Abstract
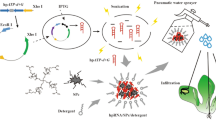
RNA interference (RNAi) has been recognized as a novel and safe strategy in pest management due to its high sequence-dependent specificity. However, the existing dsRNA delivery methods largely restrict the application of the RNAi-based pest management strategy; thus, we previously constructed a nanocarrier-based transdermal dsRNA delivery system on the soybean aphid Aphis glycines with the help of nanocarrier and detergent. In the current study, we improved our transdermal dsRNA delivery system with a smaller and cheaper nanocarrier to investigate the efficacy of spraying aphid-infested soybean seedlings to apply our RNA pesticide. A dsRNA/nanocarrier/detergent formulation was performed, and the dsRNA could penetrate the aphid body wall within 4 h with the help of nanocarrier through the topical application. Four potential RNAi target genes (TREH, ATPD, ATPE and CHS1) were selected and cloned, and their dsRNA fragments were synthesized and tested through the transdermal dsRNA delivery system. The delivered dsRNA efficiently silenced the target gene expression with the knockdown effects ranging from 86.86 to 58.87% and resulted in a high mortality up to 81.67% (dsATPD + dsATPE) through the topical application, when through the spray method, with the highest percent mortality of 78.50% (dsATPD + dsCHS1). Our novel transdermal dsRNA delivery system not only provides a powerful tool for gene functional analysis in laboratory, but also shows a great potential for the pest management in the field, which will promote the practice and development of RNAi-based pest management.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen ML, Walker WB III (2012) Saliva of Lygus lineolaris digests double stranded ribonucleic acids. J Insect Physiol 58:391–396
Bairoch A, Bucher P, Hofmann K (1997) The PROSITE database, its status in 1997. Nucl Acids Res 25:217–221
Baum JA, Roberts JK (2014) Chapter five—progress towards RNAi-mediated insect pest management. Adv Insect Physiol 47:249–295
Baum JA, Bogaert T, Clinton W, Heck GR, Feldmann P, Ilagan O, Johnson S, Plaetinck G, Munyikwa T, Pleau M (2007) Control of coleopteran insect pests through RNA interference. Nat Biotechnol 25:1322–1326
Bellés X (2010) Beyond Drosophila: RNAi in vivo and functional genomics in insects. Annu Rev Entomol 55:111–128
Bernhard W, Haagsman HP, Tschernig T, Poets CF, Postle AD, van Eijk ME, von der Hardt H (1997) Conductive airway surfactant: surface-tension function, biochemical composition, and possible alveolar origin. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 17:41–50
Bolognesi R, Ramaseshadri P, Anderson J, Bachman P, Clinton W, Flannagan R, Ilagan O, Lawrence C, Levine S, Moar W (2012) Characterizing the mechanism of action of double-stranded RNA activity against western corn rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte). PLoS ONE 7:e47534
Brisson JA (2010) Aphid wing dimorphisms: linking environmental and genetic control of trait variation. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 365:605–616
Chen J, Tang B, Chen H, Yao Q, Huang X, Chen J, Zhang D, Zhang W (2010) Different functions of the insect soluble and membrane-bound trehalase genes in chitin biosynthesis revealed by RNA interference. PLoS ONE 54:e10133
Christiaens O, Smagghe G (2014) The challenge of RNAi-mediated control of hemipterans. Curr Opin Insect Sci 6:15–21
Christiaens O, Swevers L, Smagghe G (2014) DsRNA degradation in the pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum) associated with lack of response in RNAi feeding and injection assay. Peptides 53:307–314
Combet C, Blanchet C, Geourjon C, Deléage G (2000) NPS@: network protein sequence analysis. Trends Biochem Sci 25:147–150
Cortés T, Tagu D, Simon JC, Moya A, Martínez-Torres D (2008) Sex versus parthenogenesis: a transcriptomic approach of photoperiod response in the model aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Gene 408:146–156
Dedryver CA, Le Gallic JF, Mahéo F, Simon JC, Dedryver F (2013) The genetics of obligate parthenogenesis in an aphid species and its consequences for the maintenance of alternative reproductive modes. Heredity 110:39–45
Douglas AE (1998) Nutritional interactions in insect-microbial symbioses: aphids and their symbiotic bacteria Buchnera. Annu Rev Entomol 43:17–37
Ghanim M, Kontsedalov S, Czosnek H (2007) Tissue-specific gene silencing by RNA interference in the whitefly Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius). Insect Biochem Mol Biol 37:732–738
Hardy NB, Peterson DA, von Dohlen CD (2015) The evolution of life cycle complexity in aphids: ecological optimization or historical constraint? Evolution 69:1423–1432
Harrison JS, Mondor EB (2011) Evidence for an invasive aphid “superclone”: extremely low genetic diversity in Oleander aphid (Aphis nerii) populations in the southern United States. PLoS ONE 6:e17524
He B, Chu Y, Yin M, Müllen K, An C, Shen J (2013) Fluorescent nanoparticle delivered dsRNA toward genetic control of insect pests. Adv Mater 25:4580–4584
Hofmann K, Stoffel W (1993) TMbase—a database of membrane spanning proteins segments. Biol Chem Hoppe-Seyler 374:166
Huvenne H, Smagghe G (2010) Mechanisms of dsRNA uptake in insects and potential of RNAi for pest control: a review. J Insect Physiol 56:227–235
Jiang L, Ding L, He B, Shen J, Xu Z, Yin M, Zhang X (2014) Systemic gene silencing in plants triggered by fluorescent nanoparticle-delivered double-strand RNA. Nanoscale 6:9965
Joga MR, Zotti MJ, Smagghe G, Christiaens O (2016a) RNAi efficiency, systemic properties, and novel delivery methods for pest insect control: what we know so far. Front Physiol 7:553
Joga MR, Zotti MJ, Smagghe G, Christiaens O (2016b) RNAi efficiency, systemic properties, and novel delivery methods for pest insect control: what we know so far. Front Physiol 7:553
Kong G, Braun RD, Dewhirst MW (2000) Hyperthermia enables tumor-specific nanoparticle delivery: effect of particle size. Cancer Res 60:4440–4445
Li J, Wang XP, Wang MQ, Ma WH, Hua HX (2013) Advances in the use of the RNA interference technique in Hemiptera. Insect Sci 20:31–39
Li H, Guan R, Guo H, Xiao M (2015) New insights into an RNAi approach for plant defence against piercing-sucking and stem-borer insect pests. Plant Cell Eviron 38:2277–2285
Li J, Qian J, Xu Y, Yan S, Shen J, Yin M (2019) A facile-synthesized star polycation constructed as a highly efficient gene vector in pest management. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:6316–6322
Lin X, Yao Y, Jin M, Li Q (2014) Characterization of the Distal-less gene homologue, NIDII, in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Gene 535:112–118
Liu X, He B, Xu Z, Yin M, Yang W, Zhang H, Cao J, Shen J (2014) A functionalized fluorescent dendrimer as a pesticide nanocarrier: application in pest control. Nanoscale 7:445–449
Liu X, Zheng Y, Zhang S, Liu K, Zhang S, Yin M, Zhang L, Shen J (2016) Perylenediimide-cored cationic nanocarriers deliver virus DNA to kill insect pests. Polym Chem 7:3740–3746
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆CT method. Methods 25:402–408
Mao J, Zeng F (2014) Plant-mediated RNAi of a gap gene-enhanced tobacco tolerance against the Myzus persicae. Transgenic Res 23:145–152
Mao YB, Cai WJ, Wang JW, Hong GJ, Tao XY, Wang LJ, Huang YP, Chen XY (2007) Silencing a cotton bollworm P450 monooxygenase gene by plant-mediated RNAi impairs larval tolerance of gossypol. Nat Biotechnol 25:1307–1313
Mutti NS, Park Y, Reese JC, Reeck GR (2006) RNAi knockdown of a salivary transcript leading to lethality in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. J Insect Sci 6:1–7
Pitino M, Coleman AD, Maffei ME, Ridout CJ, Hogenhout SA (2011) Silencing of aphid genes by dsRNA feeding from plants. PLoS ONE 6:e25709
San Miguel K, Scott JG (2016) The next generation of insecticides: dsRNA is stable as a foliar applied insecticide. Pest Manag Sci 72:801–809
Shakesby A, Wallace I, Isaacs H, Pritchard J, Roberts D, Douglas A (2009) A water-specific aquaporin involved in aphid osmoregulation. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 39:1–10
Shen D, Zhou F, Xu Z, He B, Li M, Shen J, Yin M, An C (2014) Systemically interfering with immune response by a fluorescent cationic dendrimer delivered gene suppression. J Mater Chem B 2:4653–4659
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Terenius O, Papanicolaou A, Garbutt JS, Eleftherianos I, Huvenne H, Kanginakudru S, Albrechtsen M, An C, Aymeric JL, Barthel A (2011) RNA interference in Lepidoptera: an overview of successful and unsuccessful studies and implications for experimental design. J Insect Physiol 57:231–245
Thairu MW, Skidmore IH, Bansal R, Nováková E, Hansen TE, Li-Byarlay H, Wickline SA, Hansen AK (2017) Efficacy of RNA interference knockdown using aerosolized short interfering RNAs bound to nanoparticles in three diverse aphid species. Insect Mol Biol 26:356–368
Thakur N, Upadhyay SK, Verma PC, Chandrashekar K, Tuli R, Singh PK (2014) Enhanced whitefly resistance in transgenic tobacco plants expressing double stranded RNA of v-ATPase A gene. PLoS ONE 9:e87235
Tomoyasu Y, Miller SC, Tomita S, Schoppmeier M, Grossmann D, Bucher G (2008) Exploring systemic RNA interference in insects: a genome-wide survey for RNAi genes in Tribolium. Genome Biol 9:R10
Upadhyay SK, Chandrashekar K, Thakur N, Verma PC, Borgio JF, Singh PK, Tuli R (2011) RNA interference for the control of whiteflies (Bemisia tabaci) by oral route. J Biosci 36:153–161
Veldhuizen EJA, Haagsman HP (2000) Role of pulmonary surfactant components in surface film formation and dynamics. Biochim Biophys Acta 1467:255–270
Wani SA, Ahmad ST (2014) Phenomenon of parthenogenesis, viviparity and endosymbiosis in aphids-a review. J Bio Innov 3:206–215
Wenger JA, Cassone BJ, Legeai F, Johnston JS, Bansal R, Yates AD, Coates BS, Pavinato VA, Michel A (2017) Whole genome sequence of the soybean aphid, Aphis glycines. Insect Biochem Mol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2017.01.005
Whangbo JS, Hunter CP (2008) Environmental RNA interference. Trends Genet 24:297–305
Whyard S, Singh AD, Wong S (2009) Ingested double-stranded RNAs can act as species-specific insecticides. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 39:824–832
Win KY, Feng SS (2005) Effects of particle size and surface coating on cellular uptake of polymeric nanoparticles for oral delivery of anticancer drugs. Biomaterials 26:2713–2722
Wurbs D, Ruf S, Bock R (2007) Contained metabolic engineering in tomatoes by expression of carotenoid biosynthesis genes from the plastid genome. Plant J 49:276–288
Xu Z, He B, Shen J, Yang W, Yin M (2013) Fluorescent water-soluble perylenediimide-cored cationic dendrimers: synthesis, optical properties, and cell uptake. Chem Commun 49:3646
Xu Z, He B, Wei W, Liu K, Yin M, Yang W, Shen J (2014) Highly water-soluble perylenediimide-cored poly(amido amine) vector for efficient gene transfection. J Mater Chem B 2:3079–3086
Yan S, Zhu J, Zhu W, Li Z, Shelton AM, Luo J, Cui J, Zhang Q, Liu X (2015) Pollen-mediated gene flow from transgenic cotton under greenhouse condition is dependent on different pollinators. Sci Rep 5:15917
Yan S, Zhu JL, Zhu WL, Qin M, Liu H, Zhao SQ, Wang L, Zhang J, Zhang QW, Liu XX (2017) The influences of wind speed on pollen-mediated gene flow from transgenic cotton. Chin J Ecol 36:2217–2223
Yan S, Zhu W, Zhang B, Zhang X, Zhu J, Shi J, Wu P, Wu F, Li X, Zhang Q, Liu X (2018) Pollen-mediated gene flow from transgenic cotton is constrained by physical isolation measures. Sci Rep 8:2862
Yin M, Shen J, Gropeanu R, Pflugfelder GO, Weil T, Müllen K (2008) Fluorescent core/shell nanoparticles for specific cell-nucleus staining. Small 4:894–898
Yu N, Christiaens O, Liu J, Niu J, Cappelle K, Caccia S, Huvenne H, Smagghe G (2013) Delivery of dsRNA for RNAi in insects: an overview and future directions. Insect Sci 20:4–14
Zha W, Peng X, Chen R, Du B, Zhu L, He G (2011) Knockdown of midgut genes by dsRNA-transgenic plant-mediated RNA interference in the hemipteran insect Nilaparvata lugens. PLoS ONE 6:e20504
Zhang X, Zhang J, Zhu KY (2010) Chitosan/double-stranded RNA nanoparticle-mediated RNA interference to silence chitin synthase genes through larval feeding in the African malaria mosquito (Anopheles gambiae). Insect Mol Biol 19:683–693
Zhang H, Li HC, Miao XX (2013a) Feasibility, limitation and possible solutions of RNAi-based technology for insect pest control. Insect Sci 20:15–30
Zhang X, Lu K, Zhou Q (2013b) Dicer1 is crucial for the oocyte maturation of telotrophic ovary in Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Hemiptera: Geometroidea). Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 84:194–208
Zhang J, Khan SA, Hasse C, Ruf S, Heckel DG, Bock R (2015a) Full crop protection from an insect pest by expression of long double-stranded RNAs in plastids. Science 347:991–994
Zhang J, Khan SA, Hasse C, Ruf S, Heckel DG, Bock R (2015b) Pest control. Full crop protection from an insect pest by expression of long double-stranded RNAs in plastids. Science 347:991–994
Zheng Y, You S, Ji C, Yin M, Yang W, Shen J (2016) Development of an amino acid-functionalized fluorescent nanocarrier to deliver a toxin to kill insect pests. Adv Mater 28:1375
Zheng Y, Hu Y, Yan S, Zhou H, Song D, Yin M, Shen J (2019) A polymer/detergent formulation improves dsRNA penetration through the body wall and RNAi-induced mortality in the soybean aphid Aphis glycines. Pest Manag Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps/5313
Zotti MJ, Smagghe G (2015) RNAi technology for insect management and protection of beneficial insects from diseases: lessons, challenges and risk assessments. Neotrop Entomol 44:197–213
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Dunlun Song and Dr. Zhen Li for providing the transcriptome data.
Funding
This research was supported by the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (6182020), National Key Research and Development Program (2017YFD0201200) and Natural Science Foundation of China (31900363).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by E. Roditakis.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, S., Qian, J., Cai, C. et al. Spray method application of transdermal dsRNA delivery system for efficient gene silencing and pest control on soybean aphid Aphis glycines. J Pest Sci 93, 449–459 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-019-01157-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-019-01157-x