Abstract
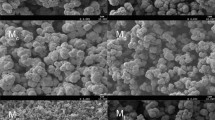
Estrogen plays a crucial role in various stages of human development and is present in the human body at trace level; therefore, an efficient strategy for the quantitative analysis of trace estrogens is required. However, this analysis is complicated by the presence of extremely complex biological matrices. To address this challenge, a novel method based on monolithic column solid-phase microextraction and ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry was developed for the sensitivity analysis of six estrogens: β-estradiol, α-estradiol, 17α-ethynylestradiol, estrone, diethylstilbestrol, and hexestrol, in human urine and serum samples. The method exhibits a low limit of detection (8.6–37 ng L−1), with wide linear ranges (0.10–25 μg L−1) for each analyte and remarkable correlation coefficients (R2 = 0.9953–0.9995). The developed method was successfully used to detect estrogens in urine and serum samples. The six analytes were satisfactorily recovered between 76.2 and 107% with relative standard deviations ranging from 2.5 to 8.3% (n = 3). The results demonstrated that the developed method, based on a poly(methacrylic acid/3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid-co-ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) monolithic column, is an effective enrichment approach toward the analysis of trace estrogens in human urine and serum samples.
Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atashgaran V, Wrin J, Barry SC, Dasari P, Ingman WV (2016) Dissecting the biology of menstrual cycle-associated breast cancer risk. Front Oncol 6:267–276
Berkane N, Liere P, Oudinet JP, Hertig A, Lefèvre G, Pluchino N, Schumacher M, Chabbert-Buffet N (2017) From pregnancy to preeclampsia: a key role for estrogens. Endocr Rev 38:123–144
Cussenot O, Azzouzi AR, Nicolaiew N, Fromont G, Mangin P, Cormier L, Fournier G, Valeri A, Larre S, Thibault F, Giordanella JP, Pouchard M, Zheng Y, Hamdy FC, Cox A, Cancel-Tassin G (2007) Combination of polymorphisms from genes related to estrogen metabolism and risk of prostate cancers: the hidden face of estrogens. J Clin Oncol 25:3596–3602
Senekjian EK, Press MF, Blough RR, Herbst AL, DeSombre ER (1989) Comparison of the quantity of estrogen receptors in human endometrium and myometrium by steroid-binding assay and enzyme immunoassay based on monoclonal antibodies to human estrophilin. Am J Obstet Gynecol 160:592–597
Rinaldi S, Moret CN, Kaaks R, Biessy C, Kurzer MS, Déchaud H, Peeters PHM, Noord PAHV (2003) Reproducibility over time of measurements of androgens, estrogens and hydroxy estrogens in urine samples from post-menopausal women. Eur J Epidemiol 18:417–424
González A, Clavijo S, Cerdà V (2019) Estrogens determination exploiting a SIA-LOV system prior in-port derivatization-large volume injection-programmable temperature vaporization-gas chromatography. Talanta 194:852–858
Asadi Atoi P, Talebpour Z, Fotouhi L (2019) Introduction of electropolymerization of pyrrole as a coating method for stir bar sorptive extraction of estradiol followed by gas chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1604:460478–460488
You J, Shi Y, Li J, Yang X, Liu Z, Zhu W, Wu Z, Xiong J (2019) Rapid quantification of human urinary estrogens and estrogen metabolites by HPLC mass spectrometry. Microchem J 147:157–162
Laforest S, Pelletier M, Denver N, Poirier B, Nguyen S, Walker BR, Durocher F, Homer NZM, Diorio C, Tchernof A, Andrew R (2019) Simultaneous quantification of estrogens and glucocorticoids in human adipose tissue by liquid-chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Steroid Biochem 195:105476–105484
Wang C, Yang L, Li N, Zhang X, Guo Y, Li C (2017) Development of immunoaffinity solid phase microextraction rods for analysis of three estrogens in environmental water samples. J Chromatogr B 1061–1062:41–48
Frederiksen H, Johannsen TH, Andersen SE, Albrethsen J, Landersoe SK, Petersen JH, Andersen AN, Vestergaard ET, Schorring ME, Linneberg A, Main KM, Andersson AM, Juul A (2020) Sex-specific estrogen levels and reference intervals from infancy to late adulthood determined by LC-MS/MS. J Clin Endocr Metab 105:754–768
Zhang J, Zang L, Wang T, Wang X, Jia M, Zhang D, Zhang H (2020) A solid-phase extraction method for estrogenic disrupting compounds based on the estrogen response element. Food Chem 333:127529–127535
Jiang Q, Xu P, Sun M (2020) Resorcinol-formaldehyde aerogel coating for in-tube solid-phase microextraction of estrogens. J Sep Sci 43:1323–1330
Ben Fredj S, Nobbs J, Tizaoui C, Monser L (2015) Removal of estrone (E1), 17β-estradiol (E2), and 17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) from wastewater by liquid-liquid extraction. Chem Eng J 262:417–426
Goh SXG, Lee HK (2017) An alternative perspective of hollow fiber-mediated extraction: Bundled hollow fiber array-liquid-phase microextraction with sonication-assisted desorption and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for determination of estrogens in aqueous matrices. J Chromatogr A 1488:26–36
Kibambe MG, Momba MNB, Daso AP, Van Zijl MC, Coetzee MAA (2020) Efficiency of selected wastewater treatment processes in removing estrogen compounds and reducing estrogenic activity using the T47D-KBLUC reporter gene assay. J Environ Manage 260:110135–110145
González A, Cerdà V (2020) Development of an automatic sequential injection analysis-lab on valve system exploiting molecularly imprinted polymers coupled with high performance liquid chromatography for the determination of estrogens in wastewater samples. Talanta 209:120564–120569
Wang Y, Jin S, Wang Q, Lu G, Jiang J, Zhu D (2013) Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 as sorbent of micro-solid-phase extraction to determine estrogens in environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A 1291:27–32
Wang J, Cheng C, Yang Y (2015) Determination of estrogens in milk samples by magnetic-solid-phase extraction technique coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography. J Food Sci 80:2655–2661
Li W, Zhang J, Zhu W, Qin P, Zhou Q, Lu M, Zhang X, Zhao W, Zhang S, Cai Z (2020) Facile preparation of reduced graphene oxide/ZnFe2O4 nanocomposite as magnetic sorbents for enrichment of estrogens. Talanta 208:120440–120447
Huang S, Ye N, Chen G, Ou R, Huang Y, Zhu F, Shen J, Ouyang G (2019) A robust and homogeneous porous poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/graphene thin film for high-efficiency laser desorption/ionization analysis of estrogens in biological samples. Talanta 195:290–297
Do Carmo SN, Merib J, Carasek E (2019) Bract as a novel extraction phase in thin-film SPME combined with 96-well plate system for the high-throughput determination of estrogens in human urine by liquid chromatography coupled to fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr B 1118–1119:17–24
Feng J, Sun M, Bu Y, Luo C (2016) Hollow fiber membrane-coated functionalized polymeric ionic liquid capsules for direct analysis of estrogens in milk samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 408:1679–1685
Feng J, Sun M, Bu Y, Luo C (2016) Development of a cheap and accessible carbon fibers-in-poly(ether ether ketone) tube with high stability for online in-tube solid-phase microextraction. Talanta 148:313–320
Wang X, Feng J, Tian Y, Li C, Ji X, Luo C, Sun M (2019) Melamine-formaldehyde aerogel functionalized with polydopamine as in tube solid-phase microextraction coating for the determination of phthalate esters. Talanta 199:317–323
Feng J, Wang X, Han S, Ji X, Li C, Luo C, Sun M (2019) An ionic-liquid-modified melamine-formaldehyde aerogel for in-tube solid-phase microextraction of estrogens followed by high performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection. Microchim Acta 186:769–776
Feng J, Loussala HM, Han S, Ji X, Li C, Sun M (2020) Recent advances of ionic liquids in sample preparation. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 125:115833–115853
Feng J, Feng J, Ji X, Li C, Han S, Sun H, Su M (2021) Recent advances of covalent organic frameworks for solid-phase microextraction. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 137:116208–116223
Sun M, Li C, Feng J, Sun H, Sun M, Feng Y, Ji X, Han S, Feng J (2022) Development of aerogels in solid-phase extraction and microextraction. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 146:116497–116513
Wang S, Geng Y, Sun X, Wang R, Zheng Z, Hou S, Wang X, Ji W (2020) Molecularly imprinted polymers prepared from a single cross-linking functional monomer for solid-phase microextraction of estrogens from milk. J Chromatogr A 1627:461400–461408
Sun M, Feng J, Bu Y, Luo C (2016) Ionic liquid coated copper wires and tubes for fiber-in-tube solid-phase microextraction. J Chromatogr A 1458:1–8
Bagheri H, Piri-Moghadam H, Ahdi T (2012) Role of precursors and coating polymers in sol-gel chemistry toward enhanced selectivity and efficiency in solid phase microextraction. Anal Chim Acta 742:45–53
Lan H, Pan D, Sun Y, Guo Y, Wu Z (2016) Thin metal organic frameworks coatings by cathodic electrodeposition for solid-phase microextraction and analysis of trace exogenous estrogens in milk. Anal Chim Acta 937:53–60
Fan Y, Feng Y, Da S, Shi Z (2004) Poly (methacrylic acid–ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) monolithic capillary for in-tube solid phase microextraction coupled to high performance liquid chromatography and its application to determination of basic drugs in human serum. Anal Chim Acta 523:251–258
Wei F, Zhang M, Feng Y (2006) Application of poly(methacrylic acid-ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) monolith microextraction coupled with capillary zone electrophoresis to the determination of opiates in human urine. Electrophoresis 27:1939–1948
Wei F, Fan Y, Zhang M, Feng Y (2005) Poly(methacrylic acid-ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) monolith in-tube solid-phase microextraction applied to simultaneous analysis of some amphetamine derivatives in urine by capillary zone electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 26:3141–3150
Hu Y, Fan Y, Li G (2012) Preparation and evaluation of a porous monolithic capillary column for microextraction of estrogens from urine and milk samples online coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1228:205–212
Ren L, Liu Z, Dong M, Ye M, Zou H (2009) Synthesis and characterization of a new boronate affinity monolithic capillary for specific capture of cis-diol-containing compounds. J Chromatogr A 1216:4768–4774
Yang X, Hu Y, Li G (2014) Online micro-solid-phase extraction based on boronate affinity monolithic column coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of monoamine neurotransmitters in human urine. J Chromatogr A 1342:37–43
Li D, Chen Y, Liu Z (2015) Boronate affinity materials for separation and molecular recognition: Structure, properties and applications. Chem Soc Rev 44:8097–8123
Chen J, Li X, Feng M, Luo K, Yang J, Bo Z (2017) Novel boronate material affords efficient enrichment of glycopeptides by synergized hydrophilic and affinity interactions. Anal Bioanal Chem 409:519–528
Zhang Q, Xia G, Liang J, Zhang X, Jiang L, Zheng Y, Wang X (2020) NH2-MIL-53(Al) Polymer monolithic column for in-tube solid-phase microextraction combined with UHPLC-MS/MS for detection of trace sulfonamides in food samples. Molecules 25:897–912
Kahraman G, Beşkardeş O, Rzaev ZMO, Pişki E (2004) Bioengineering polyfunctional copolymers. VII. Synthesis and characterization of copolymers of p-vinylphenyl boronic acid with maleic and citraconic anhydrides and their self-assembled macrobranched supramolecular architectures. Polymer 45:5813–5828
De Araújo Elpídio CM, De Araújo Padilha CE, De Sousa Júnior FC, Do Nascimento RJA, De Araújo Elpídio CM, De Oliveira Júnior SD, De Macedo GR, Dos Santos ES (2018) Fabrication and characterization of a dye-immobilized yttria-stabilized zirconia pellicular adsorbent for expanded bed adsorption chromatography. Chromatographia 81:1355–1364
Moniri E, Panahi HA, Alimadadi A (2015) Polymer-grafted nanographite support obtained using iminodiacetic acid/allyl glycidyl ether: characterization and application in the extraction and determination of enrofloxacin in biological and pharmaceutical samples. Chromatographia 79:293–301
Liu Y, Ren L, Liu Z (2011) A unique boronic acid functionalized monolithic capillary for specific capture, separation and immobilization of cis-diol biomolecules. Chem Commun 47:5067–5069
Luo X, Li G, Hu Y (2017) In-tube solid-phase microextraction based on NH2-MIL-53(Al)-polymer monolithic column for online coupling with high-performance liquid chromatography for directly sensitive analysis of estrogens in human urine. Talanta 165:377–383
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21505115), the Top Scientific and Technological Talents in Universities of Guizhou Province (KY2018078), the Science and Technology for Youth Talent Growth Project of the Guizhou Provincial Education Department (KY2020216), the Key Laboratory for Analytical Science of Food and Environment Pollution of Qianxinan (2021-2-31), and the Projects of Xingyi Normal University for Nationalities (21XYYB10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
The experiments were improved by the ethics committee of Qian Xi Nan People's Hospital. All volunteers were informed of and agreed with the objectives of the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Wang, Y., Yang, B. et al. Development of an Efficient Solid-Phase Microextraction Monolithic Column for the Analysis of Estrogens in Human Urine and Serum Samples. Chromatographia 85, 733–741 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-022-04178-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-022-04178-4