Abstract
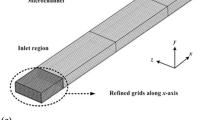
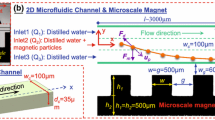
This paper demonstrates simple and cost-effective microfluidic devices for enhanced separation of magnetic particles by using soft magnetic microstructures. By injecting a mixture of iron powder and polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) into a prefabricated channel, an iron–PDMS microstructure was fabricated next to a microfluidic channel. Placed between two external permanent magnets, the magnetized iron–PDMS microstructure induces localized and strong forces on the magnetic particles in the direction perpendicular to the fluid flow. Due to the small distance between the microstructure and the fluid channel, the localized large magnetic field gradients result a vertical force on the magnetic particles, leading to enhanced separation of the particles. Numerical simulations were developed to compute the particle trajectories and agreed well with experimental data. Systematic experiments and numerical simulation were conducted to study the effect of relevant factors on the transport of superparamagnetic particles, including the shape of iron–PDMS microstructure, mass ratio of iron–PDMS composite, width of the microfluidic channel, and average flow velocity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramoff M, Magalhes P, Ram S (2004) Image processing with imagej. Biophoton Int 11(7):36–41
Balasubramanian P, Lang J, Jatana K, Miller B, Ozer E, Old M, Schuller D, Agrawal A, Teknos T, Summers JT, Lustberg M, Zborowski M, Chalmers J (2012) Multiparameter analysis, including emt markers, on negatively enriched blood samples from patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. PLoS One 7(7):e42048. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0042048
Deng T, Prentiss M, Whitesides G (2002) Fabrication of magnetic microfiltration systems using soft lithography. Appl Phys Lett 80(3):461–463
Derec C, Wilhelm C, Servais J, Bacri JC (2010) Local control of magnetic objects in microfluidic channels. Microfluid Nanofluid 8(1):123–130
Do J, Choi JW, Ahn C (2004) Low-cost magnetic interdigitated array on a plastic wafer. IEEE Trans Mag 40(4 II):3009–3011
El-Nashar D, Mansour S, Girgis E (2006) Nickel and iron nano-particles in natural rubber composites. J Mater Sci 41(16):5359–5364
Engel A, Friedrichs R (2002) On the electromagnetic force on a polarizable body. Am J Phys 70(4):428–432
Faivre M, Gelszinnis R, Degouttes J, Terrier N, Rivière C, Ferrigno R, Deman AL (2014) Magnetophoretic manipulation in microsystem using carbonyl iron-polydimethylsiloxane microstructures. Biomicrofluidics 8(5):054103
Furlani EP, Ng KC (2006) Analytical model of magnetic nanoparticle transport and capture in the microvasculature. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys 73(6):061919. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.73.061919
Furlani E, Sahoo Y (2006) Analytical model for the magnetic field and force in a magnetophoretic microsystem. J Phys D Appl Phys 39(9):1724–1732
Ganatos P, Weinbaum S, Pfeffer R (1980) A strong interaction theory for the creeping motion of a sphere between plane parallel boundaries. part 1. perpendicular motion. J Fluid Mech 99:739–753
Gelszinnis R, Faivre M, Degouttes J, Terrier N, Ferrigno R, Deman AL (2013) Magnetophoretic manipulation in microsystem using i-pdms microstructurs, vol 1. In: 17th international conference on miniaturized systems for chemistry and life sciences, pp 146–148
Gijs M (2004) Magnetic bead handling on-chip: new opportunities for analytical applications. Microfluid Nanofluid 1(1):22–40
Gijs MA, Lacharme F, Lehmann U (2009) Microfluidic applications of magnetic particles for biological analysis and catalysis. Chem Rev 110(3):1518–1563
Han KH, Bruno Frazier A (2004) Continuous magnetophoretic separation of blood cells in microdevice format. J Appl Phys 96(10):5797–5802
Hejazian M, Li W, Nguyen NT (2015) Lab on a chip for continuous-flow magnetic cell separation. Lab Chip 15(4):959–970
Inglis DW, Riehn R, Austin R, Sturm J (2004) Continuous microfluidic immunomagnetic cell separation. Appl Phys Lett 85(21):5093–5095
Krishnan GP, Leighton DT (1995) Inertial lift on a moving sphere in contact with a plane wall in a shear flow. Phys Fluids 7(11):2538–2545
Li J, Zhang M, Wang L, Li W, Sheng P, Wen W (2011) Design and fabrication of microfluidic mixer from carbonyl iron–PDMS composite membrane. Microfluid Nanofluid 10(4):919–925
Lin YA, Wong TS, Bhardwaj U, Chen JM, McCabe E, Ho CM (2007) Formation of high electromagnetic gradients through a particle-based microfluidic approach. J Micromech Microeng 17(7):1299
Lund-Olesen T, Bruus H, Hansen M (2007a) Quantitative characterization of magnetic separators: comparison of systems with and without integrated microfluidic mixers. Biomed Microdevices 9(2):195–205
Lund-Olesen T, Dufva M, Hansen M (2007b) Capture of dna in microfluidic channel using magnetic beads: increasing capture efficiency with integrated microfluidic mixer. J Magn Magn Mater 311(1 SPEC. ISS.):396–400
McDonald J, Duffy D, Anderson J, Chiu D, Wu H, Schueller O, Whitesides G (2000) Fabrication of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Electrophoresis 21(1):27–40
Meeker D (2010) Finite element method magnetics. FEMM 4:32
Nejad HR, Samiei E, Ahmadi A, Hoorfar M (2015) Gravity-driven hydrodynamic particle separation in digital microfluidic systems. RSC Adv 5:35,966–35,975
Nguyen NT (2012) Micro-magnetofluidics: interactions between magnetism and fluid flow on the microscale. Microfluid Nanofluid 12(1–4):1–16
Nguyen VC, Pho QH (2014) Preparation of chitosan coated magnetic hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and application for adsorption of reactive blue 19 and Ni2+ ions. Sci World J 2014:273082. doi:10.1155/2014/273082
Pamme N (2006) Magnetism and microfluidics. Lab Chip Miniat Chem Biol 6(1):24–38
Rida A, Gijs M (2004) Manipulation of self-assembled structures of magnetic beads for microfluidic mixing and assaying. Anal Chem 76(21):6239–6246
Safarik I, Safarikova M (1999) Use of magnetic techniques for the isolation of cells. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 722(1–2):35–53
Safarik I, Safarikova M (2004) Magnetic techniques for the isolation and purification of proteins and peptides. BioMagn Res Technol 2:7
Samiei E, Rezaei Nejad H, Hoorfar M (2015) A dielectrophoretic-gravity driven particle focusing technique for digital microfluidic systems. Appl Phys Lett 106(20):204101
Shah RK, London AL, Irvine TF, Hartnett JP (1978) Laminar flow forced convection in ducts. Academic Press, Cambridge
Shenkman R, Chalmers J, Hering B, Kirchhof N, Papas K (2009) Quadrupole magnetic sorting of porcine islets of langerhans. Tissue Eng Part C Methods 15(2):147–156
Siegel AC, Shevkoplyas SS, Weibel DB, Bruzewicz DA, Martinez AW, Whitesides GM (2006) Cofabrication of electromagnets and microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Angew Chem Int Ed 45(41):6877–6882
Smistrup K, Kjeldsen B, Reimers J, Dufva M, Petersen J, Hansen M (2005) On-chip magnetic bead microarray using hydrodynamic focusing in a passive magnetic separator. Lab Chip Miniat Chem Biol 5(11):1315–1319
Smistrup K, Bu M, Wolff A, Bruus H, Hansen MF (2008) Theoretical analysis of a new, efficient microfluidic magnetic bead separator based on magnetic structures on multiple length scales. Microfluid Nanofluid 4:565–573
Staben ME, Zinchenko AZ, Davis RH (2003) Motion of a particle between two parallel plane walls in low-reynolds-number poiseuille flow. Phys Fluids 15(6):1711–1733
Svoboda J (2001) A realistic description of the process of high-gradient magnetic separation. Miner Eng 14(11):1493–1503
Tan SH, Semin B, Baret JC (2014) Microfluidic flow-focusing in ac electric fields. Lab Chip 14(6):1099–1106
Verpoorte E (2003) Beads and chips: new recipes for analysis. Lab Chip 3(4):60N–68N
Watson J (1973) Magnetic filtration. J Appl Phys 44(9):4209–4213
White FM (1991) Viscous fluid flow, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Xia N, Hunt T, Mayers B, Alsberg E, Whitesides G, Westervelt R, Ingber D (2006) Combined microfluidic-micromagnetic separation of living cells in continuous flow. Biomed Microdevices 8(4):299–308
Yang L, Lang J, Balasubramanian P, Jatana K, Schuller D, Agrawal A, Zborowski M, Chalmers J (2009) Optimization of an enrichment process for circulating tumor cells from the blood of head and neck cancer patients through depletion of normal cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 102(2):521–534
Zhang Z, Zhou R, Brames DP, Wang C (2015) A low-cost fabrication system for manufacturing soft-lithography microfluidic master molds. Micro Nanosyst 7(1):4–12
Zhou R, Wang C (2015) Acoustic bubble enhanced pinched flow fractionation for microparticle separation. J Micromech Microeng 25(8):084005. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/25/8/084005
Zhu J, Liang L, Xuan X (2012) On-chip manipulation of nonmagnetic particles in paramagnetic solutions using embedded permanent magnets. Microfluid Nanofluid 12(1–4):65–73
Zhu T, Marrero F, Mao L (2010) Continuous separation of non-magnetic particles through negative magnetophoresis inside ferrofluids. In: 2010 IEEE 5th international conference on nano/micro engineered and molecular systems, pp 1006–1011
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at Missouri University of Science and Technology through a start-up package.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, R., Wang, C. Microfluidic separation of magnetic particles with soft magnetic microstructures. Microfluid Nanofluid 20, 48 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-016-1714-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-016-1714-5