Abstract
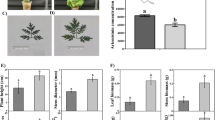
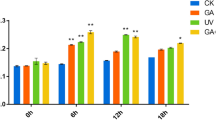
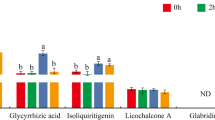
Artemisia annua L. is a medicinal plant valued for its ability to produce artemisinin, a molecule used to treat malaria. Plant nutrients, especially phosphorus (P), can potentially influence plant biomass and secondary metabolite production. Our work aimed to explore the genetic and metabolic response of A. annua to hardly soluble aluminum phosphate (AlPO4, AlP), using soluble monopotassium phosphate (KH2PO4, KP) as a control. Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) was used to analyze artemisinin. RNA sequencing, gene ontology (GO), and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analyses were applied to analyze the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) under poor P conditions. Results showed a significant reduction in plant growth parameters, such as plant height, stem diameter, number of leaves, leaf areas, and total biomass of A. annua. Conversely, LC–MS analysis revealed a significant increase in artemisinin concentration under the AlP compared to the KP. Transcriptome analysis revealed 762 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the AlP and the KP. GH3, SAUR, CRE1, and PYL, all involved in plant hormone signal transduction, showed differential expression. Furthermore, despite the downregulation of HMGR in the artemisinin biosynthesis pathway, the majority of genes (ACAT, FPS, CYP71AV1, and ALDH1) were upregulated, resulting in increased artemisinin accumulation in the AlP. In addition, 12 transcription factors, including GATA and MYB, were upregulated in response to AlP, confirming their importance in regulating artemisinin biosynthesis. Overall, our findings could contribute to a better understanding the parallel transcriptional regulation of plant hormone transduction and artemisinin biosynthesis in A. annua L. in response to hardly soluble phosphorus fertilizer.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number (s) can be found at GSA, accession number: CRA008375 at the following link: https://bigd.big.ac.cn/gsa/browse/CRA008375.
References
Aftab T, Khan MMA, Ferreira JFS (2014) Effect of mineral nutrition, growth regulators and environmental stresses on biomass production and Artemisinin concentration of Artemisia annua L. In: Aftab T, Ferreira JFS, Khan MMA, Naeem M (eds) Artemisia annua - Pharmacology and Biotechnology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 157–172
Ahmed S, Chouhan R, Junaid A et al (2023) Transcriptome analysis and differential expression in Arabidopsis thaliana in response to rohitukine (a chromone alkaloid) treatment. Funct Integr Genomics 23:35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-00961-0
Amarasinghe T, Madhusha C, Munaweera I, Kottegoda N (2022) Review on mechanisms of phosphate solubilization in rock phosphate fertilizer. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 53:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2022.2034849
Augusto L, Achat DL, Jonard M, Vidal D, Ringeval B (2017) Soil parent material—a major driver of plant nutrient limitations in terrestrial ecosystems. Glob Chang Biol 23:3808–3824. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13691
Banyai W, Kirdmanee C, Mii M, Supaibulwatana K (2010) Overexpression of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase (FPS) gene affected artemisinin content and growth of Artemisia annua L. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 103:255–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9775-8
Baraldi R, Isacchi B, Predieri S, Marconi G, Vincieri FF, Bilia AR (2008) Distribution of artemisinin and bioactive flavonoids from Artemisia annua L. during plant growth. Biochem Syst Ecol 36:340–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2007.11.002
Castrillo G, Sánchez-Bermejo E, de Lorenzo L, Crevillén P, Fraile-Escanciano A, Tc M, Mouriz A, Catarecha P, Sobrino-Plata J, Olsson S, Leo Del Puerto Y, Mateos I, Rojo E, Hernández LE, Jarillo JA, Piñeiro M, Paz-Ares J, Leyva A (2013) WRKY6 transcription factor restricts arsenate uptake and transposon activation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25:2944–2957. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.114009
Chao LM, Liu YQ, Chen DY, Xue XY, Mao YB, Chen XY (2017) Arabidopsis transcription factors SPL1 and SPL12 confer plant thermotolerance at reproductive stage. Mol Plant 10:735–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2017.03.010
Chen Y, Ye G, Zhang L, Wang Y, Zhang X, Chen D (2007) Effect of trans-Bacillus thuringiensis gene on gibberellic acid and zeatin contents and boll development in cotton. Field Crop Res 103:5–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2007.04.003
Cordovil CMdS, Bittman S, Brito LM, Goss MJ, Hunt D, Serra J, Gourley C, Aarons S, Skiba U, Amon B, Vale MJ, Cruz S, Reis R, Dalgaard T, Hutchings N (2020) Chapter 22 - Climate-resilient and smart agricultural management tools to cope with climate change-induced soil quality decline. In: Prasad MNV, Pietrzykowski M (eds) Climate change and soil interactions. Elsevier, pp 613–662
Dai X, Wang Y, Yang A, Zhang WH (2012) OsMYB2P-1, an R2R3MYB transcription factor, is involved in the regulation of phosphate-starvation responses and root architecture in rice. Plant Physiol 159:169–183. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.194217
Dai X, Wang Y, Zhang WH (2016) OsWRKY74, a WRKY transcription factor, modulates tolerance to phosphate starvation in rice. J Exp Bot 67:947–960. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv515
Davies MJ, Atkinson CJ, Burns C, Arroo R, Woolley J (2011) Increases in leaf artemisinin concentration in Artemisia annua in response to the application of phosphorus and boron. Ind Crop Prod 34(3):1465–1473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2011.05.00
Deng QW, Luo XD, Chen YL, Zhou Y, Zhang FT, Hu BL, Xie JK (2018) Transcriptome analysis of phosphorus stress responsiveness in the seedlings of Dongxiang wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Biol Res 51:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40659-018-0155-x
Dilshad E, Cusido RM, Palazon J, Estrada KR, Bonfill M, Mirza B (2015) Enhanced artemisinin yield by expression of rol genes in Artemisia annua. Malar J 14:424. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-015-0951-5
Ding X, Cao Y, Huang L, Zhao J, Xu C, Li X, Wang S (2008) Activation of the indole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase GH3-8 suppresses expansion expression and promotes salicylate- and jasmonate-independent basal immunity in rice. Plant Cell 20:228–240. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.107.055657
Ding W, Wang Y, Fang W, Gao S, Li X, Xiao K (2016) TaZAT8, a C2H2-ZFP type transcription factor gene in wheat, plays critical roles in mediating tolerance to Pi deprivation through regulating P acquisition, ROS homeostasis and root system establishment. Physiol Plant 158:297–311. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12467
Du Q, Wang K, Xu C, Zou C, Xie C, Xu Y, Li WX (2016) Strand-specific RNA-Seq transcriptome analysis of genotypes with and without low-phosphorus tolerance provides novel insights into phosphorus-use efficiency in maize. BMC Plant Biol 16:222. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-016-0903-4
El-Sappah AH, Elbaiomy RG, Elrys AS, Wang Y, Zhu Y, Huang Q, Yan K, Xianming Z, Abbas M, El-Tarabily KA, Li J (2021) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of metal tolerance protein gene family in Medicago truncatula under a broad range of heavy metal stress. Front Genet 12:713224. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.713224
El-Sappah AH, Abbas M, Rather SA, Wani SH, Soaud N, Noor Z, Qiulan H, Eldomiaty AS, Mir RR, Li J (2023) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of metal tolerance protein (MTP) gene family in soybean (Glycine max) under heavy metal stress. Mol Biol Rep 50:2975–2990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-08100-x
Giles CD, Hsu P-C, Richardson AE, Hurst MRH, Hill JE (2014) Plant assimilation of phosphorus from an insoluble organic form is improved by addition of an organic anion producing Pseudomonas sp. Soil Biol Biochem 68:263–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.09.026
Han JL, Liu BY, Ye HC, Wang H, Li ZQ, Li GF (2006) Effects of overexpression of the endogenous farnesyl diphosphate synthase on the artemisinin content in Artemisia annua L. J Integr Plant Biol 48:482–487. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2006.00208.x
Hou Z, Yin J, Lu Y, Song J, Wang S, Wei S, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Fang Z (2019) Transcriptomic analysis reveals the temporal and spatial changes in physiological process and gene expression in common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) Grown under Drought Stress. Agronomy 9:569
Hu Y, Ye X, Shi L, Duan H, Xu F (2010) Genotypic differences in root morphology and phosphorus uptake kinetics in brassica napus under low phosphorus supply. J Plant Nutr 33:889–901. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904161003658239
Ikram NK, Simonsen HT (2017) A review of biotechnological artemisinin production in plants. Front Plant Sci 8:1966
Ji Y, Xiao J, Shen Y, Ma D, Li Z, Pu G, Li X, Huang L, Liu B, Ye H, Wang H (2014) Cloning and characterization of AabHLH1, a bHLH transcription factor that positively regulates artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. Plant Cell Physiol 55:1592–1604. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcu090
Kebede B, Nigussie A, Chala M (2018) Response of Artemisia (Artemisia annua L.) to nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers in Wondo. Acad Res J Agric Sci Res 5(6):407–413. https://doi.org/10.14662/ARJASR2017.051
Kim TW, Guan S, Sun Y, Deng Z, Tang W, Shang JX, Sun Y, Burlingame AL, Wang ZY (2009) Brassinosteroid signal transduction from cell-surface receptor kinases to nuclear transcription factors. Nat Cell Biol 11:1254–1260. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1970
Kvakić M, Tzagkarakis G, Pellerin S, Ciais P, Goll D, Mollier A, Ringeval B (2020) Carbon and phosphorus allocation in annual plants: an optimal functioning approach. Front Plant Sci 11:149. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00149
Laffont C, Rey T, André O, Novero M, Kazmierczak T, Debellé F, Bonfante P, Jacquet C, Frugier F (2015) The CRE1 cytokinin pathway is differentially recruited depending on Medicago truncatula root environments and negatively regulates resistance to a pathogen. PLoS ONE 10:e0116819. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0116819
Lambers H (2022) Phosphorus acquisition and utilization in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 73:17–42. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-102720-125738
Lee K-K, Mok I-K, Yoon M-H, Kim H-J, Chung D (2012) Mechanisms of phosphate solubilization by PSB (phosphate-solubilizing bacteria) in soil. Korean J Soil Sci Fert 45:169–176. https://doi.org/10.7745/KJSSF.2012.45.2.169
Leišová-Svobodová L, Psota V, Stočes Š et al (2020) Comparative de novo transcriptome analysis of barley varieties with different malting qualities. Funct Integr Genomics 20:801–812. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-020-00750-z
Li X, Luo L, Yang J, Li B, Yuan H (2015) Mechanisms for solubilization of various insoluble phosphates and activation of immobilized phosphates in different soils by an efficient and salinity-tolerant Aspergillus niger strain An2. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175:2755–2768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1465-2
Liu C-Z, Guo C, Wang Y, Ouyang F (2003) Factors influencing artemisinin production from shoot cultures of Artemisia annua L. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 19:535–538. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025158416832
Liu X, Chu S, Sun C, Xu H, Zhang J, Jiao Y, Zhang D (2020) Genome-wide identification of low phosphorus responsive microRNAs in two soybean genotypes by high-throughput sequencing. Funct Integr Genomics 20:825–838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-020-00754-9
Lu X, Zhang L, Zhang F, Jiang W, Shen Q, Zhang L, Lv Z, Wang G, Tang K (2013) AaORA, a trichome-specific AP2/ERF transcription factor of Artemisia annua, is a positive regulator in the artemisinin biosynthetic pathway and in disease resistance to Botrytis cinerea. New Phytol 198:1191–1202. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12207
Lulie B, Nigussie A, Chala M (2017) Response of Artemisia (Artemisia annua L.) to nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers in wondo response of Artemisia (Artemisia annua L.) to nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers in Wondo Genet and Koka, Ethiopia. Acad Res J Agric Sci Res 5(6):407–413
Ma C, Wang H, Lu X, Li H, Liu B, Xu G (2007) Analysis of Artemisia annua L. volatile oil by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1150:50–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.08.080
Malhotra H, Vandana, Sharma S, Pandey R (2018) Phosphorus nutrition: plant growth in response to deficiency and excess. In: Hasanuzzaman M, Fujita M, Oku H, Nahar K, Hawrylak-Nowak B (eds) Plant nutrients and abiotic stress tolerance. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-9044-8_7
Mathelier A, Fornes O, Arenillas DJ, Chen CY, Denay G, Lee J, Shi W, Shyr C, Tan G, Worsley-Hunt R, Zhang AW, Parcy F, Lenhard B, Sandelin A, Wasserman WW (2016) JASPAR 2016: a major expansion and update of the open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D110-115. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1176
Matías-Hernández L, Jiang W, Yang K, Tang K, Brodelius PE, Pelaz S (2017) AaMYB1 and its orthologue AtMYB61 affect terpene metabolism and trichome development in Artemisia annua and Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 90:520–534. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13509
Miller SH, Browne P, Prigent-Combaret C, Combes-Meynet E, Morrissey JP, O’Gara F (2010) Biochemical and genomic comparison of inorganic phosphate solubilization in Pseudomonas species. Environmental Microbiol Reports 2:403–411. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1758-2229.2009.00105.x
Müller M, Brandes D (1997) Growth and development of Artemisia annua L. on different soil types. Verhandlungen der Gesellschaft für Ökologie 27:435–460. https://doi.org/10.24355/dbbs.084-200511080100-270
Nilsson L, Müller R, Nielsen TH (2007) Increased expression of the MYB-related transcription factor, PHR1, leads to enhanced phosphate uptake in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ 30:1499–1512. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2007.01734.x
Pacifici E, Polverari L, Sabatini S (2015) Plant hormone cross-talk: the pivot of root growth. J Exp Bot 66:1113–1121. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru534
Paddon CJ, Westfall PJ, Pitera DJ, Benjamin K, Fisher K, McPhee D, Leavell MD, Tai A, Main A, Eng D, Polichuk DR, Teoh KH, Reed DW, Treynor T, Lenihan J, Fleck M, Bajad S, Dang G, Dengrove D, Diola D, Dorin G, Ellens KW, Fickes S, Galazzo J, Gaucher SP, Geistlinger T, Henry R, Hepp M, Horning T, Iqbal T, Jiang H, Kizer L, Lieu B, Melis D, Moss N, Regentin R, Secrest S, Tsuruta H, Vazquez R, Westblade LF, Xu L, Yu M, Zhang Y, Zhao L, Lievense J, Covello PS, Keasling JD, Reiling KK, Renninger NS, Newman JD (2013) High-level semi-synthetic production of the potent antimalarial artemisinin. Nature 496:528–532. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12051
Pearse SJ, Veneklaas EJ, Cawthray G, Bolland MD, Lambers H (2007) Carboxylate composition of root exudates does not relate consistently to a crop species’ ability to use phosphorus from aluminium, iron or calcium phosphate sources. New Phytol 173:181–190. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01897.x
Pradhan M, Sahoo RK, Pradhan C, Tuteja N, Mohanty S (2017) Contribution of native phosphorous-solubilizing bacteria of acid soils on phosphorous acquisition in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Protoplasma 254:2225–2236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-017-1112-1
Qureshi MI, Israr M, Abdin M, Iqbal M (2005) Responses of Artemisia annua L. to lead and salt-induced oxidative stress. Environ Exp Bot 53:185–193
Ren H, Gray WM (2015) SAUR proteins as effectors of hormonal and environmental signals in plant growth. Mol Plant 8:1153–1164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2015.05.003
Ren P, Meng Y, Li B, Ma X, Si E, Lai Y, Wang J, Yao L, Yang K, Shang X, Wang H (2018) Molecular mechanisms of acclimatization to phosphorus starvation and recovery underlying full-length transcriptome profiling in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Front Plant Sci 9:500. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00500
Rouached H, Arpat AB, Poirier Y (2010) Regulation of phosphate starvation responses in plants: signaling players and cross-talks. Mol Plant 3:288–299. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssp120
Ryan P, Delhaize E, Jones D (2001) Function and mechanism of organic anion exudation from plant roots. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 52:527–560. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.52.1.527
Secco D, Wang C, Arpat BA, Wang Z, Poirier Y, Tyerman SD, Wu P, Shou H, Whelan J (2012) The emerging importance of the SPX domain-containing proteins in phosphate homeostasis. New Phytol 193:842–851. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.04002.x
Sharma SB, Sayyed RZ, Trivedi MH, Gobi TA (2013) Phosphate solubilizing microbes: sustainable approach for managing phosphorus deficiency in agricultural soils. SpringerPlus 2:1–14
Shen J, Rengel Z, Tang C, Zhang F (2003) Role of phosphorus nutrition in development of cluster roots and release of carboxylates in soil-grown Lupinus albus. Plant Soil 248:199–206. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022375229625
Shen J, Yuan L, Zhang J, Li H, Bai Z, Chen X, Zhang W, Zhang F (2011) Phosphorus dynamics: from soil to plant. Plant Physiol 156:997–1005. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.175232
Shen Q, Yan T, Fu X, Tang K (2016) Transcriptional regulation of artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua L. Science Bulletin 61:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-015-0983-9
Shi P, Fu X, Shen Q, Liu M, Pan Q, Tang Y, Jiang W, Lv Z, Yan T, Ma Y, Chen M, Hao X, Liu P, Li L, Sun X, Tang K (2018) The roles of AaMIXTA1 in regulating the initiation of glandular trichomes and cuticle biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. New Phytol 217:261–276. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14789
Shi J, Wang N, Zhou H, Xu Q, Yan G (2020) Transcriptome analyses provide insights into the homeostatic regulation of axillary buds in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L). BMC Plant Biol 20:228. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02436-x
Simonsen HT, Weitzel C, Christensen SB (2013) Guaianolide sesquiterpenoids: pharmacology and biosynthesis. In: Ramawat K, Mérillon JM (eds) Natural products. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-22144-6_134
Singh M (2000) Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium nutrition on herb, oil and artemisinin yield of Artemisia annua under semi-arid tropical condition. J Med Arom Plant Sci 22:368–369
Singh D, Singh CK, Taunk J et al (2021) Transcriptome skimming of lentil (Lens culinaris Medikus) cultivars with contrast reaction to salt stress. Funct Integr Genomics 21:139–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-020-00766-5
Smith SE, Smith FA (2011) Roles of arbuscular mycorrhizas in plant nutrition and growth: new paradigms from cellular to ecosystem scales. Annu Rev Plant Biol 62:227–250. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042110-103846
Stringham RW, Moore GL, Teager DS, Yue TY (2018) Analysis and isolation of potential artemisinin precursors from waste streams of Artemisia Annua extraction. ACS Omega 3:7803–7808. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b00974
Tafvizi F, Farahani F, Sheidai M, Nejadsattari T (2009) Effects of zeatin and activated charcoal in proliferation of shoots and direct regeneration in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Afr J Biotechnol 8(22):6220–6227. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB09.1211
Tang W, Kim TW, Oses-Prieto JA, Sun Y, Deng Z, Zhu S, Wang R, Burlingame AL, Wang ZY (2008) BSKs mediate signal transduction from the receptor kinase BRI1 in Arabidopsis. Science 321:557–560. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1156973
Teoh KH, Polichuk DR, Reed DW, Nowak G, Covello PS (2006) Artemisia annua L. (Asteraceae) trichome-specific cDNAs reveal CYP71AV1, a cytochrome P450 with a key role in the biosynthesis of the antimalarial sesquiterpene lactone artemisinin. FEBS Lett 580:1411–1416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2006.01.065
Todeschini V, Anastasia F, Massa N, Marsano F, Cesaro P, Bona E, Gamalero E, Oddi L, Lingua G (2022) Impact of phosphatic nutrition on growth parameters and artemisinin production in Artemisia annua plants inoculated or not with Funneliformis mosseae. Life 12(4):497. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12040497
Vance CP, Uhde-Stone C, Allan DL (2003) Phosphorus acquisition and use: critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytol 157:423–447. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00695.x
Vashisth D, Kumar R, Rastogi S, Patel VK, Kalra A, Gupta MM, Gupta AK, Shasany AK (2018) Transcriptome changes induced by abiotic stresses in Artemisia annua. Sci Rep 8:3423. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21598-1
Veneklaas EJ, Lambers H, Bragg J, Finnegan PM, Lovelock CE, Plaxton WC, Price CA, Scheible WR, Shane MW, White PJ, Raven JA (2012) Opportunities for improving phosphorus-use efficiency in crop plants. New Phytol 195:306–320. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04190.x
Vranová E, Coman D, Gruissem W (2013) Network analysis of the MVA and MEP pathways for isoprenoid synthesis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64:665–700. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050312-120116
Wan L-Y, Qi S-S, Dai Z-C, Zou CB, Song Y-G, Hu Z-Y, Zhu B, Du D-L (2018) Growth responses of Canada goldenrod (Solidago canadensis L.) to increased nitrogen supply correlate with bioavailability of insoluble phosphorus source. Ecol Res 33:261–269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11284-017-1552-2
Wang C, Ying S, Huang H, Li K, Wu P, Shou H (2009) Involvement of OsSPX1 in phosphate homeostasis in rice. The Plant j: Cell Molecular Biol 57:895–904. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03734.x
Wani KI, Choudhary S, Zehra A, Naeem M, Weathers P, Aftab T (2021) Enhancing artemisinin content in and delivery from Artemisia annua: a review of alternative, classical, and transgenic approaches. Planta 254:1–15
Wani KI, Zehra A, Choudhary S, Naeem M, Khan MMA, Khan R, Aftab T (2022) Exogenous strigolactone (GR24) positively regulates growth, photosynthesis, and improves glandular trichome attributes for enhanced artemisinin production in Artemisia annua. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-022-10654-w
Williamson LC, Ribrioux SPCP, Fitter AH, Leyser HMO (2001) Phosphate availability regulates root system architecture in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 126:875–882. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.126.2.875
Woodward AW, Bartel B (2005) Auxin: regulation, action, and interaction. Ann Bot 95:707–735. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mci083
Xiang L, Zhu S, Zhao T, Zhang M, Liu W, Chen M, Lan X, Liao Z (2015) Enhancement of artemisinin content and relative expression of genes of artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua by exogenous MeJA treatment. Plant Growth Regul 75:435–441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-014-0004-z
Xie D-Y, Ma D-M, Judd R, Jones AL (2016) Artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua and metabolic engineering: questions, challenges, and perspectives. Phytochem Rev 15:1093–1114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-016-9480-2
Yadav RK, Sangwan RS, Srivastava AK, Sangwan NS (2017) Prolonged exposure to salt stress affects specialized metabolites-artemisinin and essential oil accumulation in Artemisia annua L.: metabolic acclimation in preferential favour of enhanced terpenoid accumulation accompanying vegetative to reproductive phase transition. Protoplasma 254:505–522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-016-0971-1
Yang WT, Baek D, Yun DJ, Hwang WH, Park DS, Nam MH, Chung ES, Chung YS, Yi YB, Kim DH (2014) Overexpression of OsMYB4P, an R2R3-type MYB transcriptional activator, increases phosphate acquisition in rice. Plant Physiol Biochem: PPB 80:259–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.02.024
Yu ZX, Li JX, Yang CQ, Hu WL, Wang LJ, Chen XY (2012) The jasmonate-responsive AP2/ERF transcription factors AaERF1 and AaERF2 positively regulate artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua L. Mol Plant 5:353–365. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssr087
Zhang Y, Nowak G, Reed DW, Covello PS (2011) The production of artemisinin precursors in tobacco. Plant Biotechnol J 9:445–454. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2010.00556.x
Zhang XB, Guo LP, Qiu ZD, Qu XB, Wang H, Jing ZX, Huang LQ (2017) Analysis of spatial distribution of artemisinin in Artemisia annua in China. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica 42(22):4341–4345. https://doi.org/10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.2017.0168
Zhou Z, Tan H, Li Q, Li Q, Wang Y, Bu Q, Li Y, Wu Y, Chen W, Zhang L (2020) Trichome and artemisinin regulator 2 positively regulates trichome development and artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. New Phytol 228:932–945. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.16777
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81903752), Guangxi Major Science and Technology Project of China (GuikeAA22096021), Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (2019GXNSFBA18502), Scientific Research Funding Project of Guangxi Botanical Garden of Medicinal Plants (GYJ202013), Research and Innovation Team Building Project of Guangxi Botanical Garden of Medicinal Plants (GYCH2019008), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81560623), Key Laboratory Construction Program of Guangxi Health commission (ZJC2020003), and Hainan Natural Science Foundation (No. 2019RC316).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, L. W., Q. H., Z. Z., S. W., J. F., and A. H. El-S.; methodology, L. W., Q. H., A. H. El-S., and S. W.; software, L. W., Q. H., S. W., and A. H. El-S.; validation, L. P. and J. F.; formal analysis, L. W., Q. H., S. W., and A. H. El-S.; investigation, R. G. E., A. H. El-S., and Z. Z.; resources, W. L.; writing—original draft preparation, L. W., Q. H., S. W., and A. H. El-S.; writing—review and editing, L. W., Q. H., A. S. E., M. M. A. E., G. J., S. W., L. G., and A. H. El-S.; visualization, X. J., L. S., Z. Z.; project administration, L. W.; funding acquisition, L. W., S. W., Z. Z., and J. F. J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, L., Huang, Q., Ji, X. et al. RNA sequencing in Artemisia annua L explored the genetic and metabolic responses to hardly soluble aluminum phosphate treatment. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 141 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01067-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01067-3