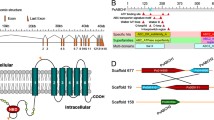
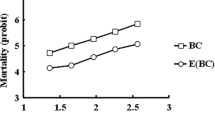
Abstract
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), a naturally occurring entomopathogenic soil bacterium, has been the active ingredient of sprayable Bt biopesticides for over a century. Insecticidal Bt Cry proteins are particularly well suited for use as plant-incorporated protectants in transgenic crops (Bt crops) due to their specificity against insect pests and safety for non-target organisms. The sustainability of these Bt products, however, has been challenged by the development of resistance in the field. RNA interference (RNAi), a species-specific control alternative that has been deregulated and commercialized in the USA and Canada, provides a new mode of action to complement the existing Bt products. Based on our preliminary research, we hypothesized that pyramiding/integrating Bt with RNAi can address/manage resistance issues related to Bt traits. To examine this overarching hypothesis, we (1) cloned and characterized a serine/threonine kinase gene (fused) of the Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway in the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.), a global superpest; (2) profiled Pxfused expression in Bt-resistant P. xylostella strains; and (3) investigated the involvement of Pxfused in Bt Cry1Ac resistance in P. xylostella. Pxfused expression was elevated ubiquitously in all Bt-resistant strains, and silencing of Pxfused led to larval and pupal mortality in both Cry1Ac-susceptible and -resistant strains, suggesting that Pxfused is a potential target for RNAi-based resistance management. Taken together, our results not only identify a molecular target to control a devastating lepidopteran pest, but also shed light on a novel resistance management strategy through the integration of two biotechnological techniques with distinct modes of action.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ascano M Jr, Robbins DJ (2004) An intramolecular association between two domains of the protein kinase Fused is necessary for Hedgehog signaling. Mol Cell Biol 24:10397–11405
Ascano M, Nybakken KE, Sosinski J, Stegman MA, Robbins DJ (2002) The carboxyl-terminal domain of the protein kinase fused can function as a dominant inhibitor of Hedgehog signaling. Mol Cell Biol 22:1555–1566
Bürglin TR (2008) The Hedgehog protein family. Genome Biol 9:241
Bardwell L, Bardwell AJ, Wu B, Waterman M (2016) Crosstalk between MAP kinase and Hedgehog pathways by direct phosphorylation of Gli transcription factors. FASEB J 30(1112):1111
Baum JA et al (2007) Control of coleopteran insect pests through RNA interference. Nat Biotechnol 25:1322–1326
Baum JA, Roberts JK (2014) Progress towards RNAi-mediated insect pest management. Adv Insect Physiol 47:249–295
Bautista MA, Miyata T, Miura K, Tanaka T (2009) RNA interference-mediated knockdown of a cytochrome P450, CYP6BG1, from the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella, reduces larval resistance to permethrin. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 39:38–46
Bellés X (2010) Beyond Drosophila: RNAi in vivo and functional genomics in insects. Annu Rev Entomol 55:111–128
Bravo A, Likitvivatanavong S, Gill SS, Soberón M (2011) Bacillus thuringiensis: a story of a successful bioinsecticide. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 41:423–431
Briscoe J, Thérond PP (2013) The mechanisms of Hedgehog signalling and its roles in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14:416–429
Castagnola A, Jurat-Fuentes JL (2016) Intestinal regeneration as an insect resistance mechanism to entomopathogenic bacteria. Curr Opin Insect Sci 15:104–110
Chen MH, Gao N, Kawakami T, Chuang PT (2005) Mice deficient in the fused homolog do not exhibit phenotypes indicative of perturbed hedgehog signaling during embryonic development. Mol Cell Biol 25:7042–7053
Christiaens O, Whyard S, Vélez AM, Smagghe G (2020) Double-stranded RNA technology to control insect pests: current status and challenges. Front Plant Sci 11:451
Deutsch CA, Tewksbury JJ, Tigchelaar M, Battisti DS, Merrill SC, Huey RB, Naylor RL (2018) Increase in crop losses to insect pests in a warming climate. Science 361:916–919
Ferré J, Van Rie J (2002) Biochemistry and genetics of insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis. Annu Rev Entomol 47:501–533
Fishilevich E et al (2019) RNAi targeting of rootworm Troponin I transcripts confers root protection in maize. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 104:20–29
Fishilevich E et al (2016) Use of chromatin remodeling ATPases as RNAi targets for parental control of western corn rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera) and Neotropical brown stink bug (Euschistus heros). Insect Biochem Mol Biol 71:58–71
Fletcher SJ, Reeves PT, Hoang BT, Mitter N (2020) A perspective on RNAi-based biopesticides. Front Plant Sci 11:51
Furlong MJ, Wright DJ, Dosdall LM (2013) Diamondback moth ecology and management: problems, progress and prospects. Annu Rev Entomol 58:517–541
Gong L, Yang X, Zhang B, Zhong G, Hu MY (2011) Silencing of Rieske iron–sulfur protein using chemically synthesised siRNA as a potential biopesticide against Plutella xylostella. Pest Manag Sci 67:514–520
Guedes RNC, Smagghe G, Stark JD, Desneux N (2016) Pesticide-induced stress in arthropod pests for optimized integrated pest management programs. Annu Rev Entomol 61:43–62
Guo Z et al (2015a) MAPK signaling pathway alters expression of midgut ALP and ABCC genes and causes resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac toxin in diamondback moth. PLoS Genet 11:e1005124
Guo Z et al (2020) MAPK-dependent hormonal signaling plasticity contributes to overcoming Bacillus thuringiensis toxin action in an insect host. Nat Commun 11:3003
Guo Z, Kang S, Zhu X, Wu Q, Wang S, Xie W, Zhang Y (2015b) The midgut cadherin-like gene is not associated with resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry1Ac in Plutella xylostella (L.). J Invertebr Pathol 126:21–30
Guo Z et al (2015c) Down-regulation of a novel ABC transporter gene (Pxwhite) is associated with Cry1Ac resistance in the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.). Insect Biochem Mol Biol 59:30–40
Guo Z et al (2015d) The novel ABC transporter ABCH1 is a potential target for RNAi-based insect pest control and resistance management. Sci Rep 5:13728
Hannon GJ (2002) RNA interference. Nature 418:244–251
Ingham PW (1998) Transducing Hedgehog: the story so far. EMBO J 17:3505–3511
Ingham PW, Nakano Y, Seger C (2011) Mechanisms and functions of Hedgehog signalling across the metazoa. Nat Rev Genet 12:393–406
Israni B, Rajam MV (2017) Silencing of ecdysone receptor, insect intestinal mucin and sericotropin genes by bacterially produced double-stranded RNA affects larval growth and development in Plutella xylostella and Helicoverpa armigera. Insect Mol Biol 26:164–180
Joga MR, Zotti MJ, Smagghe G, Christiaens O (2016) RNAi efficiency, systemic properties, and novel delivery methods for pest insect control: what we know so far. Front Physiol 7:553
Keys DN et al (1999) Recruitment of a hedgehog regulatory circuit in butterfly eyespot evolution. Science 283:532–534
Khajuria C et al (2018) Development and characterization of the first dsRNA-resistant insect population from western corn rootworm, Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte. PLoS ONE 13:e0197059
Kim E, Park Y, Kim Y (2015) A transformed bacterium expressing double-stranded RNA specific to integrin β1 enhances Bt toxin efficacy against a polyphagous insect pest, Spodoptera exigua. PLoS ONE 10:e0132631
Kupferschmidt K (2013) A lethal dose of RNA. Science 341:732–733
Lee RTH, Zhao Z, Ingham PW (2016) Hedgehog signalling. Development 143:367–372
Lei Y et al (2014) Midgut transcriptome response to a Cry toxin in the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Gene 533:180–187
Liu F, Wang X, Zhao Y, Li Y, Liu Y, Sun J (2015) Silencing the HaAK gene by transgenic plant-mediated RNAi impairs larval growth of Helicoverpa armigera. Int J Biol Sci 11:67–74
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Lu S et al (2020) CDD/SPARCLE: the conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res 48:D265–D268
Lum L et al (2003) Hedgehog signal transduction via Smoothened association with a cytoplasmic complex scaffolded by the atypical kinesin, Costal-2. Mol Cell 12:1261–1274
Maloverjan A, Piirsoo M (2012) Mammalian homologues of Drosophila fused kinase. In: Litwack G (ed) Vitamins & hormones, vol 88. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 91–113
Maloverjan A, Piirsoo M, Michelson P, Kogerman P, Østerlund T (2010) Identification of a novel serine/threonine kinase ULK3 as a positive regulator of Hedgehog pathway. Exp Cell Res 316:627–637
Mezzetti B et al (2020) RNAi: What is its position in agriculture? J Pest Sci 93:1125–1130
Ni M et al (2017) Next generation transgenic cotton: pyramiding RNAi and Bt counters insect resistance. Plant Biotechnol J 15:1204–1213
Niu J, Taning CNT, Christiaens O, Smagghe G, Wang JJ (2018) Rethink RNAi in insect pest control: challenges and perspectives. Adv Insect Physiol 55:1–17
Oh SA, Bourdon V, Dickinson HG, Twell D, Park SK (2014) Arabidopsis Fused kinase TWO-IN-ONE dominantly inhibits male meiotic cytokinesis. Plant Reprod 27:7–17
Oh SA, Johnson A, Smertenko A, Rahman D, Park SK, Hussey PJ, Twell D (2005) A divergent cellular role for the FUSED kinase family in the plant-specific cytokinetic phragmoplast. Curr Biol 15:2107–2111
Petrov K, Wierbowski BM, Salic A (2017) Sending and receiving Hedgehog signals. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 33:145–168
Préat T et al (1990) A putative serine/threonine protein kinase encoded by the segment-polarity fused gene of Drosophila. Nature 347:87–89
Robbins DJ, Fei DL, Riobo NA (2012) The Hedgehog signal transduction network. Sci Signal 5:re6
Ruel L, Gallet A, Raisin S, Truchi A, Staccini-Lavenant L, Cervantes A, Therond PP (2007) Phosphorylation of the atypical kinesin Costal2 by the kinase Fused induces the partial disassembly of the Smoothened-Fused-Costal2-Cubitus interruptus complex in Hedgehog signalling. Development 134:3677–3689
Ryan KE, Chiang C (2012) Hedgehog secretion and signal transduction in vertebrates. J Biol Chem 287:17905–17913
San Miguel K, Scott JG (2016) The next generation of insecticides: dsRNA is stable as a foliar-applied insecticide. Pest Manag Sci 72:801–809
Sanahuja G, Banakar R, Twyman RM, Capell T, Christou P (2011) Bacillus thuringiensis: a century of research, development and commercial applications. Plant Biotechnol J 9:283–300
Tabashnik BE, Carrière Y (2017) Surge in insect resistance to transgenic crops and prospects for sustainability. Nat Biotechnol 35:926–935
Tabashnik BE, Cushing NL, Finson N, Johnson MW (1990) Field development of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis in diamondback moth (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). J Econ Entomol 83:1671–1676
Takashima S, Mkrtchyan M, Younossi-Hartenstein A, Merriam JR, Hartenstein V (2008) The behaviour of Drosophila adult hindgut stem cells is controlled by Wnt and Hh signalling. Nature 454:651–655
Tang L et al (2008) tsunami, the Dictyostelium homolog of the Fused kinase, is required for polarization and chemotaxis. Genes Dev 22:2278–2290
Thérond P et al (1996) Functional domains of fused, a serine-threonine kinase required for signaling in Drosophila. Genetics 142:1181–1198
Villarreal CM, Darakananda K, Wang VR, Jayaprakash PM, Suzuki Y (2015) Hedgehog signaling regulates imaginal cell differentiation in a basally branching holometabolous insect. Dev Biol 404:125–135
Vogel E, Santos D, Mingels L, Verdonckt TW, Broeck JV (2019) RNA interference in insects: protecting beneficials and controlling pests. Front Physiol 9:1912
Wilson CW, Chuang PT (2010) Mechanism and evolution of cytosolic Hedgehog signal transduction. Development 137:2079–2094
Wilson CW et al (2009) Fused has evolved divergent roles in vertebrate Hedgehog signalling and motile ciliogenesis. Nature 459:98–102
Wilson RC, Doudna JA (2013) Molecular mechanisms of RNA interference. Annu Rev Biophys 42:217–239
Wu F, Zhang Y, Sun B, McMahon AP, Wang Y (2017) Hedgehog signaling: from basic biology to cancer therapy. Cell Chem Biol 24:252–280
Xie W et al (2012) Tissue-specific transcriptome profiling of Plutella xylostella third instar larval midgut. Int J Biol Sci 8:1142–1155
Yan S et al (2020) Spray method application of transdermal dsRNA delivery system for efficient gene silencing and pest control on soybean aphid Aphis glycines. J Pest Sci 93:449–459
Zhang X, Feng L, Qiao N, Liu Y, Zhang DC, Yin H (2019) Cloning, expression pattern and functional characterization of fused, an important kinase of the Hedgehog signalling pathway from Locusta migratoria (Orthoptera: Acridoidea). Biotechnol Biotec Eq 33:1024–1033
Zhu TT, Meng QW, Guo WC, Li GQ (2015a) RNA interference suppression of the receptor tyrosine kinase Torso gene impaired pupation and adult emergence in Leptinotarsa decemlineata. J Insect Physiol 83:53–64
Zhu X et al (2015b) Construction and characterisation of near-isogenic Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) strains resistant to Cry1Ac toxin. Pest Manag Sci 71:225–233
Zotti M, Dos Santos EA, Cagliari D, Christiaens O, Taning CNT, Smagghe G (2018) RNAi technology in crop protection against arthropod pests, pathogens and nematodes. Pest Manag Sci 74:1239–1250
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFD0200900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31630059; 31701813; 32022074), the Beijing Key Laboratory for Pest Control and Sustainable Cultivation of Vegetables and the Science and Technology Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS-ASTIP-IVFCAAS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests in this work.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Subba Reddy Palli.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, S., Sun, D., Qin, J. et al. Fused: a promising molecular target for an RNAi-based strategy to manage Bt resistance in Plutella xylostella (L.). J Pest Sci 95, 101–114 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-021-01374-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-021-01374-3