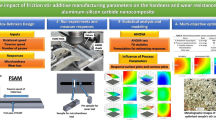
Abstract
C/SiC has excellent mechanical properties and is extensively utilized in the aerospace field. Meanwhile, it is a typical intractable material in virtue of its special intrinsic structure. To investigate the grinding force and material removal mechanism of fiber reinforced CMC, a unidirectional C/SiC composite material was designed and prepared. A series of particular surface grinding experiments were carried out, and then the grinding force model was established based on multiple-exponential function method. Furthermore, the surface morphology and grinding mechanism of the composites were analyzed. The results show that the grinding parameters (wheel speed, grinding depth, feed speed) have a significant impact on the grinding force, and the order of grinding force is as follows: Normal>Longitudinal>Transverse. The R2 (Goodness of fit) values of the grinding force model are all above 0.9, which demonstrates the models can reliably predict the grinding force of the unidirectional C/SiC composite grinding. Besides, the dominant removal mechanism of C/SiC composites is the brittle fracture, and its failure modes are the combination of matrix cracking, fiber breakage and interface debonding. Then, the factors affecting the grinding force in surface grinding of the composite are revealed. The research results can provide theoretical support for improving grinding efficiency and precision machining of composites.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu, X.T., Sun, Z.G., Yang, F.S., Chen, X.H., Song, Y.D.: Fatigue hysteresis behavior of 2.5D-woven C/SiC composites: theory and experiments. Appl. Compos. Mater. 24, 1387–1403 (2017)
Cao, X.Y., Lin, B., Zhang, X.F.: A study on grinding surface waviness of woven ceramic matrix composites. Appl.Surf. Sci. 270, 503–512 (2013)
Wang, Y.Q., Zhang, L.T., Cheng, L.F.: Effect of yarn sizes on the tensile damage evolution of a C/SiC composite fabricated by chemical vapor infiltration. Appl. Compos. Mater. 18, 165–174 (2011)
Ding, K., Fu, Y.C., Su, H.H., Chen, Y., Yu, X.Z., Ding, G.Z.: Experimental studies on drilling tool load and machining quality of C/SiC composites in rotary ultrasonic machining. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 214, 2900–2907 (2014)
Wang, Y.Q., Zhang, L.T., Cheng, L.F., Ma, J.Q., Zhang, W.H.: Tensile performance and damage evolution of a 2.5D-C/SiC composite characterized by acoustic emission. Appl. Compos. Mater. 15, 183–188 (2008)
Jiang, F.R., Cheng, L.F., Zhang, J.X., Wang, Y.G.: Fabrication of barium-strontium aluminosilicate coatings on C/SiC composites via laser cladding. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 331, 66–171 (2017)
Zhang, W.H., Cheng, L.F., Liu, Y.S., Zhang, L.T., Yang, W.B., Zhou, S.T.: Fracture behaviors and mechanism of 2D-C/SiC-BCx composite under tensile load. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 530, 297–303 (2011)
Liu, X.C., Cheng, L.F., Zhang, L.T., Dong, N., Wu, S.J., Meng, Z.X.: Tensile properties and damage evolution in a 3D-C/SiC composite at cryogenic temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 528, 7524–7528 (2011)
Liu, Q., Huang, G.Q., Xu, X.P., Fang, C.F., Cui, C.C.: A study on the surface grinding of 2D-C/SiC composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 93, 1595–1603 (2017)
Adibi, H., Esmaeili, H., Rezaei, S.M.: Study on minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) in grinding of carbon fiber-reinforced SiC matrix composites (CMCs). Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 95, 3753–3767 (2017)
Ding, K., Fu, Y.C., Su, H.H., Cui, F.F., Li, Q.L., Lei, W.N., Xu, H.X.: Study on surface/subsurface breakage in ultrasonic assisted grinding of C/SiC composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 91, 3095–3105 (2017)
Wang, H., Ning, F.D., Hu, Y.B., Fernando, P., Pei, Z.J., Cong, W.L.: Surface grinding of carbon fiber-reinforced plastic composites using rotary ultrasonic machining: effects of tool variables. Advan. Mech. Eng. 8, 1687814016670284 (2016)
Zhang, L.F., Ren, C.Z., Ji, C.H., Wang, Z.Q., Chen, G.: Effect of fiber orientations on surface grinding process of unidirectional C/SiC composites. Appl.Surf. Sci. 366, 424–431 (2016)
Cao, X.Y., Lin, B., Zhang, X.F.: Investigations on grinding process of woven ceramic matrix composite based on reinforced fiber orientations. Compos. Part B: Eng. 71, 184–192 (2015)
Cao, X.Y., Lin, B., Wang, Y., Wang, S.L.: Influence of diamond wheel grinding process on surface micro-topography and properties of SiO2/SiO2 composite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 292, 181–189 (2014)
Sasahara, H., Kikuma, T., Koyasu, R., Yao, Y.: Surface grinding of carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP) with an internal coolant supplied through grinding wheel. Precis. Eng. 38, 775–782 (2014)
Tawakoli, T., Azarhoushang, B.: Intermittent grinding of ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) utilizing a developed segmented wheel. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 51, 112–119 (2011)
Li, Z.C., Jiao, Y., Deines, T.W., Pei, Z.J., Treadwell, C.: Rotary ultrasonic machining of ceramic matrix composites: feasibility study and designed experiments. Int. J.Mach. Tools Manuf. 45, 1402–1411 (2005)
Liu, Q., Huang, G.Q., Fang, C.F., Cui, C.C., Xu, X.P.: Experimental investigations on grinding characteristics and removal mechanisms of 2D-Cf/C-SiC composites based on reinforced fiber orientations. Ceram. Int. 43, 15266–15274 (2017)
Qu, S.S., Gong, Y.D., Yang, Y.Y., Wen, X.L., Yin, G.Q.: Grinding characteristics and removal mechanisms of unidirectional carbon fiber reinforced silicon carbide ceramic matrix composites. Ceram. Int. 45, 3059–3071 (2019)
Li, Y.C., Ge, X., Wang, H., Hu, Y.B., Ning, F.D., Cong, W.L., Ren, C.Z.: Study of material removal mechanisms in grinding of C/SiC composites via single-abrasive scratch tests. Ceram. Int. 45, 4729–4738 (2019)
Du, J.G., Ming, W.Y., Ma, J., He, W.B., Cao, Y., Li, X.K., Liu, K.: New observations of the fiber orientations effect on machinability in grinding of C/SiC ceramic matrix composite. Ceram. Int. 44, 13916–13928 (2018)
Zhang, L.F., Ren, C.Z., Zhou, C.L., Xu, H.Z., Jin, X.M.: Single fiber push-out characterization of interfacial mechanical properties in unidirectional CVI-C/SiC composites by thenano-indentation technique. Appl.Surf. Sci. 357, 1427–1433 (2015)
Xie, Y.P., Cheng, L.F., Li, L.J., Mei, H., Zhang, L.T.: Fabrication of laminated SiCw/SiC ceramic composites by CVI. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 33, 1701–1706 (2013)
Nie, J.J., Xu, Y.D., Zhang, L.T., Cheng, L.F., Ma, J.Q.: Microstructure and tensile behavior of multiply needled C/SiC composite fabricated by chemical vapor infiltration. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209, 572–576 (2009)
Wei, X., Cheng, L.F., Zhang, L.T., Xu, Y.D., Zeng, Q.F.: Modeling the effects of reactor wall reaction on isothermal CVI process of C/SiC composites. Comput. Mater. Sci. 38, 702–706 (2007)
Li, K., Liao, T.W.: Surface/subsurface damage and the fracture strength of ground ceramics. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 57, 207–220 (1996)
Chuang, T., Jahanmir, S., Tang, H.C.: Finite element simulation of straight plunge grinding for advanced ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 23, 1723–1733 (2003)
Liu, Q., Huang, G.Q., Xu, X.P., Fang, C.F., Cui, C.C.: Influence of grinding fiber angles on grinding of the 2D-Cf/C-SiC composites. Ceram. Int. 44, 12774–12782 (2018)
Chakladar, N.D., Mandal, P., Potluri, P.: Effects of inter-tow angle and tow sizeon carbon fibre friction. Compos. Part A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 65, 115–124 (2014)
Malkin, S., Guo, C.: Grinding Technology: Theory and Applications of Machining with Abrasives (1989)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Scientific Research Foundation of Civil Aviation University of China (No. 2017QD08S), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 3122018C007), United National Science Funds and Civil Aviation Funds (No. U1633104), Open Funds of the State Key Lab of Digital Manufacturing Equipment & Technology (No. DMETKF2017018) and Tianjin Science Funds for the Special of Science & Technology (No.17JCTPJC51800).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Wang, S., Li, Z. et al. Influence Factors on Grinding Force in Surface Grinding of Unidirectional C/SiC Composites. Appl Compos Mater 26, 1073–1085 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-019-09767-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-019-09767-5