Abstract
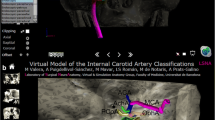
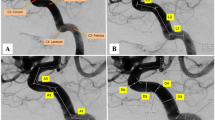
The course of the internal carotid artery (ICA) and its segment classifications were reviewed by means of a new and freely available 3D interactive model of the artery and the skull base, based on human neuroimages, that can be freely downloaded at the Public Repository of the University of Barcelona (http://diposit.ub.edu/dspace/handle/2445/112442) and runs under Acrobat Reader in Mac and Windows computers and Windows 10 tablets. The 3D-PDF allows zoom, rotation, selective visualization of structures, and a predefined sequence view. Illustrative images of the different classifications were obtained. Fischer (Zentralbl Neurochir 3:300–313, 1938) described five segments in the opposite direction to the blood flow. Gibo-Rothon (J Neurosurg 55:560–574, 1981) follow the blood flow, incorporated the cervical and petrous portions, and divided the subarachnoid course—supraclinoid—in ophthalmic, communicating, and choroidal segments, enhancing transcranial microscopic approaches. Bouthillier (Neurosurgery 38:425–433, 1996) divided the petrous portion describing the lacerum segment (exposed in transfacial procedures and exploration of Meckel’s cave) and added the clinoid segment between the proximal and distal dural rings, of interest in cavernous sinus surgery. The Kassam’s group (2014), with an endoscopic endonasal perspective, introduces the “paraclival segment,” including the “lacerum segment” and part of the intracavernous ICA, and details surgical landmarks to minimize the risk of injury. Other classifications are also analyzed. This review through an interactive 3D tool provides virtual views of the ICA and becomes an innovative perspective to the segment classifications and neuroanatomy of the ICA and surrounding structures.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulrauf SI, Ashour AM, Marvin E, Coppens J, Kang B, Hsieh TY, Nery B, Penanes JR, Alsahlawi AK, Moore S, Abou Al-Shaar H, Kemp J, Chawla K, Sujijantarat N, Najeeb A, Parkar N, Shetty V, Vafaie T, Antisdel J, Mikulec TA, Edgell R, Lebovitz J, Pierson M, Pires de Aguiar PH, Buchanan P, Di Cosola A, Stevens G (2016) Proposed clinical internal carotid artery classification system. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine 7:161–170 Erratum in J Craniovertebr Junction Spine (2016) 8:84
Bouthillier A, van Loveren HR, Keller JT (1996) Segments of the internal carotid artery: a new classification. Neurosurgery 38:425–433
Choi HC, Park SE, Choi DS, Shin HS, Kim JE, Choi HY, Park MJ, Koh EH (2018) Ruptured extracranial carotid artery: endovascular treatment with covered stent graft. J Neuroradiol 45:217–223
D’Avella E, De Notaris M, Enseñat J, Berenguer J, Gragnaniello C, Mavar M, Ferrer E, Prats-Galino A (2015) The extended endoscopic endonasal transplanum transtuberculum approach to the anterior communicating artery complex: anatomical study. Acta Neurochir 157:1495–1503
De Notaris M, Prats-Galino A, Cavallo LM, Esposito F, Iaconetta G, González JB, Montagnani S, Ferrer E, Cappabianca P (2010) Preliminary experience with a new three-dimensional computer-based model for the study and the analysis of skull base approaches. Childs Nerv Syst 26:621–626
De Notaris M, Solari D, Cavallo LM, Enseñat J, Alobid I, Soria G, Gonzalez JB, Ferrer E, Prats-Galino A (2011) The use of a three-dimensional novel computer-based model for analysis of the endonasal endoscopic approach to the midline skull base. World Neurosurg 75:106–113
De Notaris M, Palma K, Serra L, Enseñat J, Alobid I, Poblete J, González JB, Solari D, Ferrer E, Prats-Galino A (2014) A three-dimensional computer-based perspective of the skull base. World Neurosurg 82:S41–S48
De Notaris M, Prats-Galino A, Enseñat J, Topczewski T, Ferrer E, Cavallo LM, Cappabianca P, Solari D (2014) Quantitative analysis of progressive removal of nasal structures during endoscopic suprasellar approach. Laryngoscope 124:2231–2237
De Powell JJ, Froelich SC, Zimmer LA, Leach JL, Karkas A, Theodosopoulos PV, Keller JT (2014) Segments of the internal carotid artery during endoscopic transnasal and open cranial approaches: can a uniform nomenclature apply to both? World Neurosurg 82(6S):S66–S71
Dolati P, Golby A, Eichberg D, Abolfotoh M, Dunn IF, Mukundan S, Hulou MM, Al-Mefty O (2015) Pre-operative image-based segmentation of the cranial nerves and blood vessels in microvascular decompression: can we prevent unnecessary explorations? Clin Neurol Neurosurg 139:159–165
Dolati P, Eichberg D, Golby A, Zamani A, Laws E (2016) Multimodal navigation in endoscopic transsphenoidal resection of pituitary tumors using image-based vascular and cranial nerve segmentation: a prospective validation study. World Neurosurg 95:406–413
Dusick JR, Esposito F, Malkasian D, Kelly DF (2007) Avoidance of carotid artery injuries in transsphenoidal surgery with the Doppler probe and micro-hook blades. Neurosurgery 60:322–328
Fischer E (1938) Die lageabweichungen der vorderen hirnarterie im gefäbild. Zentralbl Neurochir 3:300–313
Gao Z, Chi FI (2015) Anatomy relationship around internal carotid artery in the endoscopic surgery of nasopharynx: a study based on computed tomography angiography. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base 76:176–182
Gibo H, Lenkey C, Rhoton A Jr (1981) Microsurgical anatomy of the supraclinoid portion of the internal carotid artery. J Neurosurg 55:560–574
Glasscock ME III (1969) Middle fossa approach to the temporal bone. An otologic frontier. Arch Otolaryngol 90:15–27
Gorpe P, Auperin A, Honart JF, Ton Van J, El Bedoui S, Bidault F, Temam S, Kolb R, Qassemyar Q (2018) Revisiting vascular contraindicatios for transoral robotic surgery for oropharyngeal cancer. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol 3:121–126
Harris FS, Rhoton AL (1976) Anatomy of the cavernous sinus. A microsurgical study. J Neurosurg 42:169–180
Kassam AB, Gardner P, Snyderman C, Mintz A, Carrau R (2005) Expanded endonasal approach: fully endoscopic, completely transnasal approach to the middle third of the clivus, petrous bone, middle cranial fossa and infratemporal fossa. Neurosurg Focus 19:E6
Kassam AB, Vescan AD, Carrau RL, Prevedello DM, Gardner P, Mintz AH (2008) Expanded endonasal approach: vidian canal as a landmark to the petrous internal carotid artery. J Neurosurg 108:177–183
Kawase T, Shiobara R, Toya S (1991) Anterior transpetrosaltranstentorial approach for sphenopetroclival meningiomas: surgical method and results in 10 patients. Neurosurgery 28(6):869–875 discussion 875–876
Kim B (2010) Anatomy. Blood supply to the brain. In: Citow JS, Macdonald RL, Refai D (eds) Comprehensive neurosurgery board review, 2nd edn. Thieme, New York, pp 1–110
Labib M, Prevedello D, Carrau R, Kerr E, Naudy C, Abou Al-Shaar H, Corsten M, Kassam A (2014) A road map to the internal carotid artery in expanded endoscopic endonasal approaches to the ventral cranial base. Neurosurgery 10:448–471
Lasjaunias P, Berenstein A (1978) Arterial anatomy: introduction. In: Lasjaunias P, Berenstein A (eds) Surgical Neuroangiography: functional anatomy of craniofacial arteries. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 1–32
Louw L (2015) Different ophthalmic artery origins: embriology and clinical significance. Clin Anat 28:276–576
Marcati E, Andaluz N, Froelich SC, Zimmer LA, Leach JL, Fernández-Miranda JC, Kurbanov A, Keller JT (2017) Paratrigeminal, paraclival, precavernous, or all of the above? A circumferential anatomical study of the C3-C4 transitional segment of the internal carotid artery. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown). https://doi.org/10.1093/on/opx121
Mavar-Haramija M, Prats-Galino A, Juanes-Méndez JA, Puigdellívol-Sánchez A, de Notaris M (2015) Interactive 3D-PDF presentations for the simulation and quantification of extended endoscopic endonasal surgical approaches. J Med Sys 39:127
Mujika KM, Méndez JAJ, de Miguel AF (2018) Advantages and disavantages in image processing with free software in radiology. J Med Sys 42:36
Nathal E, Castillo G (2012) Surgical treatment of paraclinoid aneurysms. In: Quiñones-Hinojosa A (ed) Schmidek and sweet operative neurosurgical techniques: indications, methods and results, 6th edn. Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 855–871
Phelps A, Naeger DM, Marcovici P (2012) Embedding 3D radiology models in portable document format. AJR Am J Roentgenol 199:1342–1344
Prasad SC, Thada N, Pallavi, Prasad KC (2011) Paragangliomas of the head&neck: the KMC experience. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 63:62–73
Prats-Galino A, Mavar M, Reina MA, Puigdellívol-Sánchez A, San-Molina J, De Andrés JA (2014) Three-dimensional interactive model of lumbar spinal structures. Anaesthesia 69:521
Prats-Galino A, Reina MA, Mavar Haramija M, Juanes Méndez JA, De Andrés JA (2015) 3D interactive model of lumbar spinal structures of anesthetic interest. Clin Anat 28:205–212
Rhoton AL (2002) The supratentorial arteries. Neurosurgery 51:53–120
Sorensen MS, Dobrzeniecki AB, Larsen P, Frisch T, Sporring J, Darvann TA (2002) The visible ear: a digital image library of the temporal bone. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 64:378–381
Spiessberger A, Baumann F, Kothbauer KF, Aref M, Marbacher S, Fandino J, Nevzati E (2019) Bony dehiscence of the horizontal petrous internal carotid artery canal: an anatomic study with surgical implications. World Neurosurg:S1878–S8750
Sun X, Uan B, Truong HQ, Borghei-Razavi H, Snyderman CH, Fernández-Miranda JC (2018) A comparative analysis of endoscopic-assisted transoral and transnasal approaches to parapharyngeal space: a cadaveric study. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base 79:229–240
Tauber M, Van Loveren HR, Jallo G, Romano A, Keller JT (1999) The enigmatic foramen lacerum. Neurosurgery 44:386–391
Tubbs RS, Hansasuta A, Loukas M, Louis RG Jr, Shoja MM, Salter EG, Oakes WJ (2007) Branches of the petrous and cavernous segments of the internal carotid artery. Clin Anat 20:596–601
Üstün ME, Büyükmumcu M, Seker M, Karabulut AK, Uysal II, Ziylan T (2004) Possibility of middle meningeal artery-to-petrous internal carotid artery bypass: an anatomic study. Skull Base 14:153–156
Valera-Melé M, Puigdellívol-Sánchez A, Mavar-Haramija M, Juanes-Méndez J, San-Román L, De Notaris M, Prats-Galino A (2018) A novel and freely available interactive 3D model of the internal carotid artery. J Med Sys 42:72
Van Loveren HR, Keller JT, El-Kalliny M, Scodary DJ, Tew JM (1991) The Dolenc technique for cavernous sinus exploration (cadaveric prosection). J Neurosurg 74:837–844
Vijaywarqiya M, Deopujari R, Athavale SA (2017) Anatomical study of petrous and cavernous parts of internal carotid artery. Anat Cell Biol 50:163–170
Wang S, Quin Y, Xiao D, Wu Z, Wei L (2018) Imaging evaluation of the location and fenestration of sellar floor during endonasal transsphenoidal surgery in patients with pituitary adenomas. World Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.04.178
Wikimedia Commons. Gray H (1918) Anatomy of the Human Body, 20th ed. Philadelphia and New York:Lea&Febiger. (https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/9/9c/Gray513.png). [Accessed June 1th, 2017]
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Olga Fuentes for her contribution to image processing.
Funding
This study was funded by the Fundació Marató TV3 Project [411/U/2011—TITLE: Quantitative analysis and computer aided simulation of minimally invasive approaches for intracranial vascular lesions].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
All procedures were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 12006 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Melé, M.V., Puigdellívol-Sánchez, A., Mavar-Haramija, M. et al. Review of the main surgical and angiographic-oriented classifications of the course of the internal carotid artery through a novel interactive 3D model. Neurosurg Rev 43, 473–482 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-018-1012-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-018-1012-7