Abstract
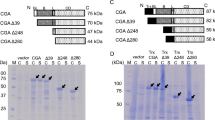
The excretion of cyclodextrin glucanotransferase (CGTase) into the culture medium offers significant advantages over cytoplasmic expression. However, the limitation of Escherichia coli is its inability to excrete high amount of CGTase outside the cells. In this study, modification of the hydrophobic region of the N1R3 signal peptide using site-saturation mutagenesis improved the excretion of CGTase. Signal peptide mutants designated M9F, V10L and A15Y enhanced the excretion of CGTase three-fold and demonstrated two-fold higher secretion rate than the wild type. However, high secretion rate of these mutants was non-productive for recombinant protein production because it caused up to a seven-fold increase in cell death compared to the wild type. Our results indicated that the excretion of CGTase is highly dependent on hydrophobicity, secondary conformation and the type and position of amino acids at the region boundary and core segment of the h-region.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakke I, Berg L, Aune TEV, Brautaset T, Sletta H, Tøndervik A, Valla S (2009) Random mutagenesis of the Pm promoter as a powerful strategy for improvement of recombinant-gene expression. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:2002–2011. doi:10.1128/AEM.02315-08
Baneyx F, Mujacic M (2004) Recombinant protein folding and misfolding in Escherichia coli. Nat Biotechnol 22:1399–1408. doi:10.1038/nbt1029
Bao RM, Yang HM, Yu CM, Zhang WF, Tang JB (2016) An efficient protocol to enhance the extracellular production of recombinant protein from Escherichia coli by the synergistic effects of sucrose, glycine, and Triton X-100. Protein Exp Purif 126:9–15. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2016.05.007
Bowers C, Lau F (2003) Secretion of LamB-LacZ by the signal recognition particle pathway of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 185:5697–5705. doi:10.1128/JB.185.19.5697
Brockmeier U, Caspers M, Freudl R, Jockwer A, Noll T, Eggert T (2006) Systematic screening of all signal peptides from Bacillus subtilis: a powerful strategy in optimizing heterologous protein secretion in Gram-positive bacteria. J Mol Biol 362:393–402. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.07.034
Chatzi KE, Sardis MF, Karamanou S, Economou A (2013) Breaking on through to the other side: protein export through the bacterial Sec system. Biochem J 449:25–37. doi:10.1042/BJ20121227
Choi JH, Lee SY (2004) Secretory and extracellular production of recombinant proteins using Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:625–635. doi:10.1007/s00253-004-1559-9
Chou YT, Gierasch LM (2005) The conformation of a signal peptide bound by Escherichia coli preprotein translocase SecA. J Biol Chem 280:32753–32760. doi:10.1074/jbc.M507532200
Chou MM, Kendall DA (1990) Polymeric sequences reveal a functional interrelationship between hydrophobicity and length of signal peptides. J Biol Chem 265:2873–2880
Chupin V, Killian JA, Breg J, de Jongh HH, Boelens R, Kaptein R, de Kruijff B (1995) PhoE signal peptide inserts into micelles as a dynamic helix-break-helix structure, which is modulated by the environment. A two-dimensional 1H NMR study. Biochemistry 34:11617–11624
Clérico EM, Maki JL, Gierasch LM (2008) Use of synthetic signal sequences to explore the protein export machinery. Biopolym Pept Sci 90:307–319. doi:10.1002/bip.20856
Dalbey RE, Wang P, van Dijl JM (2012) Membrane Proteases in the bacterial protein secretion and quality control pathway. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 76:311–330. doi:10.1128/MMBR.05019-11
De Bona P, Deshmukh L, Gorbatyuk V, Vinogradova O, Kendall DA (2012) Structural studies of a signal peptide in complex with signal peptidase I cytoplasmic domain: the stabilizing effect of membrane-mimetics on the acquired fold. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinform 80:807–817. doi:10.1002/prot.23238
Doud SK, Chou MM, Kendall DA (1993) Titration of protein transport activity by incremental changes in signal peptide hydrophobicity. Biochemistry 32:1251–1256
Douzi B, Filloux A, Voulhoux R (2012) On the path to uncover the bacterial type II secretion system. Philos Trans R Soc B 367:1059–1072. doi:10.1098/rstb.2011.0204
Emr SD, Silhavy TJ (1982) Molecular components of the signal sequence that function in the initiation of protein export. J Cell Biol 95:689–696
Fekkes P, Driessen AJ (1999) Protein targeting to the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:161–173
Filipe JM, Monteiro GA (2004) Secretion capacity limitations of the Sec pathway in Escherichia coli. J Microbiol Biotechnol 14:128–133
Fu ZB, Ng KL, Lam TL, Wong WKR (2005) Cell death caused by hyper-expression of a secretory exoglucanase in Escherichia coli. Protein Exp Purif 42:67–77. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2005.03.029
Fu ZB, Ng KL, Lam CC, Leung KC, Yip WH, Wong WKR (2006) A two-stage refinement approach for the enhancement of excretory production of an exoglucanase from Escherichia coli. Protein Exp Purif 48:205–214. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2006.01.013
Gennity J, Goldstein J, Inouye M (1990) Signal peptide mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bioenerg Biomembr 22:233–269
Heggeset TMB, Kucharova V, Naerdal I, Valla S, Sletta H, Ellingsen TE, Brautaset T (2013) Combinatorial mutagenesis and selection of improved signal sequences and their application for high-level production of translocated heterologous proteins in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:559–568. doi:10.1128/AEM.02407-12
Hikita C, Mizushima S (1992) Effects of total hydrophobicity and length of the hydrophobic domain of a signal peptide on in vitro translocation efficiency. J Biol Chem 267:4882–4888
Ismail NF, Hamdan S, Mahadi NM, Murad AMA, Rabu A, Bakar FDA, Klappa P, Illias RM (2011) A mutant l-asparaginase II signal peptide improves the secretion of recombinant cyclodextrin glucanotransferase and the viability of Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Lett 33:999–1005. doi:10.1007/s10529-011-0517-8
Izard JW, Rusch SL, Kendall DA (1996) The amino-terminal charge and core region hydrophobicity interdependently contribute to the function of signal sequences. J Biol Chem 271:21579–21582. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.35.21579
Jones JD, McKnight CJ, Gierasch LM (1990) Biophysical studies of signal peptides: implications for signal sequence functions and the involvement of lipid in protein export. J Bioenerg Biomembr 22:213–232. doi:10.1007/BF00763166
Jonet MA, Mahadi NM, Murad AMA, Rabu A, Bakar FDA, Rahim RA, Low KO, Illias RM (2012) Optimization of a heterologous signal peptide by site-directed mutagenesis for improved secretion of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 22:48–58. doi:10.1159/000336524
Jong WS, Saurí A, Luirink J (2010) Extracellular production of recombinant proteins using bacterial autotransporters. Curr Opin Biotechnol 21:646–652. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2010.07.009
Kadonaga JT, Gautier AE, Straus DR, Charles AD, Edge MD, Knowles JR (1984) The role of the β-Lactamase signal sequence in the secretion of proteins by Escherichia coli *. J Biol Chem 259:2149–2154
Kendall DA, Bock SC, Kaiser ET (1986) Idealization of the hydrophobic segment of the alkaline phosphatase signal peptide. Nature 321:706–708. doi:10.1038/321706a0
Kim SG, Kweon DH, Lee DH, Park YC, Seo JH (2005) Coexpression of folding accessory proteins for production of active cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase of Bacillus macerans in recombinant Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 41:426–432. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2005.01.017
Kim AC, Oliver DC, Paetzel M (2008) Crystal structure of a bacterial signal peptide peptidase. J Mol Biol 376:352–366. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.11.080
Kyte J, Doolittle RF (1982) A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol 157:105–132. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0
Labrou N (2010) Random mutagenesis methods for in vitro directed enzyme evolution. Curr Protein Pept Sci 11:91–100. doi:10.2174/1389209198868622037
Lehnhardt S, Pollitt S, Inouye M (1987) The differential effect on two hybrid proteins of deletion mutations within the hydrophobic region of the Escherichia coli OmpA signal peptide. J Biol Chem 262:1716–1719
Lemberg MK, Martoglio B (2002) Requirements for signal peptide peptidase-catalyzed intramembrane proteolysis. Mol Cell 10:735–744. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00655-X
Li H, Faury D, Morosoli R (2006) Impact of amino acid changes in the signal peptide on the secretion of the Tat-dependent xylanase C from Streptomyces lividans. FEMS Microbiol Lett 255:268–274. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2005.00081.x
Li ZF, Li B, Liu ZG, Wang M, Gu ZB, Du GC, Wu J, Chen J (2009) Calcium leads to further increase in glycine-enhanced extracellular secretion of recombinant alpha-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase in Escherichia coli. J Agric Food Chem 57:6231–6237. doi:10.1021/jf901239k
Li Z, Gu Z, Wang M, Du G, Wu J, Chen J (2010) Delayed supplementation of glycine enhances extracellular secretion of the recombinant alpha-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:553–561. doi:10.1007/s00253-009-2157-7
Li Z, Su L, Wang L, Liu Z, Gu Z, Chen J, Wu J (2014) Novel insight into the secretory expression of recombinant enzymes in Escherichia coli. Process Biochem 49:599–603. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2014.01.029
Li L, Park E, Ling J, Ingram J, Ploegh H, Rapoport TA (2016) Crystal structure of a substrate-engaged SecY protein-translocation channel. Nature 531:395–399. doi:10.1038/nature17163
Low KO, Mahadi NM, Illias RM (2013) Optimisation of signal peptide for recombinant protein secretion in bacterial hosts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:3811–3826. doi:10.1007/s00253-013-4831-z
Mergulhão FJM, Summers DK, Monteiro GA (2005) Recombinant protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Adv 23:177–202. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2004.11.003
Mori H, Araki M, Hikita C, Tagaya M, Mizushima S (1997) The hydrophobic region of signal peptides is involved in the interaction with membrane-bound SecA. Biochim Biophys Acta 1326:23–36. doi:10.1016/S0005-2736(97)00004-7
Ni Y, Chen R (2009) Extracellular recombinant protein production from Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Lett 31:1661–1670. doi:10.1007/s10529-009-0077-3
Nielsen H, Engelbrecht J (1997) Identification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic signal peptides and prediction of their cleavage sites artificial neural networks have been used for many biological. Protein Eng 10:1–6. doi:10.1142/S0129065797000537
Park S, Liu G, Topping TB, Cover WH, Randall LL (1988) Modulation of folding pathways of exported proteins by the leader sequence. Science 239:1033–1035. doi:10.1126/science.3278378
Patrick WM, Firth AE (2005) Strategies and computational tools for improving randomized protein libraries. Biomol Eng 22:105–112. doi:10.1016/j.bioeng.2005.06.001
Pugsley AP (1993) The complete general secretory pathway in Gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol Rev 57:50–108
Rusch SL, Kendall DA (1992) Signal sequences containing multiple aromatic residues. J Mol Biol 224:77–85. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(92)90577-7
Rusch SL, Kendall DA (2007) Interactions that drive Sec-dependent bacterial protein transport. Biochemistry 46:9665–9673. doi:10.1021/bi7010064
Rusch SL, Chen H, Izard JW, Kendall DA (1994) Signal peptide hydrophobicity is finely tailored for function. J Cell Biochem 55:209–217. doi:10.1002/jcb.240550208
Rusch SL, Mascolo CL, Kebir MO, Kendall DA (2002) Juxtaposition of signal-peptide charge and core region hydrophobicity is critical for functional signal peptides. Arch Microbiol 178:306–310. doi:10.1007/s00203-002-0453-z
Ryan P, Edwards CO (1995) Systematic introduction of proline in a eukaryotic signal sequence suggests asymmetry within the hydrophobic core. J Biol Chem 270:27876–27879. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.46.27876
Shin H-D, Chen RR (2008) Extracellular recombinant protein production from an Escherichia coli lpp deletion mutant. Biotechnol Bioeng 101:1288–1296. doi:10.1002/bit.22013
Shokri A, Sandén AM, Larsson G (2003) Cell and process design for targeting of recombinant protein into the culture medium of Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:654–664. doi:10.1007/s00253-002-1156-8
Sjöström M, Wold S, Wieslander A, Rilfors L (1987) Signal peptide amino acid sequences in Escherichia coli contain information related to final protein localization. A multivariate data analysis. EMBO J 6:823–831
Stader J, Benson SA, Silhavy TJ (1986) Kinetic analysis of lamB mutants suggests the signal sequence plays multiple roles in protein export. J Biol Chem 261:15075–15080
Stern B, Optun A, Liesenfeld M, Gey C, Gräfe M, Pryme IF (2011) Enhanced protein synthesis and secretion using a rational signal-peptide library approach as a tailored tool. BMC Proc 5(Suppl 8):O13. doi:10.1186/1753-6561-5-S8-O13
Sung CY, Gennity JM, Pollitts NS (1992) A positive residue in the hydrophobic core of the Escherichia coli lipoprotein signal peptide suppresses the secretion defect caused by an acidic amino terminus. J Biol Chem 267:997–1000
von Heijne G (1985) Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J Mol Biol 184:99–105. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(85)90046-4
von Heijne G (1990) The signal peptide. J Membr Biol 115:195–201. doi:10.1007/BF01871271
Wang L, Miller A, Kendall DA (2000) Signal peptide determinants of SecA binding and stimulation of ATPase activity. J Biol Chem 275:10154–10159. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.14.10154
Wang L, Miller A, Rusch SL, Kendall DA (2004) Demonstration of a specific Escherichia coli SecY-signal peptide interaction. Biochemistry 43:13185–13192
Wang YY, Fu ZB, Ng KL, Lam CC, Chan AKN, Sze KF, Wong WKR (2011) Enhancement of excretory production of an exoglucanase from Escherichia coli with Phage shock protein A (PspA) overexpression. J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:637–645. doi:10.4014/jmb.1101.01036
Yoon SH, Kim SK, Kim JF (2010) Secretory production of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. Recent Pat Biotechnol 4:23–29
Zalucki YM, Beacham IR, Jennings MP (2011) Coupling between codon usage, translation and protein export in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol J 6:660–667. doi:10.1002/biot.201000334
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM) under the project “Enhance Extracellular Production of Recombinant Cyclodextrin Glucanotransferase (CGTase) by Random Mutagenesis of Signal Peptide and Optimization of Medium Additives” (Grant No.: Q.J130000.7135.00H76).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ismail, A., Illias, R.M. Site-saturation mutagenesis of mutant l-asparaginase II signal peptide hydrophobic region for improved excretion of cyclodextrin glucanotransferase. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44, 1627–1641 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-017-1980-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-017-1980-6