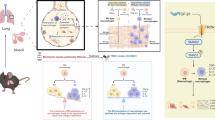
The effect of a course treatment with a sympatholytic reserpine on the infl ammatory response and connective tissue proliferation in the lungs of C57Bl/6 mice was studied on the model of toxic pulmonary fi brosis induced by intratracheal administration of bleomycin. This sympatholytic reduced infi ltration of the alveolar interstitium and alveolar ducts with infl ammatory cells (lymphocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, and plasma cells) and prevented connective tissue proliferation in the lungs. The anti-infl ammatory effect of reserpine was associated with a decrease in activity of bone marrow granulocyte-erythroid-macrophage-megakaryocyte and granulocyte precursors (proliferation and mobilization). The antifi brotic effect of reserpine was due to a decrease in the number of committed precursors for mesenchymopoiesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. D. Gol’dberg, A. M. Dygai, and V. P. Shakhov, Tissue Culture Methods in Hematology [in Russian], Tomsk (1992).
A. M. Dygai, E. G. Skurikhin, T. V. Andreeva, et al., Byull. Eksp. Biol. Med., 152, No. 8, 132-136 (2011).
A. M. Dygai, E. S. Khmelevskaya, E. G. Skurikhin, et al., Ibid., 152, No. 12, 665-671 (2011).
G. A. Merkulov, Course of Pathohistological Technique [in Russian], St. Petersburg (1969).
E. G. Skurikhin, E. S. Khmelevskaya, O. V. Pershina, et al., Kletochn. Tekhnol. Biol. Med., No. 3, 127-131 (2010).
R. A. Berg, J. Moss, B. J. Baum, and R. G. Crystal, J. Clin. Invest., 67, No. 5, 1457-1462 (1987).
S. N. Giri, D. A. Jr. Sanford, T. W. Robinson, and N. K. Tyler, Exp. Lung Res., 13, No. 4, 401-416 (1987).
W. D. Hardie, S. W. Glasser, and J. S. Hagood, Am. J. Pathol., 175, No. 1, 3-16 (2009).
D. S. Kim, H. R. Collard, and T. E. Jr. King, Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc., 3, No. 4, 285-292 (2006).
S. Massberg, P. Schaerli, I. Knezevic-Maramica, et al., Cell, 131, No. 5, 994-1008 (2007).
J. L. McQualter, K. Yuen, B. Williams, and I. Bertoncello, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 107, No. 4, 1414-1419 (2010).
A. Moeller, K. Ask, D. Warburton, et al., Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol., 40, No. 3, 362-382 (2008).
B. R. Stripp, Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc., 5, No. 6, 695-698 (2008).
D. J. Welsh, M. Harnett, M. MacLean, and A. J. Peacock, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med., 170, No. 3, 252-259 (2004).
M. S. Wilson and T. A. Wynn, Mucosal Immunol., 2, 103-121 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 153, No. 5, pp. 590-595, May, 2012
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skurikhin, E.G., Khmelevskaya, E.S., Pershina, O.V. et al. Mechanisms of the Anti-Infl ammatory and Antifi brotic Activity of a Sympatholytic Agent during Toxic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Bull Exp Biol Med 153, 638–643 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-012-1786-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-012-1786-5