Abstract
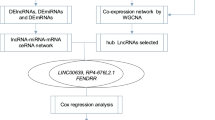
As novel master regulators of initiation and progression, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) can response to therapy in a wide variety of malignances. This study aimed to explore the regulatory mechanisms in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) by constructing lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA networks. The whole transcriptome sequence was performed in five NSCLC tissues and their corresponding paired adjacent normal tissues. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) and mRNAs expression profiles were obtained from TCGA database. “EdgeR” R package was used for gene expression comparisons and the genes with | log2FC |> 2 and false discovery rate (FDR) adjusted P<0.05 were considered significant. Totally, 559 differentially expressed lncRNAs (DELs) (235 up-regulated, 324 down-regulated) were identified via whole transcriptome sequence analysis. Subsequently, 14 up-regulated lncRNAs were obtained in the intersection of our RNA-seq data and TCGA dataset. The dysregulations of the selected lncRNAs were evaluated through GEPIA. Three candidate lncRNAs (LINC01426, TYMSOS, VPS9D1-AS1) were finally selected for further study. Through bioinformatics prediction, with the three lnRNAs and their associated miRNAs (n=14) and mRNAs (n=218), a lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network was constructed. Furthermore, Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway associated with the targeted genes were proceeded. In addition, the protein–protein interaction (PPI) network construction was performed by STRING and lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network was visualized via Cytoscape. The top ten significant hub-genes in the PPI network are identified based on their node degrees. Moreover, the lncRNA-miRNA and miRNA-mRNA interactions were predicted using the StarBase and survival analyses were performed in Kaplan-Meier plotter website. We concluded that TYMSOS/hsa-miR-101-3p/CEP55 and TYMSOS/hsa-miR-195-5p/CHEK1 ceRNA regulatory aixs may play vital roles in the occurrence and development of NSCLC, and may provide novel therapeutic targets in the future.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LncRNA:
-
Long noncoding RNA
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- TCGA:
-
The cancer genome atlas
- PPI:
-
Protein–protein interaction
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes
- DELs:
-
Differentially expressed lncRNAs
- LUAD:
-
Adenocarcinoma
- LUSC:
-
Squamous cell carcinoma
- SCLC:
-
Small cell carcinoma
- mRNA:
-
Messenger RNA
- ceRNA:
-
Competing endogenous RNA
- FC:
-
Fold change
- DEMIs:
-
Differentially expressed miRNAs
- DEMs:
-
Differentially expressed mRNAs
- STRING:
-
The search tool for the retrieval of interacting genes database
- RNA-seq:
-
RNA sequencing
- BP:
-
Biological processes
- CC:
-
Cellular components
- MF:
-
Molecular functions
- MCODE:
-
Molecular complex detection
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- MREs:
-
MiRNA response elements
References
Agromayor M, Martin-Serrano J (2013) Knowing when to cut and run: mechanisms that control cytokinetic abscission. Trends Cell Biol 23(9):433–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2013.04.006
Alcaraz-Sanabria A, Nieto-Jimenez C, Corrales-Sanchez V et al (2017) Synthetic lethality interaction between aurora kinases and CHEK1 inhibitors in ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 16(11):2552–2562. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0223
Athie A, Marchese FP, González J et al (2020) Analysis of copy number alterations reveals the lncRNA ALAL-1 as a regulator of lung cancer immune evasion. J Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201908078
Bu L, Tian Y, Wen H et al (2021) miR-195-5p exerts tumor-suppressive functions in human lung cancer cells through targeting TrxR2. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 53(2):189–200. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmaa159
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya SAH et al (2017) UALCAN: a portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia 19(8):649–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2017.05.002
Chen Y, Wang X (2020) miRDB: an online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res 48(D1):D127–D131. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz757
Chen J, Liu A, Wang Z et al (2020) LINC00173.v1 promotes angiogenesis and progression of lung squamous cell carcinoma by sponging miR-511–5p to regulate VEGFA expression. Mol Cancer 19(1):98. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01217-2
Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH et al (2014) cytoHubba: identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol 8(Suppl 4):S11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-0509-8-S4-S11
Corso D, Chemello F, Alessio E et al (2021) MyoData: an expression knowledgebase at single cell/nucleus level for the discovery of coding-noncoding RNA functional interactions in skeletal muscle. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 19:4142–4155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2021.07.020
Cunningham F, Allen JE, Allen J et al (2022) Ensembl. Nucleic Acids Res 50(D1):D988–D995. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab1049
Gong D, Feng PC, Ke XF et al (2020) Silencing Long Non-coding RNA LINC01224 Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression via MicroRNA-330-5p-Induced Inhibition of CHEK1. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 19:482–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2019.10.007
Goodall GJ, Wickramasinghe VO (2021) RNA in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 21(1):22–36. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-020-00306-0
Gu Y, Wan C, Zhou G et al (2021) TYMSOS drives the proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating ZNF703 via sponging miR-4739. Cell Biol Int 45(8):1710–1719. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11610
Guo CJ, Ma XK, Xing YH et al (2020) Distinct processing of lncRNAs contributes to non-conserved functions in stem cells. Cell 181(3):621-636.e622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.006
Han X, Huang T, Han J (2020) Long noncoding RNA VPS9D1-AS1 augments the malignant phenotype of non-small cell lung cancer by sponging microRNA-532–3p and thereby enhancing HMGA2 expression. Aging 12(1):370–386. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102628
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C (2018) The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 553(7689):446–454. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25183
Hou GX, Liu P, Yang J et al (2017) Mining expression and prognosis of topoisomerase isoforms in non-small-cell lung cancer by using Oncomine and Kaplan-Meier plotter. PLoS ONE 12(3):e0174515. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0174515
Jeffery J, Sinha D, Srihari S et al (2016) Beyond cytokinesis: the emerging roles of CEP55 in tumorigenesis. Oncogene 35(6):683–690. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.128
Karagkouni D, Paraskevopoulou MD, Tastsoglou S et al (2020) DIANA-LncBase v3: indexing experimentally supported miRNA targets on non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res 48(D1):D101–D110. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz1036
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H et al (2014) starBase v2.0: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D92-97. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1248
Li M, Ren CX, Zhang JM et al (2018) The effects of miR-195-5p/MMP14 on proliferation and invasion of cervical carcinoma cells through TNF signaling pathway based on bioinformatics analysis of microarray profiling. Cell Physiol Biochem 50(4):1398–1413. https://doi.org/10.1159/000494602
Li M, Liu Y, Jiang X et al (2021) Inhibition of miR-144-3p exacerbates non-small cell lung cancer progression by targeting CEP55[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 53(10):1398–1407. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmab118
Liang H, Yu T, Han Y et al (2018) LncRNA PTAR promotes EMT and invasion-metastasis in serous ovarian cancer by competitively binding miR-101-3p to regulate ZEB1 expression. Mol Cancer 17(1):119. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0870-5
Lin MF, Jungreis I, Kellis M (2011) PhyloCSF: a comparative genomics method to distinguish protein coding and non-coding regions. Bioinformatics 27(13):i275-282. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr209
Lin X, Wang S, Sun M et al (2019) miR-195-5p/NOTCH2-mediated EMT modulates IL-4 secretion in colorectal cancer to affect M2-like TAM polarization. J Hematol Oncol 12(1):20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-019-0708-7
Liu Z, Wang X, Yang G et al (2020) Construction of lncRNA-associated ceRNA networks to identify prognostic lncRNA biomarkers for glioblastoma. J Cell Biochem 121(7):3502–3515. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29625
Loewen G, Jayawickramarajah J, Zhuo Y et al (2014) Functions of lncRNA HOTAIR in lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol 7:90. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-014-0090-4
Matam K, Goud I, Lakshmi MA et al (2015) Correlation between EGFR gene mutations and lung cancer: a hospital-based study. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 16(16):7071–7076. https://doi.org/10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.16.7071
Mohammadi A, Mansoori B, Duijf PHG et al (2021) Restoration of miR-330 expression suppresses lung cancer cell viability, proliferation, and migration[J]. J Cell Physiol 236(1):273–283. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29840
Nagasaka M, Uddin MH, Al-Hallak MN et al (2021) Liquid biopsy for therapy monitoring in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer 20(1):82. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-021-01371-1
Paci P, Colombo T, Farina L (2014) Computational analysis identifies a sponge interaction network between long non-coding RNAs and messenger RNAs in human breast cancer. BMC Syst Biol 8:83. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-0509-8-83
Pan J, Fang S, Tian H et al (2020) lncRNA JPX/miR-33a-5p/Twist1 axis regulates tumorigenesis and metastasis of lung cancer by activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Mol Cancer 19(1):9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-1133-9
Peng WX, Koirala P, Mo YY (2017) LncRNA-mediated regulation of cell signaling in cancer. Oncogene 36(41):5661–5667. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.184
Riffo-Campos AL, Riquelme I, Brebi-Mieville P (2016) Tools for Sequence-Based miRNA Target Prediction: What to Choose? Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17121987
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y et al (2011) A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta stone of a hidden RNA language?[J]. Cell 146(3):353–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.014
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O et al (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13(11):2498–2504. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1239303
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE et al (2022) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 72(1):7–33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21708
Sticht C, de la Torre C, Parveen A et al (2018) miRWalk: an online resource for prediction of microRNA binding sites. PLoS ONE 13(10):e0206239. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0206239
Strong ME, Richards JR, Torres M et al (2021) Faradaic electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for enhanced analyte detection in diagnostics. Biosens Bioelectron 177:112949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112949
Sun CC, Li SJ, Li G et al (2016) Long Intergenic Noncoding RNA 00511 Acts as an Oncogene in Non-small-cell Lung Cancer by Binding to EZH2 and Suppressing p57. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 5(11):e385. https://doi.org/10.1038/mtna.2016.94
Sun M, Song H, Wang S et al (2017) Integrated analysis identifies microRNA-195 as a suppressor of Hippo-YAP pathway in colorectal cancer. J Hematol Oncol 10(1):79. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-017-0445-8
Sun CC, Zhu W, Li SJ et al (2020) FOXC1-mediated LINC00301 facilitates tumor progression and triggers an immune-suppressing microenvironment in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating the HIF1alpha pathway. Genome Med 12(1):77. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-020-00773-y
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B et al (2017) GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 45(W1):W98–W102. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx247
Tang S, Li S, Liu T et al (2021) MicroRNAs: Emerging oncogenic and tumor-suppressive regulators, biomarkers and therapeutic targets in lung cancer. Cancer Lett 502:71–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.12.040
Tian B, Han X, Li G et al (2020) A long intergenic non-coding RNA, LINC01426, promotes cancer progression via AZGP1 and predicts poor prognosis in patients with LUAD. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev 18:765–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtm.2020.08.001
von Mering C, Huynen M, Jaeggi D et al (2003) STRING: a database of predicted functional associations between proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 31(1):258–261. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkg034
Wang L, Park HJ, Dasari S et al (2013) CPAT: coding-potential assessment tool using an alignment-free logistic regression model. Nucleic Acids Res 41(6):e74. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt006
Wang X, Su R, Guo Q et al (2019) Competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) hypothetic model based on comprehensive analysis of long non-coding RNA expression in lung adenocarcinoma. PeerJ 7:e8024. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.8024
Wang Z, Chen X, Liu N et al (2021) A nuclear long non-coding RNA LINC00618 accelerates ferroptosis in a manner dependent upon apoptosis. Mol Ther 29(1):263–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.09.024
Xie Y, Wei RR, Huang GL et al (2014) Checkpoint kinase 1 is negatively regulated by miR-497 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Oncol 31(3):844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0844-4
Yang J, Qi M, Fei X et al (2021) LncRNA H19: a novel oncogene in multiple cancers. Int J Biol Sci 17(12):3188–3208. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.62573
Yin J, Zeng X, Ai Z et al (2020) Construction and analysis of a lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network based on competitive endogenous RNA reveal functional lncRNAs in oral cancer. BMC Med Genomics 13(1):84. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-020-00741-w
Yuan Y, Jiang X, Tang L et al (2021) FOXM1/lncRNA TYMSOS/miR-214-3p-mediated high expression of NCAPG correlates with poor prognosis and cell proliferation in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Front Mol Biosci 8:785767. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2021.785767
Zhang X, He X, Liu Y et al (2017) MiR-101-3p inhibits the growth and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer through blocking PI3K/AKT signal pathway by targeting MALAT-1. Biomed Pharmacother 93:1065–1073. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.07.005
Zhang M, Jin X, Li J et al (2021) CeRNASeek: an R package for identification and analysis of ceRNA regulation. Brief Bioinform. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbaa048
Zhou S, Yu L, Xiong M et al (2018) LncRNA SNHG12 promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis in osteosarcoma by upregulating Notch2 by sponging miR-195-5p. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 495(2):1822–1832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.12.047
Zhou M, Lu B, Tan W et al (2020) Identification of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network associated with primary open angle glaucoma. BMC Ophthalmol 20(1):104. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-020-01365-5
Zuo W, Zhang W, Xu F et al (2019) Long non-coding RNA LINC00485 acts as a microRNA-195 sponge to regulate the chemotherapy sensitivity of lung adenocarcinoma cells to cisplatin by regulating CHEK1. Cancer Cell Int 19:240. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-019-0934-7
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Henan Key Laboratory of Pharmacology for Liver Diseases for providing experimental platform support.
Funding
This work was supported by the Leading Talents of Science and Technology Innovation in Henan Province (Grant Number 20420051008), the Key Project of Discipline Construction of Zhengzhou University (Grant Number XKZDQY202009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LD and LJ were responsible for the conception and design of the research, and drafting the manuscript. TY and JL performed the data acquisition. ML and JL performed the data analysis and interpretation. QS and YW performed the statistical analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for Publication
The authors agree for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10528_2022_10299_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary file1 (TIF 2649 kb)—Fig. 1 PPI network of the DEMs in the ceRNA network. The circles represent genes, and the lines represent interactions between the proteins encoded by the genes
10528_2022_10299_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary file2 (TIF 20556 kb)—Fig. 2 Potential binding sites for TYMSOS, LINC01426 and VPS9D1-AS1 to their targeted miRNA, respectively
10528_2022_10299_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary file3 (TIF 1624 kb)—Fig. 3 Expression analysis of remaining eight hub genes based on TCGA database by GEPIA. A. Boxplots depicting the expression levels of NUF2 in LUAD and LUSC. B. Boxplots depicting the expression levels of NCAPH in LUAD and LUSC. C. Boxplots depicting the expression levels of EXO1 in LUAD and LUSC. D. Boxplots depicting the expression levels of MAD2L1 in LUAD and LUSC. E. Boxplots depicting the expression levels of KIF20A in LUAD and LUSC. F. Boxplots depicting the expression levels of TPX2 in LUAD and LUSC. G. Boxplots depicting the expression levels of CDK1in LUAD and LUSC. H. Boxplots depicting the expression levels of SHCBP1 in LUAD and LUSC
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, L., Yang, T., Liu, M. et al. Construction of lncRNA TYMSOS/hsa-miR-101-3p/CEP55 and TYMSOS/hsa-miR-195-5p/CHEK1 Axis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Biochem Genet 61, 995–1014 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-022-10299-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-022-10299-0