Abstract
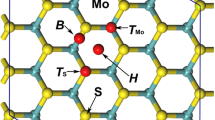
How to remove radionuclides from the radioactive wastewater quickly and efficiently is of great significance for mitigating the adverse effects of nuclear accident. Our previous researches have shown that metallic radionuclides (Cs+, Sr2+, and Ba2+) can be chemisorbed on monolayer 2H-MoS2. To enhance the adsorption capacity of the monolayer 2H-MoS2 to the metallic radionuclides, the effects of phase, strain, pressure, vacancy, and doping on the adsorption of the metallic radionuclides on the monolayer 2H-MoS2 were investigated by using the first principles calculation method in this paper. The calculation results show that the adsorption energy of the metallic radionuclides on the monolayer 2H-MoS2 is decreased by phase, strain, vacancy, and doping, while the pressure has little effect on the adsorption energy. The adsorption energy change indicates that the adsorption of the metallic radionuclides on the monolayer 2H-MoS2 is enhanced by phase, strain, vacancy, and doping. The adsorption energy change is mainly contributed by the electron structure change, which caused by phase, strain, vacancy, and doping. Especially, the change of charge transfer between the metallic radionuclides and their nearest atoms on the monolayer 2H-MoS2 is a very critical factor.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai, Y.J., Liu, Y., Lan, W.Y., Jin, J.R., Xing, J.L., Zou, Y.D., Zhao, C.F., Wang, X.K.: The effect of pH on the U(VI) sorption on graphene oxide (GO): a theoretical study. Chem. Eng. J. 343, 460 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.027
Aleman, S.E.: Modeling ion-exchange for cesium removal from alkaline radioactive waste solutions. Sep. Sci. Technol. 44(13), 2983 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1080/01496390903182545
Avramenko, V.A., Sergienko, V.I., Sokol’Nitskaya, T.A.: Application of sorption-reagent materials in the technology of liquid radioactive waste treatment. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 50(4), 593 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040579516040035
Böker, T., Severin, R., Müller, A., Janowitz, C., Manzke, R., Voss, D., Krüger, P., Mazur, A., Pollmann, J.: Band structure of MoS\(_2\), MoSe\(_2\), and alpha-MoTe\(_2\): angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy and ab-initio calculations. Phys. Rev. B 64(23), 235305 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.64.235305
Burke, K., Perdew, J.P., Wang, Y.: Derivation of a generalized gradient approximation: The PW91 density functional. In: Dobson, J.F., Vignale, G., Das, M.P. (eds.) Electronic Density Functional Theory. Springer, Boston, MA (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-0316-7_7
Cao, J., Zhou, J., Zhang, Y., Liu, X.: Theoretical study of H2 adsorbed on monolayer MoS2 doped with N, Si, P. Microelectron. Eng. 190, 63 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2018.01.012
Castro Neto, A.H., Guinea, F., Peres, N.M.R., Novoselov, K.S., Geim, A.K.: The electronic properties of graphene. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81(1), 109 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.81.109
Chang, K., Hai, X., Pang, H., Zhang, H., Shi, L., Liu, G., Liu, H., Zhao, G., Li, M., Ye, J.: Targeted synthesis of 2H- and 1T-phase MoS2 monolayers for catalytic hydrogen evolution. Adv. Mater. 28(45), 10033 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201603765
Cho, S.Y., Kim, S.J., Lee, Y., Kim, J.S., Jung, W.B., Yoo, H.W., Kim, J., Jung, H.T.: Highly enhanced gas adsorption properties in vertically aligned MoS\(_2\) layers. ACS Nano 9(9), 9314 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b04504
Choi, S.H., Stephen, B., Park, J.H., Lee, J.S., Kim, S.M., Yang, W., Kim, K.K.: Water-assisted synthesis of molybdenum disulfide film with single organic liquid precursor. Sci. Rep. 7(1), 1983 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-02228-8
Choudri, B.S., Baawain, M.: Radioactive wastes. Water Environ. Res. 87(10), 1471 (2015). https://doi.org/10.2175/106143015X14338845156065
Clark, S.J., Segall, M.D., Pickard, C.J., Hasnip, P.J., Probert, M.I.J., Refson, K., Payne, M.C.: First principles methods using CASTEP. Z. Kristallogr. 220(5/6), 567 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1524/zkri.220.5.567.65075
Corner, A., Dan, V., Spence, A., Poortinga, W., Demski, C., Pidgeon, N.: Nuclear power, climate change and energy security: exploring British public attitudes. Energy Policy 39(9), 4823 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2011.06.037
Ding, Z., Pei, Q.X., Jiang, J.W., Zhang, Y.W.: Manipulating the thermal conductivity of monolayer MoS2 via lattice defect and strain engineering. J. Phys. Chem. C 38(119), 16358 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b03607
Ding, K., Lin, Y., Huang, M.: The enhancement of NO detection by doping strategies on monolayer MoS2. Vacuum 130, 146 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2016.05.005
Fan, X., Xu, P., Zhou, D., Sun, Y., Li, Y.C., Nguyen, M.A.T., Terrones, M., Mallouk, T.E.: Fast and efficient preparation of exfoliated 2H MoS2 nanosheets by sonication-assisted lithium intercalation and infrared laser-induced 1T to 2H phase reversion. Nano Lett. 15(9), 5956 (2015a). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b02091
Fan, X., Chang, C.H., Zheng, W., Kuo, J.L., Singh, D.J.: The electronic properties of single-layer and multilayer MoS2 under high pressure. J. Phys. Chem. C 119(19), 10189 (2015b). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b00317
Fan, Y., Zhang, J., Qiu, Y., Jia, Z., Hu, G.: A DFT study of transition metal (Fe Co, Ni, Cu, Ag, Au, Rh, Pd, Pt and Ir)-embedded monolayer MoS2 for gas adsorption. Comp. Mater. Sci. 138, 255 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2017.06.029
Feng, L.P., Su, J., Liu, Z.T.: Effect of vacancies in monolayer MoS2 on electronic properties of Mo–MoS2 contacts. RSC Adv. 5(26), 20538 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra15218b
Feng, L.P., Li, A., Su, J., Zhang, Y., Liu, Z.T.: Influence of Mo-vacancy concentration on the structural, electronic and optical properties of monolayer MoS2: a first-principles study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 209, 146 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.01.015
Hao, L., Cao, Y., Jing, Z., Feng, J., Cao, J., Hai, G.: Adsorption of NO2, NH3 on monolayer MoS2 doped with Al, Si, and P: a first-principles study. Chem. Phys. Lett. 643, 27 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2015.10.077
Hirshfeld, F.L.: Bonded-atom fragments for describing molecular charge densities. Theor. Chim. Acta 44(2), 129 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00549096
Ikeda, K., Tashimo, M., Ujita, H., Matsui, K.: Nuclear energy role for sustainable development of environment, economy, and energy. J. Atom. Energy Soc. Jpn. 49(5), 330 (2007)
Jie, S., Ning, L., Zhang, Y., Feng, L., Liu, Z.: Role of vacancies in tuning the electronic properties of Au-MoS2 contact. AIP Adv. 65(7), 125706 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4927853
Kou, L., Du, A., Chen, C., Frauenheim, T.: Strain engineering of selective chemical adsorption on monolayer MoS2. Nanoscale 6(10), 5156 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR06670C
Lauritsen, J.V., Kibsgaard, J., Helveg, S., Topsoe, H., Clausen, B.S., Laegsgaard, E., Besenbacher, F.: Size-dependent structure of MoS\(_2\) nanocrystals. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2(1), 53 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2006.171
Lazar, P., Martincova, J., Otyepka, M.: Is single layer MoS2 stable in the air? Chem. Eur. J. 23(53), 13233 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201702860
Le, H.M., Bui, V.Q., Tran, P.H., Pham-Tran, N.N., Kawazoe, Y., Nguyen-Manh, D.: The prospect of sensitizing organic dyes attached to the MoS\(_2\) surface: physical insights from density functional theory investigations. Chem. Phys. Lett. 667, 290 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2016.11.007
Lebegue, S., et al.: Electronic structure of two-dimensional crystals from ab-initio theory. Phys. Rev. B 79(11), 5409 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.79.115409
Lee, C., Wei, X., Kysar, J.W., Hone, J.: Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 321(5887), 385 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1157996
Lei, W., Fei, C., Ji, X.: Shape consistency of MoS2 flakes grown using chemical vapor deposition. Appl. Phys. Express 10(6), 065201 (2017). https://doi.org/10.7567/APEX.10.065201
Li, H., Henkelman, G.: Dehydrogenation selectivity of ethanol on close-packed transition metal surfaces: a computational study of monometallic, Pd/Au, and Rh/Au catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 121(49), 27504 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b09953
Li, F., Yan, Y., Han, B., Li, L., Huang, X., Yao, M., Gong, Y., Jin, X., Liu, B., Zhu, C.: Pressure confinement effect in MoS2 monolayers. Nanoscale 7(19), 9075 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5nr00580a
Li, H., Huang, M., Cao, G.: Markedly different adsorption behaviors of gas molecules on defective monolayer MoS\(_2\): a first-principles study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18(22), 15110 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP01362G
Li, H., Shin, K., Henkelman, G.: Effects of ensembles, ligand, and strain on adsorbate binding to alloy surfaces. J. Chem. Phys. 149, 174705 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5053894
Li, H., Luo, L., Kunal, P., Duan, Z.Y., Yang, J.C., Crooks, R.M., Henkelman, G.: Oxygen reduction reaction on classically immiscible bimetallics: a case study of RhAu. J. Phys. Chem. C 122(5), 2712 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b10974
Li, H., Evans, E., Mullins, C., Henkelman, G.: Ethanol decomposition on Pd-Au alloy catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 122(38), 22024 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b08150
Li, H., Chai, W., Henkelman, G.: Selectivity for ethanol partial oxidation: the unique chemistry of single-atom alloy catalysts on Au, Ag, and Cu(111). J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 23868 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TA04572D
Li, H., Guo, S., Shin, K., Wong, M., Henkelman, G.: Design of a Pd–Au nitrite reduction catalyst by identifying and optimizing active ensembles. ACS Catal. 9(9), 7957 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.9b02182
Liu, X., Li, L., Wei, Y., Zheng, Y., Xiao, Q., Feng, B.: Facile synthesis of boron- and nitride-doped MoS\(_2\) nanosheets as fluorescent probes for the ultrafast, sensitive, and label-free detection of Hg\(^{2+}\). Analyst 140(13), 4654 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5AN00641D
Liu, X., Wang, X., Li, J., Wang, X.: Ozonated graphene oxides as high efficient sorbents for Sr(II) and U(VI) removal from aqueous solutions. Sci. China Chem. 59(7), 869 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-016-5594-z
Liu, X., Xu, X.T., Sun, J., Alsaedi, A., Hayat, T., Li, J.X., Wang, X.K.: Insight into the impact of interaction between attapulgite and graphene oxide on the adsorption of U(VI). Chem. Eng. J. 343, 217 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.02.113
Liu, L., Wu, J., Wu, L., Ye, M., Liu, X., Wang, Q., Hou, S., Lu, P., Sun, L.: Phase-selective synthesis of 1T’ MoS2 monolayers and heterophase bilayers. Nat. Mater. 17(12), 1108 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-018-0187-1
Lu, N., Guo, H., Li, L., Dai, J., Wang, L., Mei, W.N., Wu, X., Zeng, X.C.: MoS\(_2\)/MX\(_2\) heterobilayers: bandgap engineering via tensile strain or external electrical field. Nanoscale 6(5), 2879 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nr06072a
Ma, D., Ju, W., Li, T., Zhang, X., He, C., Ma, B., Lu, Z., Yang, Z.: The adsorption of CO and NO on the MoS\(_2\) monolayer doped with Au, Pt, Pd, or Ni: A first-principles study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 383, 98 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.04.171
Ma, D., Wang, Q., Li, T., He, C., Ma, B., Tang, Y., Lu, Z., Yang, Z.: Repairing sulfur vacancies in the MoS2 monolayer by using CO, NO and NO2 molecules. J. Mater. Chem. C 4(29), 7093 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TC01746K
Ma, D., Ju, W., Li, T., Gui, Y., He, C., Ma, B., Tang, Y., Lu, Z., Yang, Z.: Formaldehyde molecule adsorption on the doped monolayer MoS2: a first-principles study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 371, 180 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.02.230
Matsui, K., Ujita, H., Tashimo, M.: Role of nuclear energy in environment, economy and energy issues of the 21st century green house gas emission constraint effects. Prog. Nucl. Energy 50(2), 97 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnucene.2007.10.010
Menyah, K., Wolde-Rufael, Y.: CO\(_2\) emissions, nuclear energy, renewable energy and economic growth in the US. Energy Policy 38(6), 2911 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2010.01.024
Mu, X.L., Gao, X., Zhao, H.T., George, M., Wu, T., Zhejiang, J.: Density functional theory study of the adsorption of elemental mercury on a 1T-MoS2 monolayer. Univ Sci. A 19(1), 60 (2018)
Nayak, A.P., Pandey, T., Voiry, D., Liu, J., Moran, S.T., Sharma, A., Tan, C., Chen, C.H., Li, L.J., Chhowalla, M.: Pressure-dependent optical and vibrational properties of monolayer molybdenum disulfide. Nano Lett. 15(1), 346 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl5036397
Nguyen, E.P., Carey, B.J., Daeneke, T., Jian, Z.O., Latham, K., Zhuiykov, S., Kalantar-Zadeh, K.: Investigation of two-solvent grinding-assisted liquid phase exfoliation of layered MoS2. Chem. Mater. 27(1), 53 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm502915f
Novoselov, K.S., Geim, A.K., Morozov, S.V., Jiang, D., Zhang, Y., Dubonos, S.V., Grigorieva, I.V., Firsov, A.A.: Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 306(5696), 666 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1102896
Osmanlioglu, A.E.: Decontamination and solidification of liquid radioactive waste using natural zeolite. J. Mater. Cycles Waste 17(4), 1 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-014-0299-x
Oura, K., Lifshit, A.A., Saranin, A., Zotov, A.V., Katayarna, M.: Surface Science an Introduction. Springer, New York (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-05179-5
Pei, H., Wang, J., Yang, Q., Yang, W., Hu, N., Suo, Y., Zhang, D., Li, Z., Wang, J.: Interfacial growth of nitrogen-doped carbon with multi-functional groups on the MoS\(_2\)skeleton for efficient Pb(II) removal. Sci. Total Environ. s631–632, 912 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.324
Perdew, J.P., Yue, W.: Accurate and simple density functional for the electronic exchange energy: generalized gradient approximation. Phys. Rev. B 33(12), 8800 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.33.8800
Perdew, J.P., Burke, K., Ernzerhof, M.: Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phy. Rev. Lett. 77(18), 3865 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevlett.77.3865
Primo, A., He, J., Jurca, B., Cojocaru, B., Bucur, C., Parvulescu, V., Garcia, H.: CO2 methanation catalyzed by oriented MoS2 nanoplatelets supported on few layers graphene. Appl. Catal. B 245, 351 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.12.034
Rao, R., Islam, A.E., Campbell, P.M., Vogel, E.M., Maruyama, B.: In situ thermal oxidation kinetics in few layer MoS2. 2D Mater 4(2), 025058 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1583/aa6532
Sahoo, M.P.K., Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Shimada, T., Kitamura, T.: Modulation of gas adsorption and magnetic properties of monolayer-MoS2 by antisite defect and strain. J. Phys. Chem. C 120(26), 14113 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b03284
Sarkar, D., Xie, X., Kang, J., Zhang, H., Liu, W., Navarrete, J., Moskovits, M., Banerjee, K.: Functionalization of transition metal dichalcogenides with metallic nanoparticles: implications for doping and gas-sensing. Nano Lett. 15(5), 2852 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl504454u
Sen, H.S., Sahin, H., Peeters, F.M., Durgun, E.: Monolayers of MoS2 as an oxidation protective nanocoating material. J. Appl. Phys. 116(8), 083508 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4893790
Sharma, A., Srivastava, A., Husain, M., Khan, M.S.: Computational investigations of Cu-embedded MoS2 sheet for CO oxidation catalysis. J. Mater. Sci. 53(13), 9578 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2269-5
Shinohara, N., Yoshidaohuchi, H.: Radiocesium contamination in house dust within evacuation areas close to the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant. Environ. Int. 114, 107 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.02.015
Splendiani, A., Sun, L., Zhang, Y., Li, T., Kim, J., Chim, C.Y., Galli, G., Wang, F.: Emerging photoluminescence in monolayer MoS\(_2\). Nano Lett. 10(4), 1271 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl903868w
Sujish, D., Mohanakrishnan, G., Sharma, B.K., Babu, C.A., Rajan, K.K.: Application of nanofiltration membrane and ethyleneimine oligomer mixture for selective separation of strontium from a simulated nuclear waste solution. Desalin. Water Treat. 52(1–3), 401 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.808789
Sun, Y., Wang, X., Song, W., Lu, S., Chen, C., Wang, X.: Mechanistic insights on the decontamination of Th(IV) on graphene oxide-based composites by EXAFS and modeling techniques. Nano Environ. Sci. 4(1), 222 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6en00470a
Valsala, T.P., Sonavane, M.S., Kore, S.G., Sonar, N.L., De, V., Raghavendra, Y., Chattopadyaya, S., Dani, U., Kulkarni, Y., Changrani, R.D.: Treatment of low level radioactive liquid waste containing appreciable concentration of TBP degraded products. J. Hazard. Mater. 196(12), 22 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.08.065
Wang, H., Wen, F., Li, X., Gan, X., Yang, Y., Chen, P., Zhang, Y.: Cerium-doped MoS\(_2\) nanostructures: efficient visible photocatalysis for Cr(VI) removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 170, 190 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.06.049
Wang, Z., Sim, A., Urban, J.J., Mi, B.: Removal and recovery of heavy metal ions by two-dimensional MoS2 nanosheets: performance and mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 52, 9741 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2016.11.007
Wang, W., Yang, C., Bai, L., Li, M., Li, W.: First-principles study on the structural and electronic properties of monolayer MoS\(_2\) with S-vacancy under uniaxial tensile strain. Nanomaterials 8(2), 74 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020074
Wang, J., Deng, H., Li, X., Yang, C., Xia, Y.: Visible-light photocatalysis enhanced room-temperature formaldehyde gas sensing by MoS2/rGO hybrids. Sensor. Actuat. B 304, 127317 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127317
Xu, B., Wang, L., Chen, H.J., Zhao, J., Liu, G., Wu, M.S.: Adsorption and diffusion of lithium on 1T-MoS2 monolayer. Comput. Mater. Sci. 93, 86 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2014.06.033
Xu, Z., Lv, X., Chen, J., Jiang, L., Lai, Y., Li, J.: First principles study of adsorption and oxidation mechanism of elemental mercury by HCl over MoS\(_2\)(1 0 0) surface. Chem. Eng. J. 308, 1225 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.10.059
Xue, L., Li, Y., Liu, X., Liu, Q., Shang, J., Duan, H., Dai, L., Shui, J.: Zigzag carbon as efficient and stable oxygen reduction electrocatalyst for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Nat. Commun. 9, 3819 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06279-x
Ye, G., Gong, Y., Lin, J., Li, B., He, Y., Pantelides, S.T., Zhou, W., Vajtai, R., Ajayan, P.M.: Defects lnolayer MoS2 for improved hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Lett. 16(2), 1097 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b04331
Yeon, C., Yun, S.J., Yang, J., Youn, D.H., Lim, J.W.: Na-cation-assisted exfoliation of MX2 (M = Mo, W; X = S, Se) nanosheets in an aqueous medium with the aid of a polymeric surfactant for flexible polymer-nanocomposite memory applications. Small 14(2), 1702747 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201702747
Yu, X., Prevot, M.S., Sivula, K.: Multiflake thin film electronic devices of solution processed 2D MoS2 enabled by sonopolymer assisted exfoliation and surface modification. Chem. Mater. 26(20), 5892 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm502378g
Yue, Q., Chang, S., Qin, S., Li, J.: Functionalization of monolayer MoS\(_2\) by substitutional doping: a first-principles study. Phys. Lett. A 377(19–20), 1362 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2013.03.034
Zhang, Y.H., Chen, J.L., Yue, L.J., Zhang, H.L., Li, F.: Tuning CO sensing properties and magnetism of MoS\(_2\) monolayer through anchoring transition metal dopants. Comput. Theor. Chem. 1104, 12 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comptc.2017.01.026
Zhang, Z., Zhao, Q., Huang, M., Zhang, X., Ouyang, X.: Chemisorption of metallic radionuclides on a monolayer MoS\(_2\) nanosheet. Nanoscale Adv. 1, 114 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8na00057
Zhao, G., Wen, T., Yang, X., Yang, S., Liao, J., Hu, J., Shao, D., Wang, X.: Preconcentration of U(VI) ions on few-layered graphene oxide nanosheets from aqueous solutions. Dalton Trans. 41(20), 6182 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2DT00054G
Zhao, Q., Zhang, Z., Ouyang, X.: Adsorption of radionuclides on the monolayer MoS\(_2\). Mater. Res. Express 5, 045506 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aaba90
Zheng, Y., Yan, H., Shu, H., Zhou, X., Ding, J., Chen, X., Wei, L.: The effect of lithium adsorption on the formation of 1T-MoS2 phase based on first-principles calculation. Phys. Lett. A 380(20), 1767 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2016.03.009
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science and Technology Major Project of China (Grant No. 2019XS06004009), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 2018ZD10), and the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 1192016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Zhao, Q., Chen, K. et al. Effects of phase, strain, pressure, vacancy, and doping on the adsorption of metallic radionuclides on monolayer 2H-MoS2. Adsorption 26, 521–535 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-020-00216-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-020-00216-5