al. A constitutive expression system for Pichia pastoris based on the PGK1 promoter. Biotechnol Lett 38, 509–517 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-2002-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-2002-2