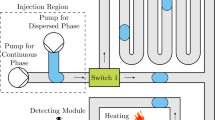
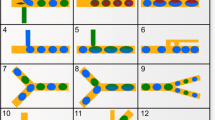
Abstract
We present a facile microfluidic droplet-on-demand (DOD) system in which a pulsed pressure generated by a high-speed solenoid valve is used to control the formation and movement of water-in-oil emulsion droplets in a T-junction microchannel. We investigated the working principle of the DOD system and established a scaling model for the droplet volume in terms of the amplitude and duration of the pulse and the hydraulic resistance of the injection channel. The droplet formation was characterized in three designs at various pressure pulses. The experimental results support our scaling model very well. In the DOD system we developed, nanoliter-volume droplets with a throughput of a few droplets per second were on-demand generated. Moreover, we examined the applicable scope of the DOD system. As examples of practical applications of the DOD system, we demonstrated a digital display module to show droplets formed at a prescribed time and a droplet array with a concentration gradient to show droplets formed with a precise volume. We expect our work can provide design guidelines for a robust DOD system and improve the capabilities of droplet-based microfluidics in ‘lab-on-a-chip’ systems.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anna SL, Bontoux N, Stone HA (2003) Formation of dispersions using “flow focusing” in microchannels. Appl Phys Lett 82:364
Atencia J, Beebe DJ (2004) Controlled microfluidic interfaces. Nature 437(7059):648–655
Baroud CN, de Saint Vincent MR, Delville J-P (2007) An optical toolbox for total control of droplet microfluidics. Lab Chip 7(8):1029–1033
Baroud CN, Gallaire F, Dangla R (2010) Dynamics of microfluidic droplets. Lab Chip 10(16):2032–2045
Bransky A, Korin N, Khoury M, Levenberg S (2008) A microfluidic droplet generator based on a piezoelectric actuator. Lab Chip 9(4):516–520
Churski K, Korczyk P, Garstecki P (2010) High-throughput automated droplet microfluidic system for screening of reaction conditions. Lab Chip 10(7):816–818
Dolega ME, Jakiela S, Razew M, Rakszewska A, Cybulski O, Garstecki P (2012) Iterative operations on microdroplets and continuous monitoring of processes within them; determination of solubility diagrams of proteins. Lab Chip 12(20):4022–4025
Fidalgo LM, Whyte G, Bratton D, Kaminski CF, Abell C, Huck WTS (2008) From microdroplets to microfluidics: selective emulsion separation in microfluidic devices. Angew Chem Int Ed 47(11):2042–2045
Galas J-C, Bartolo D, Studer V (2009) Active connectors for microfluidic drops on demand. New J Phys 11(7):075027
Garstecki P, Fuerstman MJ, Stone HA, Whitesides GM (2006) Formation of droplets and bubbles in a microfluidic T-junction—scaling and mechanism of break-up. Lab Chip 6(3):437–446
Gu H, Murade CU, Duits MH, Mugele F (2011) A microfluidic platform for on-demand formation and merging of microdroplets using electric control. Biomicrofluidics 5:011101
Guo F, Liu K, Ji XH, Ding HJ, Zhang M, Zeng Q, Liu W, Guo SS, Zhao XZ (2010) Valve-based microfluidic device for droplet on-demand operation and static assay. Appl Phys Lett 97(23):233701–233703
Jung S-Y, Retterer ST, Collier CP (2010) On-demand generation of monodisperse femtolitre droplets by shape-induced shear. Lab Chip 10(20):2688–2694
Kotulski Z, Szczepiński W (2010) Functions of Independent random variables. In: Error analysis with applications in engineering, vol 169. Solid mechanics and its applications. Springer, Netherlands, pp 91–105. doi:10.1007/978-90-481-3570-7_4
Lin B-C, Su Y-C (2008) On-demand liquid-in-liquid droplet metering and fusion utilizing pneumatically actuated membrane valves. J Micromech Microeng 18(11):115005
Lin F, Saadi W, Rhee SW, Wang S-J, Mittal S, Jeon NL (2004) Generation of dynamic temporal and spatial concentration gradients using microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 4(3):164–167
Malloggi F, Gu H, Banpurkar A, Vanapalli S, Mugele F (2008) Electrowetting—a versatile tool for controlling microdrop generation. Eur Phys J E 26(1–2):91–96
Nguyen N-T, Ting T-H, Yap Y-F, Wong T-N, Chai JC-K, Ong W-L, Zhou J, Tan S-H, Yobas L (2007) Thermally mediated droplet formation in microchannels. Appl Phys Lett 91(8):084102–084103
Niu X, Gulati S, Edel JB (2008) Pillar-induced droplet merging in microfluidic circuits. Lab Chip 8(11):1837–1841
Niu X, Gielen F, Edel JB (2011) A microdroplet dilutor for high-throughput screening. Nat Chem 3(6):437–442
Shemesh J, Nir A, Bransky A, Levenberg S (2011) Coalescence-assisted generation of single nanoliter droplets with predefined composition. Lab Chip 11(19):3225–3230
Song H, Tice JD, Ismagilov RF (2003) A microfluidic system for controlling reaction networks in time. Angew Chem 115(7):792–796
Stone HA, Stroock AD, Ajdari A (2004) Engineering flows in small devices: microfluidics toward a lab-on-a-chip. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 36:381–411
Tan SH, Murshed SMS, Nguyen NT, Wong TN, Yobas L (2008) Thermally controlled droplet formation in flow focusing geometry: formation regimes and effect of nanoparticle suspension. J Phys D Appl Phys 41(16):165501
Thorsen T, Roberts RW, Arnold FH, Quake SR (2001) Dynamic pattern formation in a vesicle-generating microfluidic device. Phys Rev Lett 86(18):4163–4166
van Steijn V, Kleijn CR, Kreutzer MT (2010) Predictive model for the size of bubbles and droplets created in microfluidic T-junctions. Lab Chip 10(19):2513–2518
Willaime H, Barbier V, Kloul L, Maine S, Tabeling P (2006) Arnold tongues in a microfluidic drop emitter. Phys Rev Lett 96(5):054501
Xu J, Attinger D (2008) Drop on demand in a microfluidic chip. J Micromech Microeng 18(6):065020
Xu J, Li S, Tan J, Luo G (2008) Correlations of droplet formation in T-junction microfluidic devices: from squeezing to dripping. Microfluid Nanofluid 5(6):711–717
Yeh C-H, Chen Y-C, Lin Y-C (2011) Generation of droplets with different concentrations using gradient-microfluidic droplet generator. Microfluid Nanofluid 11(3):245–253
Zeng S, Li B, Su X, Qin J, Lin B (2009) Microvalve-actuated precise control of individual droplets in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 9(10):1340–1343
Zheng B, Roach LS, Ismagilov RF (2003) Screening of protein crystallization conditions on a microfluidic chip using nanoliter-size droplets. J Am Chem Soc 125(37):11170–11171
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Direct Allocation Grant (No. DAG12EG07-13) from HKUST and the National Science Foundation of China (No. 61006086). The authors would like to thank Dr. Gang Li in SIMIT for his valuable suggestion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Online Resource 3: the digital character ‘5’ displaying process. (MPG 584 kb)
Online Resource 4: the DOD droplets trapping process. (MPG 1,352 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, H., Yao, S. A facile on-demand droplet microfluidic system for lab-on-a-chip applications. Microfluid Nanofluid 16, 667–675 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-013-1268-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-013-1268-8