Abstract
This article presents findings from a meta-analysis which sought to determine the effectiveness of interventions adopting a whole school approach to enhancing children and young people’s social and emotional development. Whole school interventions were included if they involved a coordinated set of activities across curriculum teaching, school ethos and environment, and family and community partnerships. A total of 45 studies (30 interventions) involving 496,299 participants were included in the analysis. Post-intervention outcomes demonstrated significant but small improvements in participants’ social and emotional adjustment (d = 0.220), behavioural adjustment (d = 0.134), and internalising symptoms (d = 0.109). Interventions were not shown to impact on academic achievement. Origin of study and the inclusion of a community component as part of a whole school approach were found to be significant moderators for social and emotional outcomes. Further research is required to determine the active ingredients of whole school interventions that we can better understand the components necessary to achieve successful outcomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Children and adolescents need a balanced set of cognitive, social and emotional skills in order to achieve positive outcomes in school, in work, and in life more generally (OECD 2015). Social and emotional skills such as understanding and managing emotions, navigating social conflicts effectively, and making responsible decisions have been shown to influence numerous measures of social outcomes, including improved health, life satisfaction, subjective wellbeing, and reduced odds of engagement in anti-social behaviours (Goodman et al. 2015). Social and emotional skills do not play a role in isolation, they interact with cognitive skills which further enhance children’s likelihood of achieving positive outcomes in life (OECD 2015).
A common approach to supporting the development of children’s social and emotional skills has been school-based interventions (Jones and Bouffard 2012; Barry et al. 2017). Schools have been identified as a key setting for building social, emotional, and behavioural outcomes because students spend a substantial amount of time there. The school also provides a socialising context in which students are able to learn a range of life skills, many of which are associated with academic success (Taylor et al. 2017; Durlak et al. 2011; Sklad et al. 2012). Many school-based programmes have targeted an interrelated set of skills that fall under the headings of mental health promotion, character education, social and emotional learning (SEL), bullying prevention, life skills, strengths-based approaches, and youth development. Over the last three decades, the concept of social and emotional learning has served as an umbrella framework for a range of approaches and appears to have the largest and most rigorously evaluated evidence base. Social and emotional learning is defined as the process through which students acquire and effectively apply the knowledge, attitudes, and skills necessary to recognise and mange emotions, solve problems effectively, and establish positive relationships with others (CASEL 2005).
A growing body of research suggests that social and emotional skills are malleable and can be effectively taught using a variety of approaches and formats including classroom-based programming and whole school approaches (Jones and Bouffard 2012). Research indicates that interventions yield most successful outcomes when they are integrated into daily practice and school culture, seek to engage all staff, reinforce skills outside of the classroom such as hallways and playgrounds, support parental engagement, and coordinate work with outside agencies (Barry et al. 2017; Jones and Bouffard 2012; Weare and Nind 2011; Ttofi and Farrington 2011; Adi et al. 2007a, b; Wilson et al. 2003). Together, these characteristics point to the importance of adopting a whole school approach to enhancing children and young people’s social and emotional skill development. Jones and Bouffard (2012) highlighted key principles of social and emotional skill development that supports a move toward that adoption of a whole school approach: (i) continuity and consistency are essential for skill development, thus efforts need to be school wide, span age ranges, and consistent across multiple contexts within the school; (ii) social, emotional, and academic skills are interdependent and, therefore, efforts should be made to promote these skills simultaneously, reducing time pressures for teachers; (iii) social and emotional skills develop in social contexts, hence relationships between students and staff and among students are an important focus in their own right; (iv) classroom and schools operate as systems and both classroom- and school-wide efforts can set positive standards and expectations that promote and reinforce social and emotional competencies.
A whole school approach aims to integrate skill development into daily interactions and practices using collaborative efforts that include all staff, teachers, families, and children (Jones and Bouffard 2012; Meyers et al. 2015). Based on the World Health Organization’s definition of a Health Promoting School (WHO 1998), a whole school approach defines the entire school community as the unit of change and involves coordinated action between three interrelated components: (i) curriculum, teaching, and learning; (ii) school ethos and environment; (iii) family and community partnerships. Effective curriculum teaching and learning involve teaching skills through the implementation of evidence-based programmes, as well as modelling social emotional competencies, and providing continuous and consistent opportunities to practice these skills during everyday classroom situations (Oberle et al. 2016). At the school level, skills are reinforced in non-curriculum-based ways through policies, social relations, whole staff training, organisational structure, and daily activities in the school that are designed to promote a positive school climate which, in turn, helps children to develop positively across academic, social, emotional, and behavioural domains (Jones and Bouffard 2012; Meyers et al. 2015). Family and community partnerships involve extending learning to the home and community contexts. Embedding families within a whole school approach reinforces the complementary roles of families and educators and extends opportunities for learning across the two contexts in which children spend most of their time. Community partners provide links with external support and mental health services in the community, thereby ensuring there is access to services for students needing additional social and emotional support.
Several countries have launched national initiatives that adopt a school-wide approach to social and emotional learning. In Australia, for example, KidsMatter Primary is a mental health and wellbeing whole school framework that supports primary schools in implementing social and emotional learning school-wide (Dix et al. 2012). Through KidsMatter Primary, schools undertake a two-to-three-year cyclical process where they plan and take action to (i) promote social and emotional learning; (ii) work authentically with parents, carers, and families; and (iii) provide support for students who may be experiencing mental health difficulties. At second level, MindMatters provides professional development, curriculum, and whole school resources aimed at improving the mental health and wellbeing of young people (Wyn et al. 2000). In the UK, the Social and Emotional Aspects of Learning (SEAL) programme was developed as a whole school framework to support the social and emotional skill development of children and young people. This resource includes a curriculum element which is designed to support both universal and targeted work and whole school materials including resources relating to staff development, school organisation, management and leadership, and school ethos (Hallam 2009; Banerjee et al. 2014).
Despite extensive investment in whole school interventions, their effectiveness remains unclear. Reviewers of the evidence to date conclude that taking a whole school approach is more likely than individual classroom-based interventions to result in enduring positive change, because of its multi-component focus (Weare and Nind 2011; Adi et al. 2007a, b; Tennant et al. 2007; Jane-llopis et al. 2005; Wells et al. 2003). However, some recent reviews suggest that whole school interventions adopting a whole school approach are failing to show impact (e.g. Durlak et al. 2011; Langford et al. 2015). To date, however, no meta-analysis has been carried out specifically on interventions adopting a whole school approach to social and emotional learning. The aim of this review was, therefore, to examine the impact of these interventions on children and young people’s outcomes including social and emotional adjustment, behavioural adjustment, academic achievement, and internalising symptoms. A secondary aim was to assess the impact of moderating variables on programme outcomes.
Methods
The PRISMA guidelines for conducting a meta-analysis (Moher et al. 2009) were followed for the planning, conducting, and reporting of results.
Selection of studies
To be eligible for inclusion, studies were required to meet four methodological criteria: (i) utilised an experimental or quasi-experimental design with a control/comparison group; (ii) reported outcomes that could be transformed to Cohen’s d effect sizes; (iii) was published after 1998, in line with the Word Health Organization’s recommendation for schools to focus on the adoption of a whole school approach (WHO 1998); (iv) was published in English. In addition, the intervention (i) adopted a whole school approach as defined by the WHO (1998), (ii) was aimed at children and young people aged 4–18 years attending primary or secondary school, (iii) adopted a competency enhancement focus or was aimed at reducing problem behaviours through the application of social and emotional skills (e.g. bullying prevention interventions). Whole school interventions and frameworks which focused on behaviour management were not included in the current review, as a separate meta-analysis of this has already been carried out (Solomon et al. 2012).
Search strategy
Academic databases including Embase, PsycInfo, Scopus, and ERIC were searched. Eleven education databases were searched: NREPP, Child Trends US, Blueprints for Healthy Youth Development, Office of Justice Programs US, RAND Promising Practice Network on Children Families and Communities, California Evidence-based Clearing House for Child Welfare, Office of Adolescent Health, Crime Solutions US, Washington State Institute Public Policy, CASEL, and Education Endowment Foundation Database, UK. Eight health promotion and public health databases were searched: Evidence for Policy and Practice Information and Coordinating Centre (EPPI-Centre); University of York National Health Service Centre for reviews and dissemination; National Institute of Clinical Excellence (NICE); British Education Index, Databases of Abstracts of Reviews of Effectiveness (DARE); Health Technology Assessment (HTA); Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews; the Campbell Collaboration; WHO programmes and projects. Additional sources included Google Scholar and reference lists of relevant articles, book chapters, and reviews. Key individuals and organisations identified through the search process were contacted to identify further details on publications. The electronic search strategy used across all databases is provided in Table 1. The search for studies was conducted between 15 August and 8 October 2015. A repeated search was conducted between 30 July and 7 August 2017 to include articles published up to July 2017.
Results literature search
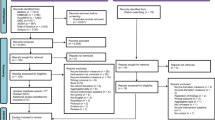
The results of the search and study selection are shown in Fig. 1. The original search, in 2015, identified 6626 citations from the academic databases and a further 32 citations from the other sources. After the removal of duplicates, 4402 abstracts were screened. A total of 392 full text articles were screened for eligibility. Of these, 348 did not fulfil the inclusion criteria and were excluded. Forty-four studies were selected for inclusion in the meta-analysis. The updated search which was carried out in August 2017 identified a further six studies. The combined searches resulted in a total of 50 articles which fulfilled the inclusion criteria. Six of the included articles reported findings from one evaluation study of the whole school intervention Positive Action. These six articles were therefore perceived as one study, resulting in 45 studies that underwent meta-analysis.
Coding
A coding sheet was developed by three authors (J.G., A.C., and M.S.). The purpose of the coding sheet was to extract all relevant information from the studies including methodological, intervention, and recipient characteristics. To check for inter-rater reliability, 10% of all the included articles were independently coded by the first and last authors (J.G. and A.C.). For all the checked articles, the percentage of agreement was above 85% and was perceived as sufficient. All differences were discussed and resolved.
Assessing quality of evidence
All studies that fulfilled the criteria for this meta-analysis underwent an assessment of their methodological quality. Following the guidelines of the Cochrane Public Health Group (Jackson and Waters 2005), the methodological quality of the intervention evaluations was assessed using the Quality Assessment Tool for Quantitative Studies (EPHPP 1998). Studies were assessed for selection bias, study design, confounders, blinding, data collection method, and dropouts. Each study was rated independently by two reviewers (J.G. and A.C.). The quality assessment results were compared and disagreements were resolved through discussion. Based on the ratings of the six components, each study received an overall rating of strong, moderate, or weak.
Outcomes and moderators
In line with other meta-analyses in this field (Payton et al. 2008; Sklad et al. 2012, four outcome categories were defined:
-
i.
Social and emotional adjustment: this category included measurements of social or emotional skills, and attitudes toward self and others.
-
ii.
Behavioural adjustment: this category included positive social behaviour, conduct problems, victimisation, and risky behaviour (e.g. substance abuse, unprotected sexual intercourse)
-
iii.
School performance: this category included all measurements of academic achievement, for example reading achievement scores or academic competence rated by the teacher
-
iv.
Internalising symptoms: this category included outcomes related to reducing psychopathology, such as depression and anxiety, and also feelings of wellbeing.
To assess the impact of moderators on programme outcomes, a number of variables were selected. Methodological variables included the following: research design (randomised controlled trial/quasi-experimental), number of months between pre- and post-intervention (12 or less/13 or more), implementation fidelity (no problems reported/problems reported/not reported), quality assessment (strong/moderate/weak), self-report measure (yes/no), and year of publication (2010 or earlier/2011 or later). Intervention characteristics selected as moderators included the following: intervention focus on behavioural problems (yes/no), school level (primary/secondary), community component included (yes/no), and targeted component included for students at risk of problem behaviour (yes/no). Lastly, a potential moderator regarding the recipient characteristics was the country where the study was carried out (United States/outside United States).
Analysis plan
Outcomes reported in the included studies were categorised into one of the four main outcome categories. The intervention and control group’s means, standard deviations, and sample size were extracted for each measurement. Standardised difference between two means “Cohen’s d” (or Cohen’s g in the case of small sample sizes) was then calculated per measurement based on means and standard deviations or other appropriate data (e.g. odds ratios). When studies failed to report means, standard deviations, or proportions, effect sizes were calculated using a t test, F-statistic, or p value and sample size.
For each effect size, the direction was determined in such a way that positive values indicated a more beneficial outcome favouring the intervention group over the control group. The variance of each effect size was calculated based on the sample sizes. It was also necessary to determine whether the design effect of clustering was taken into account in each study. If a design effect was not in place, the variances of the effect sizes were adjusted based on intercluster correlations (ICCs) of the same (or a comparable) article, resulting in true variances.
For each study, mean effect sizes for each outcome category were calculated. If different articles presented data about the same cohort, the data was combined into one mean effect size per outcome. For the mean effect sizes, it was determined whether the direction of the effect size was positive or negative. Effects sizes of 0.20 were considered small, 0.50 moderate, and 0.80 high (Lipsey and Wilson 1993). For each mean effect size, a variance was calculated based on an estimated correlation (r) and the (true) variance of the individual effect sizes (Morris 2008).
To analyse the general effectiveness of the interventions on the four main outcome categories, the Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (CMA) programme was used. A random effects model was used with a maximum likelihood estimation procedure to arrive at effect sizes (ES) and 95% confidence intervals. Outliers were removed from the main analyses. Studies were considered as outliers when their standardised residual exceeded the norm of 3.00. CMA was also used to calculate statistical heterogeneity, publication bias, and the influence of possible moderators. Heterogeneity was determined by calculating I2 values, indicating the degree of inconsistency across studies in a meta-analysis (Higgins et al. 2003). I2 values are derived from H2 values through the following formula: (H2–1) ∕ H2. Publication bias was estimated by funnel plots, Egger et al.’s (1997) regression tests, and Duval and Tweedie’s (2000) trim and fill analyses. The influence of possible moderators was determined by calculating Q values (heterogeneity between groups) and their corresponding p values, based on the Z-values of the different moderator categories (Borenstein et al. 2010). Few studies reported outcomes for subgroups or follow-up data, so it was decided not to do separate analysis for subgroups or follow-up studies.
Results
Characteristics of included interventions
Table 2 provides the summary characteristics for each study included in the meta-analysis. The 45 studies represented 30 different interventions. The total sample across the 45 studies was 496,299 students aged between 4 and 16 years. The number of students per study varied between 150 (Hennessey 2007) and 300,000 (Kärnä et al. 2011a, b), with a median of 2242 students. All studies included mixed-sex samples. Twenty-five studies (56%) were carried out outside of the United States. Twenty-eight studies (62%) employed randomised controlled designs. Only two studies (4%) presented a clear distinction between post-intervention and follow-up measurement. In total, 28 studies (62%) reported on social and emotional adjustment outcomes, 41 studies (91%) reported on behavioural adjustment outcomes, 10 studies (22%) reported on internalising symptoms outcomes, and 8 studies (18%) reported on school performance outcomes. Eighteen studies (40%) reported a high level of programme fidelity, 6 studies (13%) reported problems with fidelity, and 21 studies (47%) did not report fidelity. Of the 45 studies, 44 were published in peer-reviewed journals (98%). Regarding the quality of the evidence, 22 studies (49%) received a strong quality assessment rating, 15 studies (33%) received a moderate rating, and 8 studies (18%) received a weak quality assessment rating.
Seventeen of the whole school interventions were implemented in primary school (57%), seven interventions (23%) were implemented in secondary school, and six interventions were implemented across primary and secondary school (20%). All interventions provided teacher training and a programme manual. Ten interventions (33%) were aimed at enhancing social and emotional skills and 20 interventions (67%) were aimed at reducing bullying behaviour through the application of social and emotional skills. All interventions included a classroom curriculum, strategies addressing the whole school ethos and environment, and a parent component. Seventeen interventions (57%) included a community component. Fourteen interventions (47%) contained a targeted component aimed at addressing the needs of children at risk of developing emotional or behavioural problems.
Intervention effects
At post-intervention, there were a sufficient number of studies for each outcome category. As shown in Table 3, a small, but statistically significant increased mean effect size in the desired direction, was detected for social and emotional adjustment (d = 0.220), behavioural adjustment (d = 0.134), and internalising symptoms (d = 0.109). Across all outcomes the level of heterogeneity was high with I2 ranging from 87.99 to 99.40. The mean effect size for school performance was not found to be increased significantly (d = 0.193, 95% CI − 0.105 to 0.490, p = 0.204). When analysing the results on school performance more extensively, it is found that one highly positive effect size (Snyder et al. 2010) widened the confidence interval of the mean effect size, thus making it non-significant. However, based on the standardised residual of this study (1.44), this study was not perceived as an outlier.
Publication bias
Visual inspection of the funnel plots (supplementary materials) showed no evidence of publication bias for the outcomes “social and emotional adjustment” and “behavioural adjustment”. The distribution of both these outcomes appears close to symmetrical and Egger’s regression tests showed no signs of publication bias (respectively p values of 0.28 and 0.33). Also, Duval and Tweedie’s trim and fill indicated that for both these outcomes, no studies needed to be filled or trimmed. For “school performance”, the funnel plot showed more studies to the left of the mean. Egger’s regression test was not significant (p = 0.71), but Duval and Tweedie’s trim and fill analysis indicated that five studies needed to be trimmed, adjusting the effect size to d = 0.605. For “internalising symptoms”, the funnel plot showed more studies to the right of the mean. Egger’s regression test was again not significant (p = 0.40), but Duval and Tweedie’s trim and fill analysis indicated that three studies needed to be trimmed, adjusting the effect size to d = 0.060.
Moderators of effect sizes
Moderator analyses were carried out to determine the effect of methodological, intervention, and recipient characteristics on the two most reported outcomes: social and emotional adjustment and behavioural adjustment (Table 4). Regarding methodological characteristics, the moderator “quality assessment” was of significant influence on students’ behavioural adjustment (Q = 9.141, df = 1, p = 0.001), with the highest effect sizes reported for studies that received a moderate or weak quality assessment rating (d = 0.410 vs d = 0.090). Regarding the intervention characteristics, the inclusion of a community component as part of a whole school intervention was shown to have a significant impact on participants’ social and emotional adjustment (Q = 5.092, df = 1, p = 0.024). Results indicated that whole school interventions which contained a community component showed significantly higher effect sizes than interventions without a community component (d = 0.447 vs d = 0.152). Lastly, regarding recipient characteristics, moderator analysis revealed that interventions evaluated in the United States were found to have significantly higher social and emotional effect sizes than whole school interventions evaluated outside of the United States (d = 0.450 vs d = 0.120; Q = 4.255, df = 1, p = 0.039).
Discussion
International research highlights the importance of implementing social and emotional skill development within the context of a whole school approach which embraces the wider school, family, and community contexts (Barry et al. 2017; Oberle et al. 2016; Jones and Bouffard 2012; Weare and Nind 2011). Whole school interventions have received significant investment in the past decade; however, their impact remains unclear. The aim of this meta-analysis was to examine the effectiveness of whole school interventions on a range of social, emotional, behavioural, and academic outcomes. Whilst previous meta-analyses have examined the impact of universal social and emotional learning programmes (e.g. Durlak et al. 2011; Sklad et al. 2012; Taylor et al. 2017), this current meta-analysis is, to our knowledge, the first to examine the effectiveness of interventions that adopt a whole school approach to social and emotional skill development. The main findings indicate that whole school interventions yield small, but significant positive effects on social and emotional adjustment, behavioural adjustment, and internalising symptoms. The highest estimate obtained was for social and emotional adjustment (d = 0.220), with estimates for behavioural adjustment and internalising symptoms ranging from 0.109–0.134. Previous meta-analyses of universal social and emotional learning interventions have reported higher effect sizes across social, emotional, behavioural, and academic domains (e.g. Durlak et al. 2011; Sklad et al. 2012).
It is likely that implementation had a significant role to play in the lower effect sizes reported in this current meta-analysis. Findings from implementation science provide evidence on the importance of quality of implementation in producing programme outcomes (Durlak and DuPre 2008; Fixsen et al. 2005). Durlak and colleagues’ (Durlak et al. 2011) meta-analysis of universal social and emotional skill-based interventions reported that interventions implemented with high quality produced larger effect sizes across all six social, emotional, behavioural, and academic outcomes, compared with interventions implemented with lower quality which only achieved significant effects in two outcome categories (attitudes and conduct problems). Researchers have found that comprehensive school-wide interventions frequently encounter problems with implementation (Durlak and Dupre 2008; Wilson and Lipsey 2007; Wilson et al. 2003). These interventions require substantial planning and support as skill development extends beyond the classroom, connecting and extending learning through the school ethos and environment and in partnership with families and communities. There is a need for significant infrastructure and capacity to support system-wide implementation of whole school interventions; however, this is often missing (Spoth et al. 2013). One of the interventions included in the current meta-analysis (SEAL) was shown to have no impact on students’ social and emotional skills (Wigelsworth et al. 2012). A process evaluation revealed that a lack of buy in from staff, perceived need for the programme, insufficient training, and teachers’ self-efficacy were all related to variability in the level of implementation of the programme (Lendrum et al. 2013). Implementation research is critical to understanding the range of factors operating at the level of the intervention, provider, community, delivery, and support system which impact the quality with which a programme is implemented.
Results from this meta-analysis revealed whole school interventions did not have a significant impact on academic performance. This finding is in contrast to results from previous meta-analyses, one of which reported an 11 percentile gain in academic achievement among students who received a social and emotional learning intervention (Durlak et al. 2011). A possible explanation for the non-significant finding in this meta-analysis is the small number of studies (N = 8) in this outcome category. In addition, one study with a large effect size widened the confidence interval of the mean effect size, thus making the mean effect size non-significant. Furthermore, only one of the eight studies utilised standardised achievement test scores as a measure of academic performance. The remaining studies utilised teacher self-report data of academic competence. The low number of studies combined with the use of teacher self-report data weakens the confidence that can be placed in this finding, and as a result, this finding should be viewed with caution.
Moderator analysis indicated that studies from the United States (US) had a significantly higher effect size that non-US studies. Two possible reasons could explain this finding. Weare and Nind (2011) in their review of social and emotional skill-based interventions suggested that, compared with European and Australian interventions, US interventions are more prescriptive in their training, programme manual, and requirements for programme fidelity. They contend that some non-US interventions fail to show impact as a result of their more flexible, bottom-up approach to skill development which can make it difficult for teacher to know what to implement and how it should be implemented. Another possible reason relates to the level of district and national supports for social and emotional learning across countries. It is argued that whole school interventions are most likely to be successful, effective, and sustainable when the necessary support from educational stakeholders at national level is in place (Mart et al. 2015; Barry et al. 2017). Support from the education system at national level has the power to catalyse systemic change at school level by communicating a culture of “what matters” in school learning (Oberle et al. 2016). This support can include advocating for policies that support whole school integration of social and emotional learning, defining age-specific standards for student outcomes across social and emotional learning domains and allocating the required resources for the adoption of evidence-based interventions. All of which can assist in creating the necessary conditions for school-wide social and emotional learning. Over the past number of years, the US has made significant advancements in embedding support for social and emotional learning at district and state levels. Examples of such advancements include the development of learning standards for social and emotional skill development (Dusenbury et al. 2015) and the establishment of CASEL’s Collaborative Districts Initiative (CDI) and Collaborative States Initiative (CSI) which are designed to build systemic support for social and emotional learning. Further research is required to advance our understanding of the type of support required by schools from the education system to implement evidence-based programmes with high quality and embed them within the school system.
Additional moderator analysis revealed the impact of implementing a community component as part of a whole school approach. Examples of community components included the following: additional support from community specialists for children considered “at risk” of developing problems; the involvement of community members in school components; the implementation of intervention activities through subgroups of the community including community leaders, the media, and social workers. Results from this meta-analysis indicated that the implementation of a community component was associated with a significant higher effect size on children’s social and emotional adjustment. This finding highlights the importance of schools working collaboratively with the wider community in reaching out to and receiving support from parents and local agencies. The development of links with community agencies and services has been argued to be the most essential component of the health-promoting school approach (Goltz et al. 1997; Lister-Sharp et al. 1999; WHO 1996). Community partners provide links with external support and mental health services in the community, thereby ensuring there is access to services for students needing additional support.
Whilst the interventions varied in their inclusion of a community component and what this consisted of, all of the interventions contained a classroom curriculum, a family component, and strategies aimed at enhancing the school ethos and environment. Furthermore, a number of key practices within these components were common across the majority of interventions. At the school level, practices included the following: the provision of a guide to support schools in developing whole school policies based on the intervention’s principles; the establishment of a school committee whose goal is to plan and implement the intervention; staff meetings dedicated to planning the whole school approach, monitoring its progress and arranging professional development. The majority of interventions identified in this meta-analysis established school-wide expectations, defined school-wide rules, displayed posters in school corridors that reflected intervention concepts, and implemented a school-wide system of encouraging the use of skills. Whole staff training was a feature of all interventions and included the following: training on the application of teaching strategies throughout the school day; instructional methods in interactive teaching, positive communication, problem solving, and cooperative learning; and strategies to support collaboration with parents. Key strategies used to engage parents included letters sent to parents providing information on the intervention’s key principles, teacher-parent meetings, the provision of a parent education programme or workshop targeting risk, and protective factors in the home environment.
Limitations
The findings from this meta-analysis need to be interpreted in the context of their limitations. Firstly, just over half of the studies (54%) received a strong quality assessment rating, the remaining studies received a moderate (29%) or weak (17%) rating. Moderator analysis revealed studies with a moderate or weak rating showed significantly larger effect sizes for behavioural adjustment than high-quality studies. Lower quality studies were mostly attributed to a high rate of dropout or failure to report dropout at post-intervention. This is an issue which has been identified as one of the most common pitfalls of efficacy trials (Clarke and Barry 2015). Accurate reporting of dropout and analysis on the extent to which dropout may have introduced bias is recommended for future studies in order to strengthen the quality of the evidence base. Secondly, although a total of 48 studies were identified for inclusion in the meta-analysis, the number of studies which examined the impact of whole school interventions on academic achievement and internalising outcomes was low. As a result, the power to detect significant effect sizes was reduced. Thirdly, although significant efforts were made to identify every relevant study for this meta-analysis, we cannot be sure that we identified all possible studies, in particular, unpublished studies which have a tendency to report null effects. A final limitation was the search for English-only studies which limits the representativeness and generalisability of the analysis.
Implications for research
Eight studies (16%) provided data on academic achievement. These results highlight the need for future studies to examine the impact of whole school interventions on academic achievement. Furthermore, the use of standardised achievement test scores in determining programme impact should be prioritised. Additional research on the long-term impact of whole school interventions is required in order to determine the durability of programme outcomes. Furthermore, whilst there is emerging evidence on the economic case for investing in school-based SEL (e.g. Belfield et al. 2015), cost-benefit analysis of whole school interventions would provide an important insight into their economic returns as educational investments.
There is a need for future research to identify the essential ingredients/components of whole school interventions that have been found through research to positively affect proximal outcomes. There is a clear overlap in the core components used across whole school interventions. Identifying the components that are essential for building social and emotional skills at the level of the individual, the classroom, the whole school, the family, and the community could facilitate the use of the most effective strategies with the greatest potential for impact. Research on the identification of “essential ingredients” across evidence-based youth mental health treatment and prevention interventions has shown some promising results in this area (e.g. Chorpita and Daleiden 2009; Boustani et al. 2015). Knowing the essential components of whole school interventions could assist schools in implementing whole school programme with high quality and at the same time making the necessary adaptations to suit the local context and specific population needs.
The results from this meta-analysis highlight the current lack of emphasis on programme implementation (46% of studies did not monitor programme implementation). Programme outcomes cannot be interpreted appropriately without information on the quality of programme information or the extent of intervention delivery. A greater focus on implementation research is required in order to understand a programme’s true value and to offer guidance in terms of continual improvement to programme delivery (Durlak 2015). Furthermore, there is a need for specific implementation guidelines and tools to support the effective adoption of whole school interventions in natural contexts. CASEL’s School Theory of Action (School ToA) resource is an example of a framework which provides specific tools and resources for setting up and sustaining a whole school approach to social and emotional learning (Oberle et al. 2016). Factors known to promote sustainability and impact are addressed, including the following: ongoing professional development, ongoing assessment and evaluation, infrastructure and school-wide integration, family-school-community partnerships, and ongoing communication. The further development and testing of implementation tools and resources are essential in addressing barriers to effective integration of social and emotional learning within the wider school system.
Implications for policy and practice
The findings from this meta-analysis have a number of implications for policy makers and practitioners, responsible for implementing social and emotional skill-based interventions. The successful implementation of evidence-based whole school practices requires individual motivation, individual and organisational capacity, supportive policies, and attention to the challenges involved in changing practices as well as addressing the challenges posed by the need to adapt programmes once implemented (Oberle et al. 2016). In order for whole school interventions to be used more widely, further effort is needed to assist schools in selecting an evidence-based intervention that fits their needs, implementing it with quality and adopting methods to sustain the intervention over the long term (Wandersman and Florin 2003).
There is also a need for investment in professional development and learning for building organisational capacity in adopting a whole school approach to social and emotional learning. As part of this, there is a need to promote partnerships between teacher preparation programmes, programme developers, and implementation experts to equip trainee teachers with the competencies necessary to embed social and emotional learning within the curriculum and wider school, family, and community contexts. The provision of leadership support and ongoing professional development is also required to support the integration and sustainability of whole school interventions.
Conclusions
A growing body of research suggests that for optimal impact, social and emotional skill development needs to be embedded within a whole school, multi-modal approach. This approach typically involves coordinated action between curriculum, teaching, and learning; the school ethos and environment; and family and community partnerships. The results from this meta-analysis indicate a small, but significant positive impact of these interventions on students’ social and emotional adjustment, behavioural adjustment, and internalising symptoms. Whole school interventions were not shown to impact on academic achievement. Moderator analysis provides evidence that interventions implemented and evaluated in the US were more effective in enhancing participants’ social and emotional adjustment than non-US interventions. In order to advance our understanding of the conditions necessary to achieve successful outcomes, a greater focus on implementation research and the identification of essential components of whole school interventions is required.
References
Adi, Y., Killoran, A., Janmohamed, K., & Stewart-Brown, S. (2007a). Systematic review of the effectiveness of interventions to promote mental wellbeing in primary schools: universal approaches which do not focus on violence or bullying. London: National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence.
Adi, Y., Killoran, A., Janmohamed, K., & Stewart-Brown, S. (2007b). Systematic review of the effectiveness of interventions to promote mental wellbeing in primary schools: universal approaches with focus on prevention of violence or bullying. London: National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence.
Barry, M.M., Clarke, A.M., & Dowling, K. (2017). Promoting social and emotional wellbeing in schools. Health Education, 117(5), 434–451.
Banerjee, R., Weare, K., & Farr, W. (2014). Working with ‘Social and Emotional Aspects of Learning’ (SEAL): associations with school ethos, pupils’ social experiences, attendance, and attainment. British Education Research Journal, 40(4), 718–742.
Belfield, C., Bowden, B., Klapp, A., Levin, H., Shand, R., & Zander, S. (2015). The economic value of social and emotional learning. New York: Center for Benefit-Cost Studies in Education Teachers College, Columbia University.
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P., & Rothstein, H. R. (2010). A basic introduction to fixed-effect and random-effects models for meta-analysis. Research Synthesis Methods, 1(2), 97–111. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.12.
Boustani, M. M., Frazier, S. L., Becker, K. D., Bechor, M., Dinizulu, S. M., Hedemann, E. R., Ogle, R. R., & Pasalich, D. S. (2015). Common elements of adolescent prevention programs: minimizing burden while maximizing reach. Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research, 42(2), 209–219.
Chorpita, B. F., & Daleiden, E. L. (2009). Mapping evidence-based treatments for children and adolescents: application of the distillation and matching model of 615 treatments from 322 randomized trials. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 7(3), 566–579.
Clarke, A. M., & Barry, M. M. (2015). Supporting a whole school approach to mental health promotion and wellbeing in post-primary schools in Ireland. In S. Kutcher, Y. Wei, & M. Weist (Eds.), International school mental health for adolescents- global opportunities and challenges. UK: Cambridge Press.
Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning [CASEL]. (2005). Safe and sound: an educational leader’s guide to evidence-based social and emotional learning programs. Chicago: Illinois edition.
Dix, K. L., Slee, P. T., Lawson, M. J., & Keeves, J. P. (2012). Implementation quality of whole-school mental health promotion and students’ academic performance. Child and Adolescent Mental Health, 17(1), 45–51.
Durlak, J. A. (2015). What everyone should know about implementation. In J. A. Durlak, C. E. Domitrovich, R. P. Weissberg, & T. P. Gullotta (Eds.), Handbook of social and emotional learning: research and practice (pp. 482–499). New York: Guilford.
Durlak, J. A., & DuPre, E. P. (2008). Implementation matters: a review of research on the influence of implementation on program outcomes and the factors affecting implementation. American Journal of Community Psychology, 41(3–4), 327–350.
Durlak, J. A., Weissberg, R. P., Dymnicki, A. B., Taylor, R. D., & Schellinger, K. B. (2011). The impact of enhancing students’ social and emotional learning: a meta-analysis of school-based universal interventions. Child Development, 82(1), 405–432.
Dusenbury, L. A., Newman, J. Z., Weissberg, R., Goren, P., Domitrovice, C. E., & Mart, A. K. (2015). The case for preschool through to high school state learning standards for SEL. In J. A. Durlak, C. E. Domitrovich, R. P. Weissberg, & T. P. Gullotta (Eds.), Handbook of social and emotional learning: research and practice (pp. 482–499). New York: Guilford.
Duval, S., & Tweedie, R. (2000). Trim and Fill: a simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics, 56(2), 455–463. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0006-341X.2000.00455.x.
Effective Public Health Practice Project. (1998). Quality assessment tool for quantitative studies. Hamilton. Available from: http://www.ephpp.ca/index.html.
Egger, M., Smith, G. D., Schneider, M., & Martin, M. C. (1997). Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. British Medical Journal, 315(7109), 629–634.
Fixsen, D. L., Naoom, S. F., Blasé, K. A., Friedman, R. M., & Wallace, F. (2005). Implementation research: a synthesis of the literature. Tampa: University of South Florida, Louis de la Parte Florida Mental Health Institute, The National Implementation Research Network.
Goltz, K., Colquhoun, D., & Sheehan, M. (1997). Broadening school health education: towards the health promoting school. In D. Colquhoun, K. Goltz, & M. Sheehan (Eds.), The health promoting school, policy, programmes and practice in Australia. Marrickville: Harcourt Brace and Company.
Goodman, A., Joshi, H., Nasim, B., & Tyler, C. (2015). Social and emotional skills in childhood and their long-term effects on adult life. London: Institute of Education.
Hallam, S. (2009). An evaluation of the Social and Emotional Aspects of Learning (SEAL) programme: promoting positive behaviour, effective learning and well-being in primary school children. Oxford Review of Education, 35(3), 313–330.
Hennessey, B. A. (2007). Promoting social competence in school-aged children: the effects of the open circle program. Journal of School Psychology, 45(3), 349–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsp.2006.11.007.
Higgins, J. P. T., Thompson, S. G., Deeks, J. J., & Altman, D. G. (2003). Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. British Medical Journal, 327(7414), 557–560.
Jackson, N., & Waters, E. (2005). Criteria for the systematic review of health promotion and public health interventions. Health Promotion International, 20(4), 367–374.
Jane-Llopis, E., Barry, M. M., Hosman, C., & Patel, V. (2005). Mental health promotion works: a review. Promotion & Education, 12(Suppl 2), 9–25.
Jones, S. M., & Bouffard, S. M. (2012). Social and emotional learning in schools: from programs to strategies: social policy report. Society for Research in Child Development, 26(4), 3–22.
Langford, R., Bonell, C., Jones, H., Pouliou, T., Murphy, S., Waters, E., Komro, K., Gibbs, L., Magnus, D., & Campbell, R. (2015). The World Health Organization’s Health Promoting Schools framework: a Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health, 15(1), 130.
Lendrum, A., Humphrey, N., & Wigelsworth, M. (2013). Social and emotional aspects of learning (SEAL) for secondary schools: implementation difficulties and their implications for school-based mental health promotion. Child and Adolescent Mental Health, 18(3), 158–164.
Lipsey, M. W., & Wilson, D. B. (1993). The efficacy of psychological, educational, and behavioral treatment: confirmation from meta-analysis. American Psychologist, 48(12), 1181–1209.
Lister-Sharp, D., Chapman, S., Stewart-Brown, S., & Sowden, A. (1999). Health promoting schools and health promotion in schools: two systematic reviews. Health Technology Assessment, 3(22), 1–207.
Mart, A. K., Weissberg, R. P., & Kendziora, K. (2015). Systemic support for social and emotional learning in school districts. In J. A. Durlak, C. E. Domitrovich, R. P. Weissberg, & T. P. Gullotta (Eds.), Handbook of social and emotional learning: research and practice (pp. 482–499). New York: Guilford.
Meyers, D. C., Gil, L., Cross, R., Keister, S., Domitrovich, C. E., & Weissberg, R. P. (2015). CASEL guide for schoolwide social and emotional learning. Chicago: CASEL.
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D. G., & The PRISMA Group. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Medicine, 6(7), e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097.
Morris, S. B. (2008). Estimating effect sizes from pretest-posttest-control group designs. Organizational Research Methods, 11(2), 364–386.
Oberle, E., Domitrovich, C. E., Meyers, D. C., & Weissberg, R. P. (2016). Establishing systemic social and emotional learning approaches in schools: a framework for schoolwide implementation. Cambridge Journal of Education, 46(3), 277–297.
OECD. (2015). Skills for social progress: the power of social and emotional skills. Paris: OECD Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264226159-en.
Payton, J., Weissberg, R. P., Durlak, J. A., Dymnicki, A. B., Taylor, R. D., Schellinger, K. B., & Pachan, M. (2008). The positive impact of social and emotional learning for kindergarten to eighth-grade students: findings from three scientific reviews. Chicago: Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning.
Sklad, M., Diekstra, R., Gravesteijn, C.M., Ben, J., & Ritter, M. (2012). Effectiveness of school-based universal social, emotional and behavioral programs: do they enhance students’ development in the area of skill, behavior, and adjustment? Psychology in the Schools, 49(9), 892–909.
Solomon, B. G., Klein, S. A., Hintze, J. M., Cressey, J. M., & Peller, S. L. (2012). A meta-analysis of school-wide positive behavior support: an exploratory study using single-case synthesis. Psychology in Schools, 49(2), 105–121. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.20625.
Spoth, R., Rohrbach, L. A., Greenberg, M., Leaf, P., Brown, C. H., Fagan, A., Catalano, R. F., Pentz, M. A., Sloboda, Z., Hawkins, J. D., & Society for Prevention Research Type 2 Translational Task Force Members and Contributing Authors. (2013). Addressing core challenges for the next generation of type 2 translation research and systems: the Translation Science to Population Impact (TSci Impact) framework. Prevention Science, 14(4), 319–351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-012-0362-6.
Taylor, R. D., Oberle, E., Durlak, J. A., & Weissberg, R. P. (2017). Promoting positive youth development through school-based social and emotional learning interventions: a meta-analysis of follow-up effects. Child Development, 88(4), 1156–1171. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.12864.
Tennant, R., Goens, C., Barlow, J., Day, C., & Stewart-Brown, S. (2007). A systematic review of reviews of interventions to promote mental health and prevent mental health problems in children and young people. Journal of Public Mental Health, 6(1), 25–32.
Ttofi, M. M., & Farrington, D. P. (2011). Effectiveness of school-based programs to reduce bullying: a systematic and meta-analytic review. Journal of Experimental Criminology, 7(1), 27–56. https://doi.org/10.1080/1754730X.2008.9715730.
Wandersman, A., & Florin, P. (2003). Community interventions and effective prevention. American Psychologist, 58(6-7), 441–448.
Weare, K., & Nind, M. (2011). Mental health promotion and problem prevention in schools: what does the evidence say? Health Promotion International, 26(1), 29–69.
Wells, J., Barlow, J., & Stewart-Brown, S. (2003). A systematic review of universal approaches to mental health promotion in schools. Health Education, 103(4), 197–220.
Wilson, S. J., & Lipsey, M. W. (2007). School-based interventions for aggressive and disruptive behavior: update of a meta-analysis. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 33, 130–143.
Wilson, S. J., Lipsey, M. W., & Derzon, J. H. (2003). The effects of school-based intervention programs on aggressive behavior: a meta-analysis. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 71(1), 136–149. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.71.1.136.
World Health Organization. (1996). The status of school health. Geneva: WHO.
World Health Organization (WHO). (1998). Health Promoting evaluation: recommendations for Policy-Makers, report of the WHO European Working Group on Health Promotion Evaluation. Copenhagen: WHO.
Wyn, J., Cahill, H., & Holdsworth, R. (2000). MindMatters, a whole-school approach promoting mental health and wellbeing. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 34(4), 594–601.
References: studies included in the meta-analysis
Amundsen, E. J., & Ravndal, E. (2010). Does successful school-based prevention of bullying influence substance use among 13- to 16-year-olds? Drugs: Education, Prevention & Policy, 17(1), 42–54.
Battistich, V., Schaps, E., Watson, M., Solomon, D., & Lewis, C. (2000). Effects of the child development project on students’ drug use and other problem behaviors. Journal of Primary Prevention, 21(1), 75–99. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007057414994.
Bauer, N. S., Lozano, P., & Rivara, F. P. (2007). The effectiveness of the Olweus Bullying Prevention Program in public middle schools: a controlled trial. Journal of Adolescent Health, 40(3), 266–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2006.10.005.
Bavarian, N., Lewis, K. M., DuBois, D. L., Acock, A., Vuchinich, S., Silverthorn, N., Snyder, F. J., Day, J., Ji, P., & Flay, B. R. (2013). Using social-emotional and character development to improve academic outcomes: a matched-pair, cluster-randomized controlled trial in low-income, urban schools. The Journal of School Health, 83(11), 771–779. https://doi.org/10.1111/josh.12093.
Beran, T. N., Tutty, L., & Steinrath, G. (2004). An evaluation of a bullying prevention program for elementary schools. Canadian Journal of School Psychology, 19(1–2), 99–116. https://doi.org/10.1177/082957350401900105.
Bond, L., Patton, G., Glover, S., Carlin, J., Butler, H., Thomas, L., & Bowes, G. (2004). The Gatehouse Project: can a multilevel school intervention affect emotional wellbeing and health risk behaviours? Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 58(12), 997–1003. https://doi.org/10.1136/jech.2003.009449.
Bonell, C., Fletcher, A., Fitzgerald-Yau, N., Hale, D., Allen, E., Elbourne, D., Jones, R., Bond, L., Wiggins, M., Miners, A., Legood, R., Scott, S., Christie, D., & Viner, R. (2015). Initiating change locally in bullying and aggression through the school environment (INCLUSIVE): a pilot randomized controlled trial. Health Technology Assessment, 19(53), ISSN 1366-5278), 1–110.
Brown, E. C., Catalano, R. F., Fleming, C. B., Haggerty, K. P., & Abbott, R. D. (2005). Adolescent substance use outcomes in the Raising Healthy Children project: a two-part latent growth curve analysis. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 73(4), 699–710.
Brown, E. C., Low, S., Smith, B. H., & Haggerty, K. P. (2011). Outcomes from a school-randomized controlled trial of Steps to Respect: a bullying prevention program. School Psychology Review, 40(3), 423–443.
Catalano, R. F., Mazza, J. J., Harachi, T. W., Abbott, R. D., Haggerty, K. P., & Fleming, C. B. (2003). Raising healthy children through enhancing social development in elementary school: results after 1.5 years. Journal of School Psychology, 41(2), 143–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-4405(03)00031-1.
Conduct Problems Prevention Research Group. (2010). The effects of a multiyear universal social–emotional learning program: the role of student and school characteristics. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 78(2), 156–168. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0018607.
Cross, D., Monks, H., Hall, M., Shaw, T., Pintabona, Y., Erceg, E., Hamilton, G. J., Roberts, C., Waters, S. K., & Lester, L. (2011). Three-year results of the Friendly Schools whole-of-school intervention on children’s bullying behaviour. British Educational Research Journal, 37(1), 105–129. https://doi.org/10.1080/01411920903420024.
Cross, D., Shaw, T., Hadwen, K., Cardoso, P., Slee, P., Roberts, C., Thomas, L., & Barnes, A. (2016). Longitudinal impact of the Cyber Friendly Schools program on adolescents’ cyberbullying behavior. Aggressive Behaviour, 42(2), 166–180. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.21609.
Dray, J., Bowman, J., Campbell, E., Freund, M., Hodder, R., Wolfenden, L., Richards, J., Leane, C., Green, S., Lecathelinais, C., Oldmeadow, C., Attia, J., Gillham, K., & Wiggers, J. (2017). Effectiveness of a pragmatic school-based universal intervention targeting student resilience protective factors in reducing mental health problems in adolescents. Journal of Adolescence, 57(Supplement C), 74–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2017.03.009.
Eisen, M., Zellman, G. L., & Murray, D. M. (2003). Evaluating the Lions–Quest “Skills for Adolescence” drug education program: second-year behavior outcomes. Addictive Behaviors, 28(5), 883–897. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0306-4603(01)00292-1.
Flay, B. R., Graumlich, S., Segawa, E., Burns, J. L., Holliday, M. Y., & for the Aban Aya Investigators. (2004). Effects of 2 prevention programs on high-risk behaviors among African American youth: a randomized trial. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, 158(4), 377–384. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpedi.158.4.377.
Fonagy, P., Twemlow, S. W., Vernberg, E. M., Nelson, J. M., Dill, E. J., Little, T. D., & Sargent, J. A. (2009). A cluster randomized controlled trial of child-focused psychiatric consultation and a school systems-focused intervention to reduce aggression. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 50(5), 607–616. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2008.02025.x.
Frey, K. S., Hirschstein, M. K., Snell, J. L., Edstrom, L. V. S., MacKenzie, E. P., & Broderick, C. J. (2005). Reducing playground bullying and supporting beliefs: an experimental trial of the steps to respect program. Developmental Psychology, 41(3), 479–490. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.41.3.479.
Gradinger, P., Yanagida, T., Strohmeier, D., & Spiel, C. (2015). Prevention of cyberbullying and cyber victimization: evaluation of the ViSC social competence program. Journal of School Violence, 14(1), 87–110. https://doi.org/10.1080/15388220.2014.963231.
Hawkins, J. D., Kosterman, R., Catalano, R. F., Hill, K. G., & Abbott, R. D. (2005). Promoting positive adult functioning through social development intervention in childhood: long-term effects from the Seattle Social Development Project. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, 159(1), 25–31.
Hoglund, W. L. G., Hosan, N. E., & Leadbeater, B. J. (2012). Using your WITS: A 6-year follow-up of a peer victimization prevention program. School Psychology Review, 41(2), 193–214.
Jones, S. M., Brown, J. L., Hoglund, W. L. G., & Aber, J. L. (2010). A school-randomized clinical trial of an integrated social–emotional learning and literacy intervention: impacts after 1 school year. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 78(6), 829–842. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0021383.
Kärnä, A., Voeten, M., Little, T. D., Poskiparta, E., Alanen, E., & Salmivalli, C. (2011a). Going to scale: a nonrandomized nationwide trial of the KiVa antibullying program for grades 1–9. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 79(6), 796–805.
Kärnä, A., Voeten, M., Little, T. D., Poskiparta, E., Kaljonen, A., & Salmivalli, C. (2011b). A large-scale evaluation of the KiVa antibullying program: grades 4–6. Child Development, 82(1), 311–330. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.2010.01557.x.
Kärnä, A., Voeten, M., Little, T. D., Alanen, E., Poskiparta, E., & Salmivalli, C. (2013). Effectiveness of the KiVa Antibullying Program: grades 1–3 and 7–9. Journal of Educational Psychology, 105(2), 535–551. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0030417.
Kiviruusu, O., Björklund, K., Koskinen, H. L., Liski, A., Lindblom, J., Kuoppamäki, H., Alasuvanto, P., Ojala, T., Samposalo, H., Harmes, N., Hemminki, E., Punamäki, R., Sund, R., & Santalahti, P. (2016). Short-term effects of the “Together at School” intervention program on children’s socio-emotional skills: a cluster randomized controlled trial. BMC Psychology, 4(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-016-0133-4.
Leadbeater, B., & Sukhawathanakul, P. (2011). Multicomponent programs for reducing peer victimization in early elementary school: a longitudinal evaluation of the WITS Primary Program. Journal of Community Psychology, 39(5), 606–620. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcop.20447.
Lee, P. C., & Stewart, D. E. (2013). Does a socio-ecological school model promote resilience in primary schools? Journal of School Health, 83(11), 795–804. https://doi.org/10.1111/josh.12096.
Lewis, K. M., Bavarian, N., Snyder, F. J., Acock, A., Day, J., DuBois, D. L., Ji, P., Schure, M. B., Silverthorn, N., Vuchinich, S., & Flay, B. R. (2012). Direct and mediated effects of a social-emotional and character development program on adolescent substance use. The International Journal of Emotional Education, 4(1), 56–78.
Lewis, K. M., DuBois, D. L., Bavarian, N., Acock, A., Silverthorn, N., Day, J., Ji, P., Vuchinich, S., & Flay, B. R. (2013a). Effects of positive action on the emotional health of urban youth: a cluster-randomized trial. Journal of Adolescent Health, 53(6), 706–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2013.06.012.
Lewis, K. M., Schure, M. B., Bavarian, N., DuBois, D. L., Day, J., Ji, P., Silverthorn, N., Acock, A., Vuchinich, S., & Flay, B. R. (2013b). Problem behavior and urban, low-income youth: a randomized controlled trial of positive action in Chicago. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 44(6), 622–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amepre.2013.01.030.
Lewis, K. M., Vuchinich, S., Ji, P., DuBois, D. L., Acock, A., Bavarian, N., Day, J., Silverthorn, N., & Flay, B. R. (2015). Effects of the Positive Action program on indicators of positive youth development among urban youth. Applied Developmental Science, 20(1), 16–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888691.2015.1039123.
Lynch, K. B., Geller, S. R., & Schmidt, M. G. (2004). Multi-year evaluation of the effectiveness of a resilience-based prevention program for young children. Journal of Primary Prevention, 24(3), 335–353. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOPP.0000018052.12488.d1.
Menard, S., & Grotpeter, J. K. (2014). Evaluation of Bully-Proofing Your School as an elementary school antibullying intervention. Journal of School Violence, 13(2), 188–209. https://doi.org/10.1080/15388220.2013.840641.
Patton, G. C., Bond, L., Carlin, J. B., Thomas, L., Butler, H., Glover, S., Catalano, R., & Bowes, G. (2006). Promoting social inclusion in schools: a group-randomized trial of effects on student health risk behavior and well-being. American Journal of Public Health, 96(9), 1582–1587. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2004.047399.
Raskauskas, J. (2006). Evaluation of the Kia Kaha Anti-bullying Programme for students in years 5-8. New Zealand Police, Wellington, New Zealand.
Roland, E., Bru, E., Midthassel, U. V., & Vaaland, G. S. (2010). The Zero programme against bullying: effects of the programme in the context of the Norwegian manifesto against bullying. Social Psychology of Education, 13(1), 41–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11218-009-9096-0.
Salmivalli, C., Kärnä, A., & Poskiparta, E. (2011). Counteracting bullying in Finland: the KiVa program and its effects on different forms of being bullied. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 35(5), 405–411.
Silverthorn, N., DuBois, D. L., Lewis, K. M., Reed, A., Bavarian, N., Day, J., Ji, P., Acock, A. C., Vuchinich, S., & Flay, B. R. (2017). Effects of a school-based social-emotional and character development program on self-esteem levels and processes: a cluster-randomized controlled trial. SAGE Open, 7(3), 215824401771323. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244017713238.
Snyder, F., Flay, B., Vuchinich, S., Acock, A., Washburn, I., Beets, M., & Li, K.-K. (2010). Impact of a social-emotional and character development program on school-level indicators of academic achievement, absenteeism, and disciplinary outcomes: a matched-pair, cluster randomized, controlled trial. Journal of Research on Educational Effectiveness, 3(1), 26–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/19345740903353436.
Snyder, F. J., Vuchinich, S., Acock, A., Washburn, I. J., & Flay, B. R. (2012). Improving elementary school quality through the use of a social-emotional and character development program: a matched-pair, cluster-randomized, controlled trial in Hawai’i. The Journal of School Health, 82(1), 11–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1746-1561.2011.00662.x.
Solomon, D., Battistich, V., Watson, M., Schaps, E., & Lewis, C. (2000). A six-district study of educational change: direct and mediated effects of the child development project. Social Psychology of Education, 4(1), 3–51. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009609606692.
Stevens, V., De Bourdeaudhuij, I., & Van Oost, P. (2000). Bullying in Flemish schools: an evaluation of anti-bullying intervention in primary and secondary schools. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 70(2), 195–210. https://doi.org/10.1348/000709900158056.
Washburn, I. J., Acock, A., Vuchinich, S., Snyder, F., Li, K.-K., Ji, P., Day, J., DuBois, D., & Flay, B. R. (2011). Effects of a social-emotional and character development program on the trajectory of behaviors associated with social-emotional and character development: findings from three randomized trials. Prevention Science, 12(3), 314–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-011-0230-9.
Wigelsworth, M., Humphrey, N., & Lendrum, A. (2012). A national evaluation of the impact of the secondary social and emotional aspects of learning (SEAL) programme. Educational Psychology, 32(2), 213–238. https://doi.org/10.1080/01443410.2011.640308.
Williford, A., Boulton, A., Noland, B., Little, T. D., Kärnä, A., & Salmivalli, C. (2012). Effects of the KiVa anti-bullying program on adolescents’ depression, anxiety, and perception of peers. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 40(2), 289–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-011-9551-1.
Williford, A., Elledge, L. C., Boulton, A. J., DePaolis, K. J., Little, T. D., & Salmivalli, C. (2013). Effects of the KiVa Antibullying Program on cyberbullying and cybervictimization frequency among Finnish youth. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 42(6), 820–833. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2013.787623.
Wong, D. S. W., Cheng, C. H. K., Ngan, R. M. H., & Ma, S. K. (2011). Program effectiveness of a restorative whole-school approach for tackling school bullying in Hong Kong. International Journal of Offender Therapy and Comparative Criminology, 55(6), 846–862. https://doi.org/10.1177/0306624X10374638.
Yang, A., & Salmivalli, C. (2015). Effectiveness of the KiVa antibullying programme on bully-victims, bullies and victims. Educational Research, 57(1), 80–90. https://doi.org/10.1080/00131881.2014.983724.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Jochem M. Goldberg. Psychology, Health and Technology – University of Twente, Drienerlolaan 5, 7523NJ, Enschede, Netherlands. E-mail: j.m.goldberg@utwente.nl; Web site: https://www.utwente.nl/en/bms/pht/
Current themes of research:
Whole School Approach. Positive Psychology in Education. Wellbeing and engagement.
Most relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:
Teuntje R. Elfrink, Jochem M. Goldberg, Karlein M.G. Schreurs, Ernst T. Bohlmeijer, Aleisha M. Clarke, (2017) Positive educative programme: a whole school approach to supporting children’s well-being and creating a positive school climate: a pilot study, Health Education, Vol. 117 Issue: 2, pp. 215–230, https://doi.org/10.1108/HE-09-2016-0039
Marcin Sklad. University College Roosevelt – Utrecht University, Lange Noordstraat 1, 4331 CB, Middelburg, Netherlands. E-mail: m.sklad@ucr.nl; Web site: www.ucr.nl
Current themes of research:
Pedagogical knowledge of parents. Effectiveness of school-based socio-emotional learning programs. Innovative educational methods.
Most relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:
Diekstra, R., Sklad, M., Ben, J., Ritter, M. (2008), Teaching social and emotional skills worldwide: a meta-analytic review of effectiveness. In: Social and emotional education: an international analysis. Fundacion Marcelino Botin.
Gravesteijn, C., Diekstra, R., Sklad, M., Winter, M. (2011). The effects of a Dutch school-based social and emotional learning programme (SEL) on suicidality in adolescents. The International Journal of Mental Health Promotion, 13(4), pp. 4–16.
Sklad, M., Diekstra, R., Gravesteijn, C.M., Ben, J., Ritter, M. (2012), Effectiveness of school-based universal social, emotional and behavioral programs: do they enhance students’ development in the area of skill, behavior, and adjustment?, Psychology in the Schools, 49(9), 892–909
Teuntje R. Elfrink. Psychology, Health and Technology – University of Twente, Drienerlolaan 5, 7523NJ, Enschede, Netherlands. E-mail: t.r.elfrink@utwente.nl; Web site: https://www.utwente.nl/en/bms/pht/
Current themes of research:
Whole School Approach. Positive Psychology in Education. Wellbeing and engagement.
Most relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:
Teuntje R. Elfrink, Jochem M. Goldberg, Karlein M.G. Schreurs, Ernst T. Bohlmeijer, Aleisha M. Clarke, (2017) Positive educative programme: a whole school approach to supporting children’s well-being and creating a positive school climate: a pilot study, Health Education, Vol. 117 Issue: 2, pp.215–230, https://doi.org/10.1108/HE-09-2016-0039
Karlein M. G. Schreurs. Psychology, Health and Technology – University of Twente, Drienerlolaan 5, 7523NJ, Enschede, Netherlands. E-mail: k.m.g.schreurs@utwente.nl; Web site: https://www.utwente.nl/en/bms/pht/
Current themes of research:
Whole School Approach. Positive Psychology in Education. Wellbeing and engagement.
Most relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:
Teuntje R. Elfrink, Jochem M. Goldberg, Karlein M.G. Schreurs, Ernst T. Bohlmeijer, Aleisha M. Clarke, (2017) Positive educative programme: a whole school approach to supporting children’s well-being and creating a positive school climate: a pilot study, Health Education, Vol. 117 Issue: 2, pp.215–230, https://doi.org/10.1108/HE-09-2016-0039
Ernst T. Bohlmeijer. Psychology, Health and Technology – University of Twente, Drienerlolaan 5, 7523NJ, Enschede, Netherlands. E-mail: e.t.bohlmeijer@utwente.nl; Web site: https://www.utwente.nl/en/bms/pht/
Current themes of research:
Whole School Approach. Positive Psychology in Education. Wellbeing and engagement.
Most relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:
Teuntje R. Elfrink, Jochem M. Goldberg, Karlein M.G. Schreurs, Ernst T. Bohlmeijer, Aleisha M. Clarke, (2017) Positive educative programme: a whole school approach to supporting children’s well-being and creating a positive school climate: a pilot study, Health Education, Vol. 117 Issue: 2, pp.215–230, https://doi.org/10.1108/HE-09-2016-0039
Aleisha M. Clarke. What works assessment – Early intervention foundation, 10 Salamanca Place, London, SE1 7HB, UK. E-mail: Aleisha.clarke@eif.org.uk; Web site: http://www.eif.org.uk/
Current themes of research:
Child and adolescent mental health. Wellbeing. Programme development. Implementation and evaluation research.
Most relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:
Barry, M.M., Clarke, A.M., & Dowling, K. (2017). Promoting social and emotional wellbeing in schools. Health Education, 117(5), 434–451.
Barry, M.M., Clarke, A.M., Moreale, S.E., Field, C.A. (2017) A review of the evidence on the effects of community-based programs on young people’s social and emotional skills development. Adolescent Research Review. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s40894-017-0055-2
Clarke, A.M., Kuosmanen, T., & Barry, M.M. (2015). A systematic review of online youth mental health promotion and prevention interventions. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 44(1): 90–113.
Clarke, A.M., & Barry, M.M (2015). Supporting a whole school approach to mental health promotion and wellbeing in post-primary schools in Ireland. In S. Kutcher, Y. Wei, & M. Weist (Eds), International school mental health for adolescents- global opportunities and challenges. UK: Cambridge Press.
Clarke, A.M., Bunting, B., & Barry, M.M. (2014). Evaluating the implementation of a school-based emotional wellbeing programme: a cluster randomised trial of Zippy’s Friends for children in disadvantaged primary schools. Health Education Research, 29(5), 786–798.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 130 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Goldberg, J.M., Sklad, M., Elfrink, T.R. et al. Effectiveness of interventions adopting a whole school approach to enhancing social and emotional development: a meta-analysis. Eur J Psychol Educ 34, 755–782 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-018-0406-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-018-0406-9