Abstract
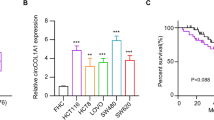
CircRNAs are a member of noncoding RNAs and have been verified to play an important regulatory role in cancers. In CRC, the regulatory mechanisms of various circRNAs have not been elucidated. The expression of circPACRGL and miR-330-3p was detected with qRT-PCR. The protein expression of CDK4, MMP-9, Bcl-2, Bax, cellular nucleic acid-binding protein (CNBP) and β-actin was measured with western blot. Cell proliferation was analyzed using MTT assay, colony formation assay, and EDU assay. Cell apoptosis was detected using flow cytometry. Cell migration and invasion were measured with wound healing and transwell invasion assay. Luciferase reporter assay and RIP assay was used to determine the relationship of among miR-330-3p, circPACRGL and CNBP in CRC cells. In this study, we found that circPACRGL and CNBP expressed high and miR-330-3p expressed low in CRC tissues and cells. Functional experiments showed that inhibition of circPACRGL reduced cell proliferation, migration and invasion in CRC. In addition, knockdown of circPACRGL contributed to cell apoptosis in CRC. Dual-luciferase report assay determined that circPACRGL was a miR-330-3p sponge molecular and CNBP was a target of miR-330-3p. Reversed experiments showed that the effects of sh-circPACRGL transfection on CRC cells were rescued by up-regulating CNBP expression. In this study, we for the first time found a novel regulatory network of circPACRGL in CRC. The results manifested that circPACRGL affected tumor growth by targeting miR-330-3p/CNBP axis in CRC, highlighting the potential of circPACRGL as a therapeutic target for colorectal cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not Applicable.
References
Zhao P, Dai M, Chen W, Li N (2010) Cancer Trends in China. Jpn J Clin Oncol 40:281–285
Vega P, Valentin F, Cubiella J (2015) Colorectal cancer diagnosis: pitfalls and opportunities. World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology 7:422–433
Whittemore AS, Wuwilliams AH, Lee MM, Shu Z, Gallagher RP, Dengao J, Lun Z, Xianghui W, Kun C, Jung DL (1990) Diet, physical activity, and colorectal cancer among Chinese in North America and China. J Natl Cancer Inst 82:915–926
Ashwal-Fluss R, Meyer M, Pamudurti NR, Ivanov A, Bartok O, Hanan M, Evantal N, Memczak S, Rajewsky N, Kadener S (2014) circRNA Biogenesis Competes with Pre-mRNA Splicing. Mol Cell 56:55–66
Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J (2017) Insights into circular RNA biology. RNA Biol 14:1035–1045. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2016.1271524
Frankel LB, Lund AH (2012) MicroRNA regulation of autophagy. Carcinogenesis 33:2018–2025
Kristensen LS, Hansen TB, Venø MT, Kjems J (2018) Circular RNAs in cancer: opportunities and challenges in the field. Oncogene 37:555–565
Meng S, Zhou H, Feng Z, Xu Z, Tang Y, Li P, Wu M (2017) CircRNA: functions and properties of a novel potential biomarker for cancer. Mol Cancer 16:94. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0663-2
Pervouchine DD (2019) Circular exonic RNAs: When RNA structure meets topology. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 1862:194384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2019.05.002
Vo JN, Cieslik M, Zhang Y, Shukla S, Xiao L, Zhang Y, Wu YM, Dhanasekaran SM, Engelke CG, Cao X, Robinson DR, Nesvizhskii AI, Chinnaiyan AM (2019) The Landscape of Circular RNA in Cancer. Cell 176:869-881.e13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.12.021
Yu T, Wang Y, Fan Y, Fang N, Wang T, Xu T, Shu Y (2019) CircRNAs in cancer metabolism: a review. J Hematol Oncol 12:90. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-019-0776-8
Zhang H, Wang G, Ding C, Liu P, Wang R, Ding W, Tong D, Wu D, Li C, Wei Q (2017) Increased circular RNA UBAP2 acts as a sponge of miR-143 to promote osteosarcoma progression. Oncotarget 8:61687–61697
Liu Z, Yu Y, Huang Z, Kong Y, Hu X, Xiao W, Quan J, Fan X (2019) CircRNA-5692 inhibits the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by sponging miR-328-5p to enhance DAB2IP expression. Cell Death Dis 10:900. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-2089-9
Li H, Jin X, Liu B, Zhang P, Chen W, Li Q (2019) CircRNA CBL.11 suppresses cell proliferation by sponging miR-6778–5p in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 19:826. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-019-6017-2
Shang A, Gu C, Wang W, Wang X, Sun J, Zeng B, Chen C, Chang W, Ping Y, Ji P, Wu J, Quan W, Yao Y, Zhou Y, Sun Z, Li D (2020) Exosomal circPACRGL promotes progression of colorectal cancer via the miR-142-3p/miR-506-3p- TGF-β1 axis. Mol Cancer 19:117. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01235-0
Xu H, Liu Y, Cheng P, Wang C, Liu Y, Zhou W, Xu Y, Ji G (2020) CircRNA_0000392 promotes colorectal cancer progression through the miR-193a-5p/PIK3R3/AKT axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 39:283. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-020-01799-1
Zhang HD, Jiang LH, Sun DW, Hou JC, Ji ZL (2017) CircRNA: a novel type of biomarker for cancer. Breast Cancer 25:1–7
Chen D, Chenyue Z, Jiamao L, Xinyu S, Haiyong W (2018) Screening differential circular RNA expression profiles reveal that hsa_circ_0128298 is a biomarker in the diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res 10:1275–1283
Yang H, Li X, Meng Q, Sun H, Wu S, Hu W, Liu G, Li X, Yang Y, Chen R (2020) CircPTK2 (hsa_circ_0005273) as a novel therapeutic target for metastatic colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer 19:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-1139-3
Allantaz F, Cheng DT, Bergauer T, Ravindran P, Rossier MF, Ebeling M, Badi L, Reis B, Bitter H, D’Asaro M (2012) Expression profiling of human immune cell subsets identifies miRNA−mRNA regulatory relationships correlated with cell type specific expression. PLoS ONE 7:e29979
Feng Z, Ruyou X, Yingnan W, Xiaoying L, Shuang Z, Wenying H (2018) Comprehensive analysis of circRNA expression pattern and circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis in rabbits. Aging 10(9):2266–2283
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Yao S, Zheng P, Wu H, Song LM, Ying XF, Xing C, Li Y, Xiao ZQ, Zhou XN, Shen T, Chen L, Liu YH, Lai MD, Mei L, Gao TM, Li JM (2015) Erbin interacts with c-Cbl and promotes tumourigenesis and tumour growth in colorectal cancer by preventing c-Cbl-mediated ubiquitination and down-regulation of EGFR. J Pathol 236:65–77. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.4502
Chen T, Yang Z, Liu C, Wang L, Yang J, Chen L, Li W (2019) Circ_0078767 suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer by protecting RASSF1A expression via sponging miR-330-3p. Cell Prolif 52:e12548. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12548
Huang Y, Sun H, Ma X, Zeng Y, Pan Y, Yu D, Liu Z, Xiang Y (2020) HLA-F-AS1/miR-330-3p/PFN1 axis promotes colorectal cancer progression. Life Sci 254:117180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117180
Jin Z, Jia B, Tan L, Liu Y (2019) miR-330-3p suppresses liver cancer cell migration by targeting MAP2K1. Oncol Lett 18:314–320. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10280
Shen L, Yi S, Huang L, Li S, Bai F, Lei S, Breitzig M, Czachor A, Sun H, Zheng Q, Wang F (2019) miR-330-3p promotes lung cancer cells invasion, migration, and metastasis by directly targeting hSOD2b. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 66:21–32. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.1691
Wei CH, Wu G, Cai Q, Gao XC, Tong F, Zhou R, Zhang RG, Dong JH, Hu Y, Dong XR (2017) MicroRNA-330-3p promotes cell invasion and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer through GRIA3 by activating MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. J Hematol Oncol 10:125. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-017-0493-0
Wang H, Chen SH, Kong P, Zhang LY, Zhang LL, Zhang NQ, Gu H (2018) Increased expression of miR-330-3p: a novel independent indicator of poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:1726–1730. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201803_14587
Calcaterra NB, Armas P, Weiner AM, Borgognone M (2010) CNBP: a multifunctional nucleic acid chaperone involved in cell death and proliferation control. IUBMB Life 62:707–714. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.379
Lee EH, Lee TA, Yoo HJ, Lee S, Park B (2019) CNBP controls tumor cell biology by regulating tumor‐promoting gene expression. Molecular Carcinogenesis.
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This work was supported by Funded project of “Double first-class” discipline (Traditional Chinese Medicine) construction in Jiangxi Province [NO.JXSYLXK-ZHY1054]; Science and Technology Research Project of Education Department of Jiangxi Province [No.201210, 200143]; Scientific planning and Planning Fund project of Jiangxi Health Commission [NO.20195637, 20165401]; Science and Technology Project of Jiangxi Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine [NO.2019A106]; 2019 University-level Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Plan for College Students of Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine [NO.201910412045]; Csco-Hengrui Cancer Research Fund (Y-HR2017-128).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have been involved in the management of the patient and in the conception of the manuscript. The specific authors’ contribution is as follows. Haiyun Liu and Zhijian He: writing the drafting of the manuscript. Qianxia Lin, Wenchun Zhang and Xiaomin Wang: data collection. Yulong Ji, Yongqing Fang and Yuan Hu: analysis and interpretation. Xinrong Hu: software, reviewing and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was permitted by the Ethics Committee of Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Fang, Y., Hou, B. et al. CircPACRGL promoted cell proliferation, migration and invasion as well as inhibited cell apoptosis in colorectal cancer via regulation of the miR-330-3p/CNBP axis. Mol Cell Biochem 478, 1633–1644 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04543-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04543-9