Abstract
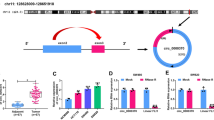
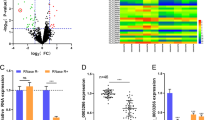
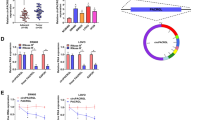
Dysregulation of circRNAs is associated with human cancer progression, but its expression pattern and function in cancer are not fully understood. The aim of our study is to investigate the effects of circ_0001821 on colorectal cancer (CRC) proliferation, migration, invasion, and stemness. The expression level of circ_0001821 in CRC tissues and cells was detected by quantitative real-time PCR. The effects of circ_0001821 silencing on the proliferation, migration, invasion, and stemness of CRC cells were examined by cell counting kit-8, 5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine, transwell, sphere formation, and western blot assays. Bioinformatics and dual-luciferase reporter gene assay were used to verify the relationship between circ_0001821 and miR-339-3p, miR-339-3p and CST1 in CRC cells. Circ_0001821 was highly expressed in CRC tissues and cells. Circ_0001821 silencing inhibited the proliferation, migration, invasion, and stemness of CRC cells, and transfection of miR-339-3p inhibitor partly attenuated this effect. In addition, circ_0001821 can bind miR-339-3p to regulate CST1 expression. Circ_0001821 silencing also curbed tumor growth in vivo. Circ_0001821 promoted CRC cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and stemness by regulating the miR-339-3p/CST1 axis.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Buccafusca G et al (2019) Early colorectal cancer: diagnosis, treatment and survivorship care. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 136:20–30
Chatila R et al (2021) Epidemiology and survival of colorectal cancer in Lebanon: a sub-national retrospective analysis. Cancer Control 28:10732748211041220
Chen C et al (2020) The circular RNA 001971/miR-29c-3p axis modulates colorectal cancer growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis through VEGFA. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 39(1):91
Chen S et al (2021) CST1 promoted gastric cancer migration and invasion through activating Wnt pathway. Cancer Manag Res 13:1901–1907
Dai DN et al (2017) Elevated expression of CST1 promotes breast cancer progression and predicts a poor prognosis. J Mol Med (berl) 95(8):873–886
Flemming A (2019) The enigma of circular RNA. Nat Rev Immunol 19(6):351
Hansen TB et al (2013) Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 495(7441):384–388
Hao S et al (2019) Emerging roles of circular RNAs in colorectal cancer. Onco Targets Ther 12:4765–4777
Jiang J et al (2018) Let7d inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation through the CST1/p65 pathway. Int J Oncol 53(2):781–790
Jin YD et al (2019) Hsa_circ_0005075 predicts a poor prognosis and acts as an oncogene in colorectal cancer via activating Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(8):3311–3319
Keum N, Giovannucci E (2019) Global burden of colorectal cancer: emerging trends, risk factors and prevention strategies. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 16(12):713–732
Kong S et al (2019) Identification of hsa_circ_0001821 as a novel diagnostic biomarker in gastric cancer via comprehensive circular RNA profiling. Front Genet 10:878
Li Y et al (2015) Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: a promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Res 25(8):981–984
Li Y et al (2019) A novel circFMN2 promotes tumor proliferation in CRC by regulating the miR-1182/hTERT signaling pathways. Clin Sci (lond) 133(24):2463–2479
Li G et al (2021) CircRNA hsa_circ_0014130 function as a miR-132–3p sponge for playing oncogenic roles in bladder cancer via upregulating KCNJ12 expression. Cell Biol Toxicol 38:1079–1096
Li S et al (2021) CircDOCK1 promotes the tumorigenesis and cisplatin resistance of osteogenic sarcoma via the miR-339-3p/IGF1R axis. Mol Cancer 20(1):161
Li C et al (2022) High expression of circ_0001821 promoted colorectal cancer progression through miR-600/ISOC1 axis. Biochem Genet 2022:1–18
Liang R, Tang Y (2020) LINC00467 knockdown repressed cell proliferation but stimulated cell apoptosis in glioblastoma via miR-339-3p/IP6K2 axis. Cancer Biomark 28(2):169–180
Liu L, Zhang F, Li J (2021a) CircRNA circ_0001821 predicts an unfavorable prognosis and promotes the proliferation of multiple myeloma. Hematology 26(1):716–723
Liu Y et al (2021b) Circ_0001821 knockdown suppresses growth, metastasis, and TAX resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer cells by regulating the miR-526b-5p/GRK5 axis. Pharmacol Res Perspect 9(4):e00812
Panda AC (2018) Circular RNAs Act as miRNA sponges. Adv Exp Med Biol 1087:67–79
Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ (2017) MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16(3):203–222
Siegel RL et al (2017) Colorectal cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin 67(3):177–193
Simon K (2016) Colorectal cancer development and advances in screening. Clin Interv Aging 11:967–976
Sung H et al (2021) Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249
Vo JN et al (2019) The landscape of circular RNA in cancer. Cell 176(4):869-881 e13
Weber CE et al (2016) miR-339-3p is a tumor suppressor in melanoma. Cancer Res 76(12):3562–3571
Xue M et al (2020) Circular RNA circ-LDLRAD3 serves as an oncogene to promote non-small cell lung cancer progression by upregulating SLC1A5 through sponging miR-137. RNA Biol 17(12):1811–1822
Zhang Z, Deng X (2022) circ_0001821 contributes to the development of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by regulating MicroRNA-148a-3p/EGFR axis and activating phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Mol Cell Biol 42(3):e0008921
Zhao ZJ, Shen J (2017) Circular RNA participates in the carcinogenesis and the malignant behavior of cancer. RNA Biol 14(5):514–521
Zhou C, Lu Y, Li X (2015) miR-339-3p inhibits proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett 10(5):2842–2848
Zhou X et al (2021) Circ-MBOAT2 knockdown represses tumor progression and glutamine catabolism by miR-433-3p/GOT1 axis in pancreatic cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 40(1):124
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CL designed and performed the research; CL and TM analyzed the data; CL wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
This study was permitted by the Ethics Committee of Suzhou Hospital of Anhui Medical University.
Consent to participate
Written informed consents were obtained from all participants.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Mei, T. Circ_0001821 Potentiates Cell Growth, Metastasis, and Stemness in Colorectal Cancer by Regulating miR-339-3p/CST1. Biochem Genet 61, 1451–1469 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-022-10329-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-022-10329-x