Abstract
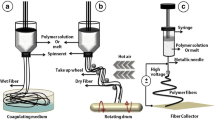
Small-diameter tissue-engineered vascular grafts are urgently needed for clinic arterial substitute. To simulate the structures and functions of natural blood vessels, we designed a novel triple-layer poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) fibrous vascular graft by combining E-jet 3D printing and electrospinning techniques. The resultant vascular graft consisted of an interior layer comprising 3D-printed highly aligned strong fibers, a middle layer made by electrospun densely fibers, and an exterior structure composed of mixed fibers fabricated by co-electrospraying. The biocompatible triple-layer graft was used for in vivo implantation, and results demonstrated that the longitudinally-aligned fibers within the lumen of the graft could enhance the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells, while maintained good mechanical properties. The exterior layer provided a pathway that encouraged cells to migrate into the scaffold after implantation. This experimental graft overcame the limitations of conventionally electrospun vascular grafts of inadequate porosity and lowly cell penetration. The unique structure of the triple-layer vascular graft promoted cell growth and infiltration in vivo, thus provided an encouraging substitute for in situ tissue engineering.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, B. M., A. O. Gee, R. B. Metter, A. S. Nathan, R. L. Marklein, J. A. Burdick, and R. L. Mauck. The potential to improve cell infiltration in composite fiber-aligned electrospun scaffolds by the selective removal of sacrificial fibers. Biomaterials 29:2348–2358, 2008.
Campbell, J. J., A. Husmann, R. D. Hume, C. J. Watson, and R. E. Cameron. Development of three-dimensional collagen scaffolds with controlled architecture for cell migration studies using breast cancer cell lines. Biomaterials 114:34–43, 2017.
Caracciolo, P. C., M. I. Rial-Hermida, F. Montini-Ballarin, G. A. Abraham, A. Concheiro, and C. Alvarez-Lorenzo. Surface-modified bioresorbable electrospun scaffolds for improving hemocompatibility of vascular grafts. Mater Sci Eng C 75:1115–1127, 2017.
Chan-Park, M. B., J. Y. Shen, Y. Cao, Y. Xiong, Y. Liu, S. Rayatpisheh, G. C.-W. Kang, and H. P. Greisler. Biomimetic control of vascular smooth muscle cell morphology and phenotype for functional tissue-engineered small-diameter blood vessels. J Biomed Mater Res A 88:1104–1121, 2009.
Dwivedi, N., V. Kumar, A. Shrivastava, and R. Nareliya. Burst pressure assessment of pressure vessel using finite element analysis: a review. J Press Vessel Technol ASME 135:044502–044505, 2013.
Eichhorn, S. J., and W. W. Sampson. Statistical geometry of pores and statistics of porous nanofibrous assemblies. J R Soc Interface 2:309–318, 2005.
Ekaputra, A. K., G. D. Prestwich, S. M. Cool, and D. W. Hutmacher. Combining electrospun scaffolds with electrosprayed hydrogels leads to three-dimensional cellularization of hybrid constructs. Biomacromolecules 9:2097–2103, 2008.
Garg, K., N. A. Pullen, C. A. Oskeritzian, J. J. Ryan, and G. L. Bowlin. Macrophage functional polarization (M1/M2) in response to varying fiber and pore dimensions of electrospun scaffolds. Biomaterials 34:4439–4451, 2013.
Ghanian, M. H., Z. Farzaneh, J. Barzin, M. Zandi, M. Kazemi-Ashtiani, M. Alikhani, M. Ehsani, and H. Baharvand. Nanotopographical control of human embryonic stem cell differentiation into definitive endoderm. J Biomed Mater Res A 103:3539–3553, 2015.
Han, F., X. Jia, D. Dai, X. Yang, J. Zhao, Y. Zhao, Y. Fan, and X. Yuan. Performance of a multilayered small-diameter vascular scaffold dual-loaded with VEGF and PDGF. Biomaterials 34:7302–7313, 2013.
Horst, M., V. Milleret, S. Nötzli, S. Madduri, T. Sulser, R. Gobet, and D. Eberli. Increased porosity of electrospun hybrid scaffolds improved bladder tissue regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A 102:2116–2124, 2014.
Hu, J., D. Kai, H. Ye, L. Tian, X. Ding, S. Ramakrishna, and X. J. Loh. Electrospinning of poly(glycerol sebacate)-based nanofibers for nerve tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C 70:1089–1094, 2017.
Hu, C., C. Tercero, S. Ikeda, M. Nakajima, H. Tajima, Y. Shen, T. Fukuda, and F. Arai. Biodegradable porous sheet-like scaffolds for soft-tissue engineering using a combined particulate leaching of salt particles and magnetic sugar particles. J Biosci Bioeng 116:126–131, 2013.
Kim, H. N., A. Jiao, N. S. Hwang, M. S. Kim, D. H. Kang, D.-H. Kim, and K.-Y. Suh. Nanotopography-guided tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65:536–558, 2013.
Koobatian, M. T., S. Row, R. J. Smith, Jr, C. Koenigsknecht, S. T. Andreadis, and D. D. Swartz. Successful endothelialization and remodeling of a cell-free small-diameter arterial graft in a large animal model. Biomaterials 76:344–358, 2016.
Lee, J., A. A. Abdeen, K. L. Wycislo, T. M. Fan, and K. A. Kilian. Interfacial geometry dictates cancer cell tumorigenicity. Nat Mater 15:856–862, 2016.
Li, Y., K. Jiang, J. Feng, J. Liu, R. Huang, Z. Chen, J. Yang, Z. Dai, Y. Chen, N. Wang, W. Zhang, W. Zheng, G. Yang, and X. Jiang. Construction of small-diameter vascular graft by shape-memory and self-rolling bacterial cellulose membrane. Adv Healthc Mater 6:1601343–1601352, 2017.
Li, D., T. Wu, N. He, J. Wang, W. Chen, L. He, C. Huang, H. A. Ei-Hamshary, S. S. Al-Deyab, and Q. Ke. Three-dimensional polycaprolactone scaffold via needleless electrospinning promotes cell proliferation and infiltration. Colloids Surf B 121:432–443, 2014.
Liu, T., R. Huang, J. Zhong, Y. Yang, Z. Tan, and W. Tan. Control of cell proliferation in E-jet 3D-printed scaffolds for tissue engineering applications: the influence of the cell alignment angle. J Mater Chem B 5:3728–3738, 2017.
Loh, X. J., P. Peh, S. Liao, C. Sng, and J. Li. Controlled drug release from biodegradable thermoresponsive physical hydrogel nanofibers. J Control Release 143:175–182, 2010.
Mozaffarian, D., E. J. Benjamin, A. S. Go, D. K. Arnett, M. J. Blaha, M. Cushman, F. S. De, J. P. Després, H. J. Fullerton, and V. J. Howard. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2015 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 131:e29–322, 2015.
Peng, X. F., H. Y. Mi, X. Jing, P. Yu, J. P. Qu, and B. Y. Chen. Preparation of highly porous interconnected poly(lactic acid) scaffolds based on a novel dynamic elongational flow procedure. Mater Des 101:285–293, 2016.
Pu, J., F. Yuan, S. Li, and K. Komvopoulos. Electrospun bilayer fibrous scaffolds for enhanced cell infiltration and vascularization in vivo. Acta Biomater 13:131–141, 2015.
Seifu, D. G., A. Purnama, K. Mequanint, and D. Mantovani. Small-diameter vascular tissue engineering. Nat Rev Cardiol 10:410–421, 2013.
Tan, Z., H. Wang, X. Gao, T. Liu, and Y. Tan. Composite vascular grafts with high cell infiltration by co-electrospinning. Mater Sci Eng C 67:369–377, 2016.
Visser, J., F. P. W. Melchels, J. E. Jeon, E. M. van Bussel, L. S. Kimpton, H. M. Byrne, W. J. A. Dhert, P. D. Dalton, D. W. Hutmacher, and J. Malda. Reinforcement of hydrogels using three-dimensionally printed microfibres. Nat Commun 6:6933, 2015.
Wei, C., and J. Dong. Direct fabrication of high-resolution three-dimensional polymeric scaffolds using electrohydrodynamic hot jet plotting. J Micromech Microeng 23:025017, 2013.
Wei, C., and J. Dong. Hybrid hierarchical fabrication of three-dimensional scaffolds. J Manuf Process 16:257–263, 2014.
World Health Organization. World health statistics 2017: monitoring health for the SDGs, sustainable development goals. Geneva. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO, 2017.
Zhu, T., K. Yu, M. A. Bhutto, X. Guo, W. Shen, J. Wang, W. Chen, H. El-Hamshary, S. S. Al-Deyab, and X. Mo. Synthesis of RGD-peptide modified poly(ester-urethane) urea electrospun nanofibers as a potential application for vascular tissue engineering. Chem Eng J 351:177–190, 2017.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31600782), Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Committee (No. JCYJ20170818112151323), and Scientific Research Foundation of Hunan University (No. 53112102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Kent Leach oversaw the review of this article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, R., Gao, X., Wang, J. et al. Triple-Layer Vascular Grafts Fabricated by Combined E-Jet 3D Printing and Electrospinning. Ann Biomed Eng 46, 1254–1266 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-018-2065-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-018-2065-z