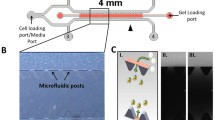
Abstract
The identification of novel, synthetic targeting ligands to endothelial receptors has led to the rapid development of targeted nanoparticles for drug, gene and imaging probe delivery. Central to development and optimization are effective models for assessing particle binding in vitro. Here, we developed a simple and cost effective method to quantitatively assess nanoparticle accumulation under physiologically-relevant laminar flow. We designed reversibly vacuum-sealed PDMS microfluidic chambers compatible with 35 mm petri dishes, which deliver uniform or gradient shear stress. These chambers have sufficient surface area for facile cell collection for particle accumulation quantitation through FACS. We tested this model by synthesizing and flowing liposomes coated with APN (K D ~ 300 μM) and VCAM-1-targeting (K D ~ 30 μM) peptides over HUVEC. Particle binding significantly increased with ligand concentration (up to 6 mol%) and decreased with excess PEG. While the accumulation of particles with the lower affinity ligand decreased with shear, accumulation of those with the higher affinity ligand was highest in a low shear environment (2.4 dyne/cm2), as compared with greater shear or the absence of shear. We describe here a robust flow chamber model that is applied to optimize the properties of 100 nm liposomes targeted to inflamed endothelium.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, K. C., and D. A. Hammer. The forward rate of binding of surface-tethered reactants: effect of relative motion between two surfaces. Biophys. J. 76:1280–1292, 1999.
Charoenphol, P., R. B. Huang, and O. Eniola-Adefeso. Potential role of size and hemodynamics in the efficacy of vascular-targeted spherical drug carriers. Biomaterials 31:1392–1402, 2010.
Chen, A. N., and T. R. Pan. Three-dimensional fit-to-flow microfluidic assembly. Biomicrofluidics 5:46505–46509, 2011.
Evans, E., and K. Kinoshita. Using force to probe single-molecule receptor-cytoskeletal anchoring beneath the surface of a living cell. Methods Cell Biol. 83:373–396, 2007.
Farokhzad, O. C., A. Khademhosseini, S. Jon, A. Hermmann, J. Cheng, C. Chin, A. Kiselyuk, B. Teply, G. Eng, and R. Langer. Microfluidic system for studying the interaction of nanoparticles and microparticles with cells. Anal. Chem. 77:5453–5459, 2005.
Harris, S. S., and T. D. Giorgio. Convective flow increases lipoplex delivery rate to in vitro cellular monolayers. Gene Ther. 12:512–520, 2005.
Jeong, J. H., M. Lee, W. J. Kim, J. W. Yockman, T. G. Park, Y. H. Kim, and S. W. Kim. Anti-GAD antibody targeted non-viral gene delivery to islet beta cells. J. Controlled Release 107:562–570, 2005.
Kelly, K. A., M. Nahrendorf, A. M. Yu, F. Reynolds, and R. Weissleder. In vivo phage display selection yields atherosclerotic plaque targeted peptides for imaging. Mol. Imaging Biol. 8:201–207, 2006.
Klibanov, A. L., K. Maruyama, V. P. Torchilin, and L. Huang. Amphipathic polyethyleneglycols effectively prolong the circulation time of liposomes. FEBS Lett. 268:235–237, 1990.
Korn, C. B., and U. S. Schwarz. Mean first passage times for bond formation for a Brownian particle in linear shear flow above a wall. J. Chem. Phys. 126:095103, 2007.
Kuo, S. C., and D. A. Lauffenburger. Relationship between receptor/ligand binding affinity and adhesion strength. Biophys. J. 65:2191–2200, 1993.
Lee, S. Y., M. Ferrari, and P. Decuzzi. Shaping nano-/micro-particles for enhanced vascular interaction in laminar flows. Nanotechnology 20:495101, 2009.
Matsumura, Y., and H. Maeda. A new concept for macromolecular therapeutics in cancer chemotherapy: mechanism of tumoritropic accumulation of proteins and the antitumor agent SMANCS. Cancer Res. 46:6387–6392, 1986.
Nahrendorf, M., F. A. Jaffer, K. A. Kelly, D. E. Sosnovik, E. Aikawa, P. Libby, and R. Weissleder. Noninvasive vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 imaging identifies inflammatory activation of cells in atherosclerosis. Circulation 114:1504–1511, 2006.
Nahrendorf, M., E. Keliher, P. Panizzi, H. Zhang, S. Hembrador, J. L. Figueiredo, E. Aikawa, K. Kelly, P. Libby, and R. Weissleder. 18F-4V for PET-CT imaging of VCAM-1 expression in atherosclerosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2:1213–1222, 2009.
Papahadjopoulos, D., T. M. Allen, A. Gabizon, E. Mayhew, K. Matthay, S. K. Huang, K. D. Lee, M. C. Woodle, D. D. Lasic, C. Redemann, and F. J. Martin. Sterically stabilized liposomes—improvements in pharmacokinetics and antitumor therapeutic efficacy. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88:11460–11464, 1991.
Pasqualini, R., E. Koivunen, R. Kain, J. Lahdenranta, M. Sakamoto, A. Stryhn, R. A. Ashmun, L. H. Shapiro, W. Arap, and E. Ruoslahti. Aminopeptidase N is a receptor for tumor-homing peptides and a target for inhibiting angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 60:722–727, 2000.
Plesniak, L. A., B. Salzameda, H. Hinderberger, E. Regan, J. Kahn, S. A. Mills, P. Teriete, Y. Yao, P. Jennings, F. Marassi, and J. A. Adams. Structure and activity of CPNGRC: a modified CD13/APN peptidic homing motif. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 75:551–562, 2010.
Prabhakarpandian, B., Y. Wang, A. Rea-Ramsey, S. Sundaram, M. F. Kiani, and K. Pant. Bifurcations: focal points of particle adhesion in microvascular networks. Microcirculation 18:380–389, 2011.
Ruoslahti, E. Vascular zip codes in angiogenesis and metastasis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 32:397–402, 2004.
Schaff, U. Y., M. M. Xing, K. K. Lin, N. Pan, N. L. Jeon, and S. I. Simon. Vascular mimetics based on microfluidics for imaging the leukocyte–endothelial inflammatory response. Lab Chip 7:448–456, 2007.
Smith, M. L., M. J. Smith, M. B. Lawrence, and K. Ley. Viscosity-independent velocity of neutrophils rolling on p-selectin in vitro or in vivo. Microcirculation 9:523–536, 2002.
Tsou, J. K., R. M. Gower, H. J. Ting, U. Y. Schaff, M. F. Insana, A. G. Passerini, and S. I. Simon. Spatial regulation of inflammation by human aortic endothelial cells in a linear gradient of shear stress. Microcirculation 15:311–323, 2008.
Usami, S., H. H. Chen, Y. Zhao, S. Chien, and R. Skalak. Design and construction of a linear shear stress flow chamber. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 21:77–83, 1993.
Wattenbarger, M. R., D. J. Graves, and D. A. Lauffenburger. Specific adhesion of glycophorin liposomes to a lectin surface in shear flow. Biophys. J. 57:765–777, 1990.
Xia, Y. N., and G. M. Whitesides. Soft lithography. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 28:153–184, 1998.
Zhang, H., J. Kusunose, A. Kheirolomoom, J. W. Seo, J. Qi, K. D. Watson, H. A. Lindfors, E. Ruoslahti, J. L. Sutcliffe, and K. W. Ferrara. Dynamic imaging of arginine-rich heart-targeted vehicles in a mouse model. Biomaterials 29:1976–1988, 2008.
Zhao, S., A. Chen, A. Revzin, and T. Pan. Stereomask lithography (SML): a universal multi-object micro-patterning technique for biological applications. Lab Chip 11:224–230, 2011.
Zhao, S., H. Cong, and T. Pan. Direct projection on dry-film photoresist (DP(2)): do-it-yourself three-dimensional polymer microfluidics. Lab Chip 9:1128–1132, 2009.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr Shengping Qin for the CFD modeling used for preliminary analysis and Arnold Chan for the fabrication of prototype PDMS molds. This work was supported by the Bioengineering research partnership NIHR01CA103828, NIHT32EB003827 and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Contract no. HHSN268201000043.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor K. A. Athanasiou oversaw the review of this article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kusunose, J., Zhang, H., Gagnon, M.K.J. et al. Microfluidic System for Facilitated Quantification of Nanoparticle Accumulation to Cells Under Laminar Flow. Ann Biomed Eng 41, 89–99 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-012-0634-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-012-0634-0