Abstract
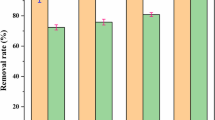
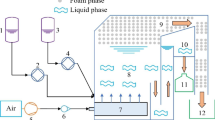
We studied the removal mechanism and affecting factors of Fe2+-based replacement–precipitation process for treating CuEDTA-containing wastewaters. Since Fe2+ was easily oxidized to Fe3+ in the presence of oxygen, the chelated copper was removed by the synergetic effect of Fe3+ replacement and NaOH precipitation. Our experiments showed that the copper removal efficiency was considerably dependant on pH conditions of the solution and molar ratio of Fe2+/Cu2+.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fu FL, Zeng HY, Cai QH, Qiu RL, Yu JM, Xiong Y (2007) Effective removal of coordinated copper from wastewater using a new dithiocarbamate-type supramolecular heavy metal precipitant. Chemosphere 69:1783–1789. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.05.063
Gyliene O, Rekertas R, Salkauskas M (2002) Removal of free and complexed heavy-metal ions by sorbents produced from fly (Musca domestica) larva shells. Water Res 36:4128–4136. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00105-7
Inczédy J (1976) Analytical applications of complex equilibria. Ellis Horwood, Chichester
Juang RS, Wang YC (2002) Effect of added complexing anions on cation exchange of Cu(II) and Zn(II) with a strong-acid resin. Ind Eng Chem Res 41:5558–5564. doi:10.1021/ie0202017
Kari FG, Giger W (1996) Speciation and fate of ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA) in municipal wastewater treatment. Water Res 30:122–134. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(95)00125-5
Korshin GV, Chang HS, Frenkel AI, Ferguson JF (2007) Structural study of the incorporation of heavy metals into solid phase formed during the oxidation of EDTA by permanganate at high pH. Environ Sci Technol 41:2560–2565. doi:10.1021/es062554t
Nowack B, Kari FG, Krüger HG (2001) The remobilization of metals from iron oxides and sediments by metal-EDTA complexes. Water Air Soil Pollut 125:243–257. doi:10.1023/A:1005296312509
Ureña-Nuñez F, Barrera-Díaz C, Bilyeu Bryan (2007) Gamma radiation-polymerized Zn(II) methacrylate as a sorbent for removal of Pb(II) ions from wastewater. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:3382–3389. doi:10.1021/ie0612111
Xue HB, Sigg L (1993) Free cupric ion concentration and Cu(II) speciation in a eutrophic lake. Limnol Oceanogr 38:1200–1213
Zhao D, Sengupta AK (2000) Ligand separation with a copper(II)-loaded polymeric ligand exchanger. Ind Eng Chem Res 39:455–462. doi:10.1021/ie990740k
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Nature Science Foundations of China (50578163), the Special Foundation of Sun Yat-Sen University, Science and the Technology Research Programs of Guangdong Province (0711220600311 and 9251027501000005) and Guangzhou City (2006Z2-E0031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, S., Qu, J. & Xiong, Y. Removal of chelated copper from wastewaters by Fe2+-based replacement–precipitation. Environ Chem Lett 8, 339–342 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-009-0230-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-009-0230-1