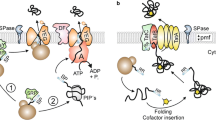
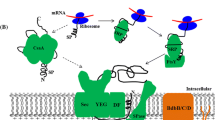
Abstract
Escherichia coli—the powerhouse for recombinant protein production—is rapidly gaining status as a reliable and efficient host for secretory expression. An improved understanding of protein translocation processes and its mechanisms has inspired and accelerated the development of new tools and applications in this field and, in particular, a more efficient secretion signal. Several important characteristics and requirements are summarised for the design of a more efficient signal peptide for the production of recombinant proteins in E. coli. General approaches and strategies to optimise the signal peptide, including the selection and modification of the signal peptide components, are included. Several challenges in the secretory production of recombinant proteins are discussed, and research approaches designed to meet these challenges are proposed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams H, Scotti PA, De Cock H, Luirink J, Tommassen J (2002) The presence of a helix breaker in the hydrophobic core of signal sequences of secretory proteins prevents recognition by the signal-recognition particle in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem 269:5564–5571
Allet B, Bernard AR, Hochmann A, Rohrbach E, Graber P, Magnenat E, Mazzei GJ, Bernasconi L (1997) A bacterial signal peptide directs efficient secretion of eukaryotic proteins in the baculovirus expression system. Protein Expr Purif 9:61–68
Andersson H, Von Heijne G (1991) A 30-residue-long “export initiation domain” adjacent to the signal sequence is critical for protein translocation across the inner membrane of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:9751–9754
Asakura A, Minami M, Ota Y (1995) Convenient desktop-scale production of the extracellular domain of the human growth hormone receptor by an insect–baculovirus secretion system using a protein-free culture. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 59:1976–1978
Bakkes PJ, Jenewein S, Smits SH, Holland IB, Schmitt L (2010) The rate of folding dictates substrate secretion by the Escherichia coli hemolysin type 1 secretion system. J Biol Chem 285:40573–40580
Beena K, Udgaonkar JB, Varadarajan R (2004) Effect of signal peptide on the stability and folding kinetics of maltose binding protein. Biochemistry 43:3608–3619
Bensing BA, Siboo IR, Sullam PM (2007) Glycine residues in the hydrophobic core of the GspB signal sequence route export toward the accessory Sec pathway. J Bacteriol 189:3846–3854
Berks BC, Sargent F, Palmer T (2000) The Tat protein export pathway. Mol Microbiol 35:260–274
Bowers CW, Lau F, Silhavy TJ (2003) Secretion of LamB-LacZ by the signal recognition particle pathway of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 185:5697–5705
Brockmeier U, Caspers M, Freudl R, Jockwer A, Noll T, Eggert T (2006) Systematic screening of all signal peptides from Bacillus subtilis: a powerful strategy in optimizing heterologous protein secretion in gram-positive bacteria. J Mol Biol 362:393–402
Campion SR, Elsasser E, Chung R (1997) Amino-terminal charge affects the periplasmic accumulation of recombinant heregulin/EGF hybrids exported using the Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase signal sequence. Protein Expr Purif 10:331–339
Caspers M, Brockmeier U, Degering C, Eggert T, Freudl R (2010) Improvement of Sec-dependent secretion of a heterologous model protein in Bacillus subtilis by saturation mutagenesis of the N-domain of the AmyE signal peptide. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:1877–1885
Champion MM, Williams EA, Kennedy GM, Champion PA (2012) Direct detection of bacterial protein secretion using whole colony proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics 11:596–604
Chen R (2012) Bacterial expression systems for recombinant protein production: E. coli and beyond. Biotechnol Adv 30:1102–1107
Chen H, Kim J, Kendall DA (1996) Competition between functional signal peptides demonstrates variation in affinity for the secretion pathway. J Bacteriol 178:6658–6664
Chen N, Hong F-L, Wang H-H, Yuan Q-H, Ma W-Y, Gao X-N, Shi R, Zhang R-J, Sun C-S, Wang S-B (2012) Modified recombinant proteins can be exported via the Sec pathway in Escherichia coli. PLoS One 7:e42519
Cho AR, Yoo SK, Kim EJ (2000) Cloning, sequencing and expression in Escherichia coli of a thermophilic lipase from Bacillus thermoleovorans ID-1. FEMS Microbiol Lett 186:235–238
Choi JH, Lee SY (2004) Secretory and extracellular production of recombinant protein using Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:625–635
Choi JH, Jeong KJ, Kim SC, Lee SY (2000) Efficient secretory production of alkaline phosphatase by high cell density culture of recombinant Escherichia coli using the Bacillus sp. endoxylanase signal sequence. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53:640–645
Choi JH, Keum KC, Lee SY (2006) Production of recombinant proteins by high cell density culture of Escherichia coli. Chem Eng Sci 61:876–885
Choo K, Tan T, Ranganathan S (2005) SPdb—a signal peptide database. BMC Bioinformatics 6:249
Chou KC, Shen HB (2007) Signal-CF: a subsite-coupled and window-fusing approach for predicting signal peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 357:633–640
Chou Y-T, Gierasch LM (2005) The conformation of a signal peptide bound by Escherichia coli preprotein translocase SecA. J Biol Chem 280:32753–32760
Coloma MJ, Hastings A, Wims LA, Morrison SL (1992) Novel vectors for the expression of antibody molecules using variable regions generated by polymerase chain reaction. J Immunol Methods 152:89–104
De Vrije T, De Swart RL, Dowhan W, Tommassen J, De Kruijff B (1988) Phosphatidylglycerol is involved in protein translocation across Escherichia coli inner membranes. Nature 334:173–175
Degering C, Eggert T, Puls M, Bongaerts J, Evers S, Maurer KH, Jaeger KE (2010) Optimization of protease secretion in Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis by screening of homologous and heterologous signal peptides. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:6370–6376
Demain AL, Vaishnav P (2009) Production of recombinant proteins by microbes and higher organisms. Biotechnol Adv 27:297–306
Economou A, Wickner W (1994) SecA promotes preprotein translocation by undergoing ATP-driven cycles of membrane insertion and deinsertion. Cell 78:835–843
Fang N, Zhong CQ, Liang X, Tang XF, Tang B (2010) Improvement of extracellular production of a thermophilic subtilase expressed in Escherichia coli by random mutagenesis of its N-terminal propeptide. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:1473–1481
Fariselli P, Finocchiaro G, Casadio R (2003) SPEPlip: the detection of signal peptide and lipoprotein cleavage sites. Bioinformatics 19:2498–2499
Frank K, Sippl MJ (2008) High-performance signal peptide prediction based on sequence alignment techniques. Bioinformatics 24:2172–2176
Fu ZB, Ng KL, Lam TL, Wong WK (2005) Cell death caused by hyper-expression of a secretory exoglucanase in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 42:67–77
Gelis I, Bonvin AM, Keramisanou D, Koukaki M, Gouridis G, Karamanou S, Economou A, Kalodimos CG (2007) Structural basis for signal-sequence recognition by the translocase motor SecA as determined by NMR. Cell 131:756–769
Geller B, Zhu HY, Cheng S, Kuhn A, Dalbey RE (1993) Charged residues render pro-OmpA potential dependent for initiation of membrane translocation. J Biol Chem 268:9442–9447
Georgiou G, Segatori L (2005) Preparative expression of secreted proteins in bacteria: status report and future prospects. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16:538–545
Geukens N, Frederix F, Reekmans G, Lammertyn E, Van Mellaert L, Dehaen W, Maes G, Anné J (2004) Analysis of type I signal peptidase affinity and specificity for preprotein substrates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 314:459–467
Golden A, Austen DA, Van Schravendijk MR, Sullivan BJ, Kawasaki ES, Osburne MS (1998) Effect of promoters and signal sequences on the production of secreted HIV-1 gp120 protein in the baculovirus system. Protein Expr Purif 14:8–12
Goudenege D, Avner S, Lucchetti-Miganeh C, Barloy-Hubler F (2010) CoBaltDB: complete bacterial and archaeal orfeomes subcellular localization database and associated resources. BMC Microbiol 10:88
Gouridis G, Karamanou S, Gelis I, Kalodimos CG, Economou A (2009) Signal peptides are allosteric activators of the protein translocase. Nature 462:363–367
Gray GL, Baldridge JS, Mckeown KS, Heyneker HL, Chang CN (1985) Periplasmic production of correctly processed human growth hormone in Escherichia coli: natural and bacterial signal sequences are interchangeable. Gene 39:247–254
Hardy SJ, Randall LL (1991) A kinetic partitioning model of selective binding of nonnative proteins by the bacterial chaperone SecB. Science 251:439–443
Hikita C, Mizushima S (1992a) Effects of total hydrophobicity and length of the hydrophobic domain of a signal peptide on in vitro translocation efficiency. J Biol Chem 267:4882–4888
Hikita C, Mizushima S (1992b) The requirement of a positive charge at the amino terminus can be compensated for by a longer central hydrophobic stretch in the functioning of signal peptides. J Biol Chem 267:12375–12379
Hiller K, Grote A, Scheer M, Munch R, Jahn D (2004) PrediSi: prediction of signal peptides and their cleavage positions. Nucleic Acids Res 32:W375–379
Humphreys DP, Sehdev M, Chapman AP, Ganesh R, Smith BJ, King LM, Glover DJ, Reeks DG, Stephens PE (2000) High-level periplasmic expression in Escherichia coli using a eukaryotic signal peptide: importance of codon usage at the 5′ end of the coding sequence. Protein Expr Purif 20:252–264
Hytonen VP, Laitinen OH, Airenne TT, Kidron H, Meltola NJ, Porkka EJ, Horha J, Paldanius T, Maatta JA, Nordlund HR, Johnson MS, Salminen TA, Airenne KJ, Yla-Herttuala S, Kulomaa MS (2004) Efficient production of active chicken avidin using a bacterial signal peptide in Escherichia coli. Biochem J 384:385–390
Inouye M, Halegoua S (1980) Secretion and membrane localization of proteins in Escherichia coli. CRC Crit Rev Biochem 7:339–371
Inouye S, Soberon X, Franceschini T, Nakamura K, Itakura K, Inouye M (1982) Role of positive charge on the amino-terminal region of the signal peptide in protein secretion across the membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 79:3438–3441
Ismail NF, Hamdan S, Mahadi NM, Murad AM, Rabu A, Bakar FD, Klappa P, Illias RM (2011) A mutant l-asparaginase II signal peptide improves the secretion of recombinant cyclodextrin glucanotransferase and the viability of Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Lett 33:999–1005
Itoh Y, Kanoh KI, Nakamura K, Takase K, Yamane K (1990) Artificial insertion of peptides between signal peptide and mature protein: effect on secretion and processing of hybrid thermostable α-amylases in Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli cells. J Gen Microbiol 136:1551–1558
Izard JW, Kendall DA (1994) Signal peptides: exquisitely designed transport promoters. Mol Microbiol 13:765–773
Jehl M-A, Arnold R, Rattei T (2011) Effective—a database of predicted secreted bacterial proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D591–D595
Jobling MG, Palmer LM, Erbe JL, Holmes RK (1997) Construction and characterization of versatile cloning vectors for efficient delivery of native foreign proteins to the periplasm of Escherichia coli. Plasmid 38:158–173
Joly JC, Leung WC, Swartz JR (1998) Overexpression of Escherichia coli oxidoreductases increases recombinant insulin-like growth factor-I accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:2773–2777
Jonet MA, Mahadi NM, Murad AM, Rabu A, Bakar FD, Rahim RA, Low KO, Illias RM (2012) Optimization of a heterologous signal peptide by site-directed mutagenesis for improved secretion of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 22:48–58
Kaderbhai MA, Davey HM, Kaderbhai NN (2004) A directed evolution strategy for optimized export of recombinant proteins reveals critical determinants for preprotein discharge. Protein Sci 13:2458–2469
Kaderbhai NN, Ahmed K, Kaderbhai MA (2010) Export of a hyperexpressed mammalian globular cytochrome b5 precursor in Escherichia coli is dramatically affected by the nature of the amino acid flanking the secretory signal sequence cleavage bond. Protein Sci 19:1344–1353
Kajikawa A, Ichikawa E, Igimi S (2010) Development of a highly efficient protein-secreting system in recombinant Lactobacillus casei. J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:375–382
Kall L, Krogh A, Sonnhammer EL (2007) Advantages of combined transmembrane topology and signal peptide prediction—the Phobius web server. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W429–W432
Karamyshev AL, Karamysheva ZN, Kajava AV, Ksenzenko VN, Nesmeyanova MA (1998) Processing of Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase: role of the primary structure of the signal peptide cleavage region. J Mol Biol 277:859–870
Kebir MO, Kendall DA (2002) SecA specificity for different signal peptides. Biochemistry 41:5573–5580
Keller RC, Ten Berge D, Nouwen N, Snel MM, Tommassen J, Marsh D, De Kruijff B (1996) Mode of insertion of the signal sequence of a bacterial precursor protein into phospholipid bilayers as revealed by cysteine-based site-directed spectroscopy. Biochemistry 35:3063–3071
Kim CK, Lee SY, Kwon OJ, Lee SM, Nah SY, Jeong SM (2007) Secretory expression of active clostripain in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 131:346–352
Kirkpatrick RB, Ganguly S, Angelichio M, Griego S, Shatzman A, Silverman C, Rosenberg M (1995) Heavy chain dimers as well as complete antibodies are efficiently formed and secreted from Drosophila via a BiP-mediated pathway. J Biol Chem 270:19800–19805
Kotzsch A, Vernet E, Hammarström M, Berthelsen J, Weigelt J, Gräslund S, Sundström M (2011) A secretory system for bacterial production of high-profile protein targets. Protein Sci 20:597–609
Kouwen TRHM, Nielsen AK, Denham EL, Dubois J-YF, Dorenbos R, Rasmussen MD, Quax WJ, Freudl R, Van Dijl JM (2010) Contributions of the pre- and pro-regions of a Staphylococcus hyicus lipase to secretion of a heterologous protein by Bacillus subtilis. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:659–669
Kwon MJ, Park SL, Kim SK, Nam SW (2002) Overproduction of Bacillus macerans cyclodextrin glucanotransferase in E. coli by coexpression of GroEL/ES chaperone. J Microbiol Biotechnol 12:1002–1005
Li Z, Gu Z, Wang M, Du G, Wu J, Chen J (2010) Delayed supplementation of glycine enhances extracellular secretion of the recombinant alpha-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:553–561
Liu S, Zhang D, Wang M, Cui W, Chen K, Liu Y, Du G, Chen J, Zhou Z (2011) The pro-region of Streptomyces hygroscopicus transglutaminase affects its secretion by Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett 324:98–105
Low KO, Jonet MA, Ismail NF, Illias RM (2012) Optimization of a Bacillus sp signal peptide for improved recombinant protein secretion and cell viability in Escherichia coli: is there an optimal signal peptide design? Bioengineered 3:334–338
Luirink J, Dobberstein B (1994) Mammalian and Escherichia coli signal recognition particles. Mol Microbiol 11:9–13
Malten M, Nahrstedt H, Meinhardt F, Jahn D (2005) Coexpression of the type I signal peptidase gene sipM increases recombinant protein production and export in Bacillus megaterium MS941. Biotechnol Bioeng 91:616–621
Mathiesen G, Sveen A, Brurberg M, Fredriksen L, Axelsson L, Eijsink V (2009) Genome-wide analysis of signal peptide functionality in Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1. BMC Genomics 10:425
Matsuyama S, Fujita Y, Mizushima S (1993) SecD is involved in the release of translocated secretory proteins from the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. EMBO J 12:265–270
Menne KM, Hermjakob H, Apweiler R (2000) A comparison of signal sequence prediction methods using a test set of signal peptides. Bioinformatics 16:741–742
Mergulhao FJM, Summers DK, Monteiro GA (2005) Recombinant protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Adv 23:177–202
Miyata T, Miyazawa S, Yasunaga T (1979) Two types of amino acid substitutions in protein evolution. J Mol Evol 12:219–236
Mori H, Araki M, Hikita C, Tagaya M, Mizushima S (1997) The hydrophobic region of signal peptides is involved in the interaction with membrane-bound SecA. Biochim Biophys Acta 1326:23–36
Mujacic M, Bader MW, Baneyx F (2004) Escherichia coli Hsp31 functions as a holding chaperone that cooperates with the DnaK-DnaJ-GrpE system in the management of protein misfolding under severe stress conditions. Mol Microbiol 51:849–859
Muller M (2005) Twin-arginine-specific protein export in Escherichia coli. Res Microbiol 156:131–136
Nesmeyanova MA, Karamyshev AL, Karamysheva ZN, Kalinin AE, Ksenzenko VN, Kajava AV (1997) Positively charged lysine at the N-terminus of the signal peptide of the Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase provides the secretion efficiency and is involved in the interaction with anionic phospholipids. FEBS Lett 403:203–207
Ni Y, Chen R (2009) Extracellular recombinant protein production from Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Lett 31:1661–1670
Orth JD, Conrad TM, Na J, Lerman JA, Nam H, Feist AM, Palsson BO (2011) A comprehensive genome-scale reconstruction of Escherichia coli metabolism—2011. Mol Syst Biol 7:535
Paetzel M, Dalbey RE, Strynadka NC (1998) Crystal structure of a bacterial signal peptidase in complex with a beta-lactam inhibitor. Nature 396:186–190
Palmer T, Berks BC (2012) The twin-arginine translocation (Tat) protein export pathway. Nat Rev Microbiol 10:483–496
Papanikou E, Karamanou S, Economou A (2007) Bacterial protein secretion through the translocase nanomachine. Nat Rev Microbiol 5:839–851
Park SL, Kwon MJ, Kim SK, Nam SW (2004) GroEL/ES chaperone and low culture temperature synergistically enhanced the soluble expression of CGTase in E. coli. J Mol Biol 14:216–219
Petersen TN, Brunak S, Von Heijne G, Nielsen H (2011) SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat Methods 8:785–786
Peterson JH, Woolhead CA, Bernstein HD (2003) Basic amino acids in a distinct subset of signal peptides promote interaction with the signal recognition particle. J Biol Chem 278:46155–46162
Phoenix DA, Kusters R, Hikita C, Mizushima S, De Kruijff B (1993) OmpF-Lpp signal sequence mutants with varying charge hydrophobicity ratios provide evidence for a phosphatidylglycerol-signal sequence interaction during protein translocation across the Escherichia coli inner membrane. J Biol Chem 268:17069–17073
Puziss JW, Harvey RJ, Bassford PJ (1992) Alterations in the hydrophilic segment of the maltose-binding protein (MBP) signal peptide that affect either export or translation of MBP. J Bacteriol 174:6488–6497
Qian ZG, Xia XX, Choi JH, Lee SY (2008) Proteome-based identification of fusion partner for high-level extracellular production of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 101:587–601
Ray MVL, Meenan CP, Consalvo AP, Smith CA, Parton DP, Sturmer AM, Shields PP, Mehta NM (2002) Production of salmon calcitonin by direct expression of a glycine-extended precursor in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 26:249–259
Rusch SL, Kendall DA (2007) Interactions that drive Sec-dependent bacterial protein transport. Biochemistry 46:9665–9673
Rusch SL, Chen H, Izard JW, Kendall DA (1994) Signal peptide hydrophobicity is finely tailored for function. J Cell Biochem 55:209–217
Rusch SL, Mascolo CL, Kebir MO, Kendall DA (2002) Juxtaposition of signal-peptide charge and core region hydrophobicity is critical for functional signal peptides. Arch Microbiol 178:306–310
Saleh MT, Fillon M, Brennan PJ, Belisle JT (2001) Identification of putative exported/secreted proteins in prokaryotic proteomes. Gene 269:195–204
Schneider G, Wrede P (1994) The rational design of amino acid sequences by artificial neural networks and simulated molecular evolution: de novo design of an idealized leader peptidase cleavage site. Biophys J 66:335–344
Shen HB, Chou KC (2007) Signal-3L: a 3-layer approach for predicting signal peptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 363:297–303
Shokri A, Sanden AM, Larsson G (2003) Cell and process design for targeting of recombinant protein into the culture medium of Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:654–664
Sletta H, Tøndervik A, Hakvåg S, Aune TEV, Nedal A, Aune R, Evensen G, Valla S, Ellingsen TE, Brautaset T (2007) The presence of N-terminal secretion signal sequences leads to strong stimulation of the total expression levels of three tested medically important proteins during high-cell-density cultivations of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:906–912
Sommer B, Friehs K, Flaschel E (2010) Efficient production of extracellular proteins with Escherichia coli by means of optimized coexpression of bacteriocin release proteins. J Biotechnol 145:350–358
Steiner D, Forrer P, Stumpp MT, Pluckthun A (2006) Signal sequences directing cotranslational translocation expand the range of proteins amenable to phage display. Nat Biotech 24:823–831
Suominen I, Meyer P, Tilgmann C, Glumoff T, Glumoff V, Käpylä J, Mäntsälä P (1995) Effects of signal peptide mutations on processing of Bacillus stearothermophilus α-amylase in Escherichia coli. Microbiology 141:649–654
Takemori D, Yoshino K, Eba C, Nakano H, Iwasaki Y (2012) Extracellular production of phospholipase A2 from Streptomyces violaceoruber by recombinant Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 81:145–150
Tan NS, Ho B, Ding JL (2002) Engineering a novel secretion signal for cross-host recombinant protein expression. Protein Eng 15:337–345
Terpe K (2006) Overview of bacterial expression systems for heterologous protein production: from molecular and biochemical fundamentals to commercial systems. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:211–222
Tian P, Bernstein HD (2009) Identification of a post-targeting step required for efficient cotranslational translocation of proteins across the Escherichia coli inner membrane. J Biol Chem 284:11396–11404
Tomkiewicz D, Nouwen N, Driessen AJM (2008) Kinetics and energetics of the translocation of maltose binding protein folding mutants. J Mol Biol 377:83–90
Tong L, Lin Q, Wong WKR, Ali A, Lim D, Sung WL, Hew CL, Yang DSC (2000) Extracellular expression, purification, and characterization of a winter flounder antifreeze polypeptide from Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 18:175–181
Uhlen M, Abrahmsen L (1989) Secretion of recombinant proteins into the culture medium by Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem Soc Trans 17:340–341
Ulbrandt ND, London E, Oliver DB (1992) Deep penetration of a portion of Escherichia coli SecA protein into model membranes is promoted by anionic phospholipids and by partial unfolding. J Biol Chem 267:15184–15192
Umakoshi M, Hirasawa T, Furusawa C, Takenaka Y, Kikuchi Y, Shimizu H (2011) Improving protein secretion of a transglutaminase-secreting Corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain on the basis of 13C metabolic flux analysis. J Biosci Bioeng 112:595–601
Valent QA, Scotti PA, High S, De Gier JW, Von Heijne G, Lentzen G, Wintermeyer W, Oudega B, Luirink J (1998) The Escherichia coli SRP and SecB targeting pathways converge at the translocon. EMBO J 17:2504–2512
Viklund H, Elofsson A (2008) OCTOPUS: improving topology prediction by two-track ANN-based preference scores and an extended topological grammar. Bioinformatics 24:1662–1668
Vlasuk GP, Inouye S, Ito H, Itakura K, Inouye M (1983) Effects of the complete removal of basic amino acid residues from the signal peptide on secretion of lipoprotein in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 258:7141–7148
Von Heijne G (1984) How signal sequences maintain cleavage specificity. J Mol Biol 173:243–251
Wang J, Ho B, Ding J (2001) Functional expression of full length Limulus Factor C in stably transformed Sf9 cells. Biotechnol Lett 23:71–76
Watanabe K, Tsuchida Y, Okibe N, Teramoto H, Suzuki N, Inui M, Yukawa H (2009) Scanning the Corynebacterium glutamicum R genome for high-efficiency secretion signal sequences. Microbiology 155:741–750
Wen C, Gan R, Zhu S (2003) Construction of secretory expression system suitable to express glucagon under the control of PL promoter. Curr Microbiol 47:0180–0185
Wickner W, Moore K, Dibb N, Geissert D, Rice M (1987) Inhibition of purified Escherichia coli leader peptidase by the leader (signal) peptide of bacteriophage M13 procoat. J Bacteriol 169:3821–3822
Wong W-KR, Ali AB, Ma MC (2003) Cloning, expression, and characterization of diuretic hormone Manduca diuresin from Manduca sexta in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 29:51–57
Wong WKR, Fu Z, Wang YY, Ng KL, Chan AKN (2012) Engineering of efficient Escherichia coli excretion systems for the production of heterologous proteins for commercial applications. Recent Patents on Chemical Engineering 5:45–55
Wrede P, Landt O, Klages S, Fatemi A, Hahn U, Schneider G (1998) Peptide design aided by neural networks: biological activity of artificial signal peptidase I cleavage sites. Biochemistry 37:3588–3593
Yamanaka H, Okamoto K (1996) Amino acid residues in the pro region of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin I that affect efficiency of translocation across the inner membrane. Infect Immun 64:2700–2708
Yoon SH, Kim SK, Kim JF (2010) Secretory production of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. Recent Pat Biotechnol 4:23–29
Zalucki YM, Power PM, Jennings MP (2007) Selection for efficient translation initiation biases codon usage at second amino acid position in secretory proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 35:5748–5754
Zalucki YM, Beacham IR, Jennings MP (2009) Biased codon usage in signal peptides: a role in protein export. Trends Microbiol 17:146–150
Zalucki YM, Beacham IR, Jennings MP (2011) Coupling between codon usage, translation and protein export in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol J 6:660–667
Zhang H, Li Z, Qian Y, Zhang Q, Du P, Gan R, Ye Q (2007) Cultivation of recombinant Escherichia coli for secretory production of human epidermal growth factor under control of PL promoter. Enzyme Microb Technol 40:708–715
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Noor Faizah Ismail for the critical reading of the manuscript. Support from Abdul Munir Abdul Murad, Amir Rabu and Farah Diba Abu Bakar of Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia and Raha Abdul Rahim of Universiti Putra Malaysia is greatly appreciated. This work was supported by the Genomics and Molecular Biology Initiatives Programme of the Malaysia Genome Institute, Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation Malaysia (Project No. 07-05-MGI-GMB011) and the Exploration Research Grant Scheme (R.J130000.7835.4L046), Universiti Teknologi Malaysia. Kheng Oon Low is a researcher of Universiti Teknologi Malaysia under the Post-Doctoral Fellowship Scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Low, K.O., Muhammad Mahadi, N. & Md. Illias, R. Optimisation of signal peptide for recombinant protein secretion in bacterial hosts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 3811–3826 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4831-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4831-z