Abstract
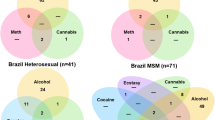
Stimulant use is associated with higher HIV viral load (VL) and sexual HIV transmission risk among men who have sex with men (MSM) living with HIV. There is little research on willingness of drug users living with HIV to fully participate in studies, especially those involving self-collection of biomarker data. This study presents findings from an at-home dried blood spot collection study measuring laboratory-quantified VL among U.S. HIV-positive MSM who reported high-risk sexual behavior and/or suboptimal antiretroviral therapy (ART) adherence to assess the association between drug-use behavior and (1) ability to complete a study protocol and (2) VL outcomes. Among recruited participants (n = 766), 35% reported stimulant drug use (amphetamines, cocaine, crack, crystal meth, ecstasy, or a combination of stimulant drugs), 39% reported using other drugs (heroin, marijuana, prescription opioids, and others), and 27% reported no drug use in the past 3 months. In all, 61% of enrolled participants completed the study protocol. Stimulant drug users were less likely (ARR 0.84; 95% CI 0.72–0.98) to complete the protocol than other drug users. Furthermore, other drug users were significantly less likely than non-drug users (ARR 0.52; 95% CI 0.28–0.97) to have an HIV VL result ≥ 1500 copies/mL. This study provides important estimates regarding the likelihood of participation in biomedical research activities among HIV-positive MSM with varying drug-use behaviors, showing that it is feasible to conduct such biomedical studies with drug-using MSM who report high-risk sexual behavior and struggle with their ART adherence.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez-Muñoz, M. T., Zaragoza-Rodríguez, S., Rojas-Montes, O., Palacios-Saucedo, G., Vázquez-Rosales, G., Gómez-Delgado, A., & Muñoz, O. (2005). High correlation of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 viral load measured in dried-blood spot samples and in plasma under different storage conditions. Archives of Medical Research,36(4), 382–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2005.03.010.
Attia, S., Egger, M., Muller, M., Zwahlen, M., & Low, N. (2009). Sexual transmission of HIV according to viral load and antiretroviral therapy: Systematic review and meta-analysis. AIDS,23(11), 1397–1404. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAD.0b013e32832b7dca.
Ballester, J., Valentine, G., & Sofuoglu, M. (2017). Pharmacological treatments for methamphetamine addiction: Current status and future directions. Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology,10(3), 305–314. https://doi.org/10.1080/17512433.2017.1268916.
Booth, R. E., Watters, J. K., & Chitwood, D. D. (1993). HIV risk-related sex behaviors among injection drug users, crack smokers, and injection drug users who smoke crack. American Journal of Public Health,83(8), 1144–1148. https://doi.org/10.2105/ajph.83.8.1144.
Braine, N., Des Jarlais, D. C., Goldblatt, C., Zadoretzky, C., & Turner, C. (2005). HIV risk behavior among amphetamine injectors at US syringe exchange programs. AIDS Education and Prevention,17(6), 515–424.
Brown, D. M., Thorne, J. E., Foster, G. L., Duncan, J. L., Brune, L. M., Muñana, A., … Jabs, D. A. (2006). Factors affecting attrition in a longitudinal study of patients with AIDS. AIDS Care,18(7), 821–829. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540120500466747.
Bruce, R. D., Kresina, T. F., & McCance-Katz, E. F. (2010). Medication-assisted treatment and HIV/AIDS: aspects in treating HIV-infected drug users. AIDS,24(3), 331–340. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAD.0b013e32833407d3.
Buchacz, K., McFarland, W., Kellogg, T. A., Loeb, L., Holmberg, S. D., Dilley, J., & Klausner, J. D. (2005). Amphetamine use is associated with increased HIV incidence among men who have sex with men in San Francisco. AIDS,19(13), 1423–1424. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.aids.0000180794.27896.fb.
Bush, K., Kivlahan, D. R., McDonell, M. B., Fihn, S. D., Bradley, K. A., & for the Ambulatory Care Quality Improvement, P. (1998). The audit alcohol consumption questions (audit-c): An effective brief screening test for problem drinking. Archives of Internal Medicine,158(16), 1789–1795. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.158.16.1789.
Cappelle, D., Yegles, M., Neels, H., van Nuijs, A. L. N., De Doncker, M., Maudens, K., … Crunelle, C. L. J. F. T. (2015). Nail analysis for the detection of drugs of abuse and pharmaceuticals: A review. Forensic Toxicology,33(1), 12–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-014-0258-1.
Carrico, A. W., Hunt, P. W., Neilands, T. B., Dilworth, S. E., Martin, J. N., Deeks, S. G., & Riley, E. D. (2019). Stimulant use and viral suppression in the era of universal antiretroviral therapy. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes,80(1), 89–93. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAI.0000000000001867.
Carrico, A. W., Riley, E. D., Johnson, M. O., Charlebois, E. D., Neilands, T. B., Remien, R. H., … Rotheram-Borus, M. J. (2011). Psychiatric risk factors for HIV disease progression: The role of inconsistent patterns of anti-retroviral therapy utilization. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes,56(2), 146–150. https://doi.org/10.1097/qai.0b013e318201df63.
Carrico, A. W., Shoptaw, S., Cox, C., Stall, R., Li, X., Ostrow, D. G., … Plankey, M. W. (2014). Stimulant use and progression to AIDS or mortality after the initiation of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes,67(5), 508–513. https://doi.org/10.1097/qai.0000000000000364.
Cassol, S., Gill, M. J., Pilon, R., Cormier, M., Voigt, R. F., Willoughby, B., & Forbes, J. (1997). Quantification of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA from dried plasma spots collected on filter paper. Journal of Clinical Microbiology,35(11), 2795–2801.
Cattie, J., Marquine, M. J., Bolden, K. A., Obermeit, L. C., Morgan, E. E., Franklin, D. R., … Woods, S. P. (2015). Predictors of attrition in a cohort study of HIV infection and methamphetamine dependence. Journal of Substance Use,20(6), 407–416. https://doi.org/10.3109/14659891.2014.942397.
Claus, R. E., Kindleberger, L. R., & Dugan, M. C. (2002). Predictors of attrition in a longitudinal study of substance abusers. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs,34(1), 69–74. https://doi.org/10.1080/02791072.2002.10399938.
Cohen, M. S., Chen, Y. Q., McCauley, M., Gamble, T., Hosseinipour, M. C., Kumarasamy, N., … HPTN 052 Study Team (2011). Prevention of HIV-1 infection with early antiretroviral therapy. New England Journal of Medicine,365, 493–505. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1105243.
Colfax, G., Coates, T. J., Husnik, M. J., Huang, Y., Buchbinder, S., Koblin, B., … Explore Study Team. (2005). Longitudinal patterns of methamphetamine, popper (amyl nitrite), and cocaine use and high-risk sexual behavior among a cohort of San Francisco men who have sex with men. Journal of Urban Health,82(1), i62. https://doi.org/10.1093/jurban/jti025.
Colfax, G., & Shoptaw, S. (2005). The methamphetamine epidemic: Implications for HIV prevention and treatment. Current HIV/AIDS Reports,2(4), 194–199.
Cottler, L. B., Compton, W. M., Ben-Abdallah, A., Horne, M., & Claverie, D. (1996). Achieving a 96.6 percent follow-up rate in a longitudinal study of drug abusers. Drug and Alcohol Dependence,41(3), 209–217.
de Wit, H. (2009). Impulsivity as a determinant and consequence of drug use: A review of underlying processes. Addiction Biology,14(1), 22–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1369-1600.2008.00129.x.
Eisinger, R. W., Dieffenbach, C. W., & Fauci, A. S. (2019). HIV viral load and transmissibility of HIV infection: Undetectable equals untransmittable. Journal of the American Medical Association,321(5), 451–452. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2018.21167.
Ellis, R. J., Childers, M. E., Cherner, M., Lazzaretto, D., Letendre, S., Grant, I., & HIV Neurobehavioral Research Center Group. (2003). Increased human immunodeficiency virus loads in active methamphetamine users are explained by reduced effectiveness of antiretroviral therapy. The Journal of Infectious Diseases,188(12), 1820–1826.
Ersche, K. D., Jones, P. S., Williams, G. B., Smith, D. G., Bullmore, E. T., & Robbins, T. W. (2013). Distinctive personality traits and neural correlates associated with stimulant drug use versus familial risk of stimulant dependence. Biological Psychiatry,74(2), 137–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.11.016.
Ferro, E. G., Weikum, D., Vagenas, P., Copenhaver, M. M., Gonzales, P., Peinado, J., … Altice, F. L. (2015). Alcohol use disorders negatively influence antiretroviral medication adherence among men who have sex with men in Peru. AIDS Care,27(1), 93–104. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540121.2014.963013.
Fleury, M.-J., Grenier, G., Bamvita, J.-M., Perreault, M., & Caron, J. (2015). Typology of individuals with substance dependence based on a montreal longitudinal catchment area study. Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research,42(4), 405–419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10488-014-0581-1.
Gamarel, K. E., Woolf-King, S. E., Carrico, A. W., Neilands, T. B., & Johnson, M. O. (2015). Stimulant use patterns and HIV transmission risk among HIV-serodiscordant male couples. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes,68(2), 147–151. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAI.0000000000000418.
Garrido, C., Zahonero, N., Corral, A., Arredondo, M., Soriano, V., & de Mendoza, C. (2009). Correlation between human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) RNA measurements obtained with dried blood spots and those obtained with plasma by use of Nuclisens EasyQ HIV-1 and Abbott RealTime HIV load tests. Journal of Clinical Microbiology,47(4), 1031–1036. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.02099-08.
Gilbert, M., Hottes, T. S., Kerr, T., Taylor, D., Fairley, C. K., Lester, R., … Ogilvie, G. (2013). Factors associated with intention to use internet-based testing for sexually transmitted infections among men who have sex with men. Journal of Medical Internet Research,15(11), e254. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.2888.
Grant, R. M., Lama, J. R., Anderson, P. L., McMahan, V., Liu, A. Y., Vargas, L., … Glidden, D. V. (2010). Preexposure chemoprophylaxis for HIV prevention in men who have sex with men. New England Journal of Medicine,363(27), 2587–2599. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1011205.
Hall, E. W., Ricca, A. V., Khosropour, C. M., & Sullivan, P. S. (2017). Capturing HIV incidence among MSM through at-home and self-reported facility-based testing. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes,75(5), e142–e144. https://doi.org/10.1097/qai.0000000000001338.
Hirshfield, S., Downing, M. J., Jr., Parsons, J. T., Grov, C., Gordon, R. J., Houang, S. T., … Chiasson, M. A. (2016). Developing a video-based eHealth intervention for HIV-positive gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. JMIR Research Protocols,5(2), e125. https://doi.org/10.2196/resprot.5554.
Hirshfield, S., Teran, R. A., Downing, M. J., Chiasson, M. A., Tieu, H. V., Dize, L., & Gaydos, C. A. (2018). Quantification of HIV-1 RNA among men who have sex with men using an at-home self-collected dried blood spot specimen: Feasibility study. JMIR Public Health Surveill,4(4), e10847. https://doi.org/10.2196/10847.
Horvath, K. J., Carrico, A. W., Simoni, J., Boyer, E. W., Amico, K. R., & Petroll, A. E. (2013). Engagement in HIV medical care and technology use among stimulant-using and nonstimulant-using men who have sex with men. AIDS Research and Treatment, 121352. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/121352.
Landovitz, R. J., Fletcher, J. B., Shoptaw, S., & Reback, C. J. (2015). Contingency management facilitates the use of postexposure prophylaxis among stimulant-using men who have sex with men. Open Forum Infectious Diseases,2(1), ofu114. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofu114.
Langebeek, N., Gisolf, E. H., Reiss, P., Vervoort, S. C., Hafsteinsdóttir, T. B., Richter, C., … Nieuwkerk, P. T. (2014). Predictors and correlates of adherence to combination antiretroviral therapy (ART) for chronic HIV infection: A meta-analysis. BMC Medicine,12(1), 142. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-014-0142-1.
Li, D. H., Janulis, P., & Mustanski, B. (2019). Predictors of correspondence between self-reported substance use and urinalysis screening among a racially diverse cohort of young men who have sex with men and transgender women. Addictive Behaviors,88, 6–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2018.08.004.
Lim, S. H., Ostrow, D., Stall, R., Chmiel, J., Herrick, A., Shoptaw, S., … Plankey, M. (2012). Changes in stimulant drug use over time in the MACS: Evidence for resilience against stimulant drug use among men who have sex with men. AIDS and Behavior,16(1), 151–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-010-9866-x.
Low, A. J., Mburu, G., Welton, N. J., May, M. T., Davies, C. F., French, C., … Vickerman, P. (2016). Impact of opioid substitution therapy on antiretroviral therapy outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinical Infectious Diseases,63(8), 1094–1104. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciw416.
Malta, M., Magnanini, M. M. F., Strathdee, S. A., & Bastos, F. I. (2010). Adherence to antiretroviral therapy among HIV-infected drug users: A meta-analysis. AIDS and Behavior,14(4), 731–747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-008-9489-7.
Manak, M. M., Hack, H. R., Shutt, A. L., Danboise, B. A., Jagodzinski, L. L., & Peel, S. A. (2018). Stability of human immunodeficiency virus serological markers in samples collected as HemaSpot and Whatman 903 dried blood spots. Journal of Clinical Microbiology,56, e00933. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.00933-18.
Mansergh, G., Purcell, D. W., Stall, R., McFarlane, M., Semaan, S., Valentine, J., & Valdiserri, R. (2006). CDC consultation on methamphetamine use and sexual risk behavior for HIV/STD infection: Summary and suggestions. Public Health Reports,121(2), 127–132. https://doi.org/10.1177/003335490612100205.
Marks, G., Gardner, L. I., Rose, C. E., Zinski, A., Moore, R. D., Holman, S., … Giordano, T. P. (2015). Time above 1500 copies: A viral load measure for assessing transmission risk of HIV-positive patients in care. AIDS,29(8), 947–954. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAD.0000000000000640.
Mayer, K. H., Skeer, M. R., O’Cleirigh, C., Goshe, B. M., & Safren, S. A. (2014). Factors associated with amplified HIV transmission behavior among american men who have sex with men engaged in care: Implications for clinical providers. Annals of Behavioral Medicine,47(2), 165–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12160-013-9527-1.
McCarty-Caplan, D., Jantz, I., & Swartz, J. (2014). MSM and drug use: A latent class analysis of drug use and related sexual risk behaviors. AIDS and Behavior,18(7), 1339–1351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-013-0622-x.
McCray, E., & Mermin, J. (2017). Dear colleague: September 27, 2017. https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/library/dcl/dcl/092717.html.
Morin, S. F., Myers, J. J., Shade, S. B., Koester, K., Maiorana, A., & Rose, C. D. (2007). Predicting HIV transmission risk among HIV-infected patients seen in clinical settings. AIDS and Behavior,11(1), 6–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-007-9253-4.
National Institute on Drug Abuse. (2018). MDMA (Ecstasy/Molly). https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/drugfacts/mdma-ecstasymolly.
Oldfield, B. J., Muñoz, N., Mcgovern, M. P., Funaro, M., Villanueva, M., Tetrault, J. M., & Edelman, E. J. (2018). Integration of care for HIV and opioid use disorder: A systematic review of interventions in clinical and community-based settings. AIDS,33, 873–884. https://doi.org/10.1097/qad.0000000000002125.
Palamar, J. J., Salomone, A., Cleland, C. M., & Sherman, S. (2018). Willingness to provide a hair sample for drug testing among electronic dance music party attendees. Substance Abuse,25, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/08897077.2018.1469106.
Quinn, T. C., Wawer, M. J., Sewankambo, N., Serwadda, D., Li, C., Wabwire-Mangen, F., … Gray, R. H. (2000). Viral load and heterosexual transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Rakai Project Study Group. New England Journal of Medicine,342(13), 921–929. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm200003303421303.
Rondinelli, A. J., Ouellet, L. J., Strathdee, S. A., Latka, M. H., Hudson, S. M., Hagan, H., & Garfein, R. S. (2009). Young adult injection drug users in the United States continue to practice HIV risk behaviors. Drug and Alcohol Dependence,104(1), 167–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2009.05.013.
Santos, G.-M., Coffin, P. O., Das, M., Matheson, T., DeMicco, E., Raiford, J. L., … Herbst, J. H. (2013). Dose–response associations between number and frequency of substance use and high-risk sexual behaviors among HIV-negative substance-using men who have sex with men (SUMSM) in San Francisco. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes,63(4), 540–544. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAI.0b013e318293f10b.
Sharma, A., Stephenson, R. B., White, D., & Sullivan, P. S. (2014). Acceptability and intended usage preferences for six HIV testing options among internet-using men who have sex with men. SpringerPlus,3(1), 109. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-3-109.
Sharma, A., Sullivan, P. S., & Khosropour, C. M. (2011). Willingness to take a free home HIV test and associated factors among internet-using men who have sex with men. Journal of the International Association of Physicians in AIDS Care,10, 357–364. https://doi.org/10.1177/1545109711404946.
Shoptaw, S. (2017). HIV positive gay men, MSM, and substance use: Perspectives on HIV prevention. In L. Wilton (Ed.), Understanding prevention for HIV positive gay men: Innovative approaches in addressing the AIDS epidemic (pp. 75–92). New York, NY: Springer.
Shoptaw, S., & Reback, C. J. (2007). Methamphetamine use and infectious disease-related behaviors in men who have sex with men: Implications for interventions. Addiction,102(s1), 130–135. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2006.01775.x.
Stall, R., & Purcell, D. W. (2000). Intertwining epidemics: A review of research on substance use among men who have sex with men and its connection to the AIDS epidemic. AIDS and Behavior,4(2), 181–192. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1009516608672.
The Lancet HIV. (2017). U = U taking off in 2017. Lancet HIV,4(11), e475. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2352-3018(17)30183-2.
Verdejo-García, A., Lawrence, A. J., & Clark, L. (2008). Impulsivity as a vulnerability marker for substance-use disorders: Review of findings from high-risk research, problem gamblers and genetic association studies. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews,32(4), 777–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2007.11.003.
Walters, S. M., Rivera, A. V., Reilly, K. H., Anderson, B. J., Bolden, B., Wogayehu, A., … Braunstein, S. (2018). Exchange sex among persons who inject drugs in the new york metropolitan area: The importance of local context, gender and sexual identity. AIDS and Behavior,22(9), 2773–2787. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-018-2039-z.
Wilson, I. B., Lee, Y., Michaud, J., Fowler, F. J., & Rogers, W. H. (2016). Validation of a new three-item self-report measure for medication adherence. AIDS and Behavior,20(11), 2700–2708. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-016-1406-x.
Zhang, J., & Yu, K. F. (1998). What’s the relative risk? A method of correcting the odds ratio in cohort studies of common outcomes. Journal of the American Medical Association,280(19), 1690–1691. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.280.19.1690.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health (R01-MH100973-03S1) to Sabina Hirshfield, principal investigator. Richard Teran was supported by a pre-doctoral fellowship in the Global HIV Implementation Science Research training program sponsored by the Mailman School of Public Health, Columbia University, with funding from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (T32 AI114398, PI: Howard). Suzan Walters was supported with funding from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (T32 DA007233-31, PI: Falkin) and Interdisciplinary Research Training Institute on Hispanic Drug Abuse (R25 DA026401; PI Avelardo Valdez). The authors would like to thank Steven Houang, Irene Yoon, and Dayana Bermudez for their contributions to study enrollment, data collection, and retention activities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teran, R.A., Carrico, A.W., Horvath, K.J. et al. Stimulant Use and Study Protocol Completion: Assessing the Ability of Men Who Have Sex with Men to Collect Dried Blood Spots for Laboratory Measurement of HIV Viral Load. Arch Sex Behav 49, 195–209 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10508-019-01515-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10508-019-01515-x