Abstract
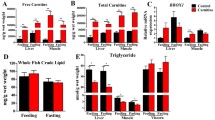
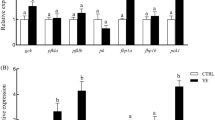
Carbohydrates are the most economical source of energy in fish feeds, but most fish have limited ability to utilize carbohydrates. It has been reported that phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 (pck1) is involved in carbohydrate metabolism, lipid metabolism, and other metabolic processes. However, direct evidence is lacking to fully understand the relationship between pck1 and glucose and lipid metabolism. Here, we generated a pck1 knockout zebrafish by CRISPR/cas9 system, and a high-carbohydrate diet was provided to 60 days post-fertilization (dpf) for 8 weeks. We found that pck1-deficient zebrafish displayed decreased plasma glucose, elevated mRNA levels of glycolysis-related genes (gck, pfk, pk), and reduced the transcriptional levels of gluconeogenic genes (pck1, fbp1a) in liver. We also found decreased triglyceride, total cholesterol, and lipid accumulation and in pck1−/− zebrafish, along with downregulation of genes for lipolysis (acaca) and lipogenesis (cpt1). In addition, the observation of HE staining revealed that the total muscle area of pck1−/− was substantially less than that of WT zebrafish and real-time PCR suggested that GH/IGF-1 signaling (ulk2, stat1b) may be suppressed in pck1-deficient fish. Taken together, these findings suggested that pck1 may play an important role in the high-carbohydrate diet utilization of fish and significantly affected lipid metabolism and protein synthesis in zebrafish. pck1 knockout mutant line could facilitate a further mechanism study of pck1-associated metabolic regulation and provide new information for improving carbohydrate utilization traits.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are available from the corresponding author by request.
References
Alexander C, Sahu N, Pal A, Akhtar M (2011) Haemato-immunological and stress responses of Labeo rohita (Hamilton) fingerlings: effect of rearing temperature and dietary gelatinized carbohydrate. J Anim Physiol An N 95(5):653–663. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0396.2010.01096.x
Arai T, Kano F, Murata M (2015) Translocation of forkhead box O1 to the nuclear periphery induces histone modifications that regulate transcriptional repression of PCK1 in HepG2 cells. Genes Cells 20(4):340–357. https://doi.org/10.1111/gtc.12226
Beddow SA, Gattu AK, Gattu DF, Paolella L, Alqarzaee L, Tashkandi N, Popov VB, Church CD, Rodeheffer MS, Cline GW, Geisler JG, Bhanot S, Samuel VT (2019) PEPCK1 antisense oligonucleotide prevents adiposity and impairs hepatic glycogen synthesis in high-fat male fed rats. Endocrinology 160(1):205–219. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2018-00630
Borrebaek B, Christophersen B (2000) Hepatic glucose phosphorylating activities in perch (Perca fluviatilis) after different dietary treatments. Comp Biochem Physiol B 125(3):387–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0305-0491(99)00185-6
Cai W, Liang X-F, Yuan X, Liu L, He S, Li J, Li B, Xue M (2018) Different strategies of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) responding to insufficient or excessive dietary carbohydrate. Aquaculture 497:292–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.07.042
Enes P, Panserat S, Kaushik S, Oliva-Teles A (2009) Nutritional regulation of hepatic glucose metabolism in fish. Fish Physiol Biochem 35(3):519–539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-008-9259-5
Enes P, Panserat S, Kaushik S, Oliva-Teles AA (2006) Effect of normal and waxy maize starch on growth, food utilization and hepatic glucose metabolism in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) juveniles. Comp Biochem Phys A 143(1):89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2005.10.027
Forbes JL, Kostyniuk DJ, Mennigen JA, Weber J-M (2019) Glucagon regulation of carbohydrate metabolism in rainbow trout: in vivo glucose fluxes and gene expression. J Exp Biol 222(24):jeb211730. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.211730
Fowler LA, Williams MB, D'Abramo LR, Watts SA (2020) Zebrafish nutrition—moving forward. In: The zebrafish in biomedical research. Academic Press, pp 379–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-812431-4.00033-6
Fowler LA, Williams MB, Dennis-Cornelius LN, Farmer S, Barry RJ, Powell ML, Watts SA (2019) Influence of commercial and laboratory diets on growth, body composition, and reproduction in the zebrafish Danio rerio. Zebrafish 16(6):508–521. https://doi.org/10.1089/zeb.2019.1742
Fuqua JD, Hughes J, Kuennen D, Harris M, Turner K, Kronemberger A, Ebert S, Dierdorff J, Zhu ZY, Zingman L, Adams C, Lira VA (2020) Skeletal muscle ULK1 and ULK2 jointly couple muscle mass with force and are required for survival under low nutrient availability. FASEB J 34(S1):1–1. https://doi.org/10.1096/fasebj.2020.34.s1.03974
Fuqua JD, Mere CP, Kronemberger A, Blomme J, Bae D, Turner KD, Harris MP, Scudese E, Edwards M, Ebert SM, Sousa L, Bodine SC, Yang L, Adams CM, Lira VA (2019) ULK2 is essential for degradation of ubiquitinated protein aggregates and homeostasis in skeletal muscle. FASEB J 33(11):11735–12745. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201900766R
Gao Y, Dai Z, Shi C, Zhai G, Jin X, He J, Lou Q, Yin Z (2016) Depletion of myostatin b promotes somatic growth and lipid metabolism in zebrafish. Front Endocrinol 7:88. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2016.00088
Goldberg AA, Nkengfac B, Sanchez AMJ, Moroz N, Qureshi ST, Koromilas AE, Wang S, Burelle Y, Hussain SN, Kristof AS (2017) Regulation of ULK1 expression and autophagy by STAT1. J Biol Chem 292(5):1899–1909. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.771584
Goodwin AE, Lochmann RT, Tieman DM, Mitchell AJ (2002) Massive hepatic necrosis and nodular regeneration in largemouth bass fed diets high in available carbohydrate. J World Aquacult Soc 33(4):466–477. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-7345.2002.tb00026.x
Hanson RW, Hakimi P (2008) Born to run; the story of the PEPCK-Cmus mouse. Biochimie. 90(6):838–842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2008.03.009
Hanson RW, Reshef L (1997) Regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem 66(1):581–611. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.66.1.581
Hemre GI, Mommsen T, Krogdahl A (2002) Carbohydrates in fish nutrition: effects on growth, glucose metabolism and hepatic enzymes. Aquacult Nutr 8(3):175–194. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2095.2002.00200.x
Idris RIR, Taufek NM, Nordin NFH, Al-Saari N (2022) Zebrafish nutrition: promoting fish health and welfare of the animal model in Halal science research. Halalpshere 2(1):106–121
Kamstra K (2021) Leptin and glucose homeostasis in the Zebrafish. University of Otago http://hdl.handle.net/10523/10918
Ko C-W, Counihan D, Wu J, Hatzoglou M, Puchowicz MA, Croniger CM (2018) Macrophages with a deletion of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 (Pck1) gene have a more proinflammatory phenotype. J Biol Chem 293(9):3399–3409. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.819136
Koo BC, Kwon MS, Nam Y, Kim T (2018) Expression of PCK1 gene in skeletal muscle cells using muscle-specific promoter. In: The 18th International Symposium on Developmental Biotechnology, p 78-78
Krogdahl A, Hemre GI, Mommsen T (2005) Carbohydrates in fish nutrition: digestion and absorption in postlarval stages. Aquacult Nutr 11(2):103–122. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2004.00327.x
Kuo T, McQueen A, Chen T-C, Wang J-C (2015) Regulation of glucose homeostasis by glucocorticoids. In: Glucocorticoid signaling, pp 99–126
Labun K, Montague TG, Gagnon JA, Thyme SB, Valen E (2016) CHOPCHOP v2: a web tool for the next generation of CRISPR genome engineering. Nucleic Acids Res 44(W1):W272–W276. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw398
Li S, Li Z, Zhang J, Sang C, Chen N (2019a) The impacts of dietary carbohydrate levels on growth performance, feed utilization, glycogen accumulation and hepatic glucose metabolism in hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus ♀ × E. lanceolatus♂). Aquaculture 512:734351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734351
Li RX, Liu HY, Li SY, Tan BP, Dong XH, Chi SY, Yang QH, Zhang S, Chen LQ (2019b) Nutritional regulation of gene expression and enzyme activity of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in the hepatic gluconeogenesis pathway in golden pompano (Trachinotus ovatus). Aquacult Res 50(2):634–643. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.13941
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Marandel L, Seiliez I, Véron V, Skiba-Cassy S, Panserat S (2015) New insights into the nutritional regulation of gluconeogenesis in carnivorous rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): a gene duplication trail. Physiol Genomics 47(7):253–263. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00026.2015
Matte A, Tari LW, Goldie H, Delbaere LT (1997) Structure and mechanism of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase. J Biol Chem 272(13):8105–8108. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.13.8105
Mofarrahi M, Sigala I, Guo Y, Godin R, Davis EC, Petrof B, Sandri M, Burelle Y (2012) Autophagy and skeletal muscles in sepsis. PloS One 7(10):e47265. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0047265
Moon TW (2001) Glucose intolerance in teleost fish: fact or fiction? Comp Biochem Physiol B 129(2-3):243–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1096-4959(01)00316-5
Moreira I, Peres H, Couto A, Enes P, Oliva-Teles A (2008) Temperature and dietary carbohydrate level effects on performance and metabolic utilisation of diets in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) juveniles. Aquaculture 274(1):153–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.11.016
Olswang Y, Cohen H, Papo O, Reshef L (2002) A mutation in the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ-binding site in the gene for the cytosolic form of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase reduces adipose tissue size and fat content in mice. P Natl Acad Sci USA 99(2):625–630. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.022616299
Panserat S, Plagnes-Juan E, Kaushik S (2001) Nutritional regulation and tissue specificity of gene expression for proteins involved in hepatic glucose metabolism in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J Exp Biol 204(13):2351–2360. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.204.13.2351
Pilkis SJ, Granner D (1992) Molecular physiology of the regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis and glycolysis. Annu Rev Biochem 54(1):885–909. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.004321
Polakof S, Panserat S, Soengas JL, Moon TW (2012) Glucose metabolism in fish: a review. J Comp Physiol B 182(8):1015–1045. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-012-0658-7
Ren K, Torres R (2009) Role of interleukin-1β during pain and inflammation. Brain Res Rev 60(1):57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresrev.2008.12.020
Reshef L, Olswang Y, Cassuto H, Blum B, Croniger CM, Kalhan SC, Tilghman SM, Hanson RW (2003) Glyceroneogenesis and the triglyceride/fatty acid cycle. J Biol Chem 278(33):30413–30416. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R300017200
Schiaffino S, Mammucari C (2011) Regulation of skeletal muscle growth by the IGF1-Akt/PKB pathway: insights from genetic models. Skelet Muscle 1(1):1–14 http://www.skeletalmusclejournal.com/content/1/1/4
Schreurs M, Kuipers F, Van Der Leij F (2010) Regulatory enzymes of mitochondrial β-oxidation as targets for treatment of the metabolic syndrome. Obes Rev 11(5):380–388. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2009.00642.x
Seiliez I, Médale F, Aguirre P, Panserat S, Skiba-Cassy S (2013) Postprandial regulation of growth-and metabolism-related factors in zebrafish. Zebrafish 10(2):237–248. https://doi.org/10.1089/zeb.2012.0835
Semakova J, Hyroššová P, Méndez-Lucas A, Cutz E, Bermudez J, Burgess S, Alcántara S, Perales JC (2017) PEPCK-C reexpression in the liver counters neonatal hypoglycemia in Pck1del/del mice, unmasking role in non-gluconeogenic tissues. J Physiol Biochem 73(1):89–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-016-0528-y
She P, Shiota M, Shelton KD, Chalkley R, Postic C, Magnuson MA (2000) Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase is necessary for the integration of hepatic energy metabolism. Mol Cell Biol 20(17):6508–6517. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.20.17.6508-6517.2000
Shi L, An S, Liu Y, Liu J, Wang F (2020) PCK1 regulates glycolysis and tumor progression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma through LDHA. Oncotargets Ther 13:2613. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S241717
Tang Y, Zhang Y, Wang C, Sun Z, Li L, Cheng S, Zhou W (2018) Overexpression of PCK1 gene antagonizes hepatocellular carcinoma through the activation of gluconeogenesis and suppression of glycolysis pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem 47(1):344–355. https://doi.org/10.1159/000489811
Wang A, Zhang Z, Ding Q, Yang Y, Bindelle J, Ran C (2021) Intestinal Cetobacterium and acetate modify glucose homeostasis via parasympathetic activation in zebrafish. Gut Microbes 13(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2021.1900996
Wang J, Liang X-F, He S, Li J, Huang K, Zhang Y-P, Huang D (2018) Lipid deposition pattern and adaptive strategy in response to dietary fat in Chinese perch (Siniperca chuatsi). Nutr Metab 15(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12986-018-0315-6
Wassana P, Prathomya P, Jakovlić I, Liu H, Zhao Y-H, Wang W-M (2017) Transcriptomics, metabolomics and histology indicate that high-carbohydrate diet negatively affects the liver health of blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). BMC Genomics 18(1):856. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-4246-9
Williams MB (2021) Importance of the zebrafish model for understanding nutrition. The University of Alabama at Birmingham
Wilson RP (1994) Utilization of dietary carbohydrate by fish. Aquaculture 124(1-4):67–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(94)90363-8
Xu J, He GL, Chen LT, Xie SW, Chi SY, Zhang S, Cao JM, Tan BP (2022a) Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and G protein-coupled bile acid receptor 1 (TGR5) signaling pathways improved the hepatic lipid metabolism in hybrid grouper. Aquacult Rep 22:100997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2021.100997
Xu J, Shi ML, Chi SY, Zhang S, Cao JM, Tan BP, Xie SW (2022b) The effects of a mixture of antibiotics on the intestinal microbiota and hepatic lipid deposition in hybrid grouper fed bile acids diet. Aquacult Rep 24:101169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2022.101169
Yang B-Y, Zhai G, Gong Y-L, Peng X-Y, Shang G-H, Han D, Jin J-Y, Liu H-K, Du Z-Y, Yin Z, Xie S-Q (2018) Different physiological roles of insulin receptors in mediating nutrient metabolism in zebrafish. Am J Physiol-Endoc M 315(1):E38–E51. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00227.2017
Yang J, Kalhan SC, Hanson RW (2009) What is the metabolic role of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase? J Biol Chem 284(40):27025–27029. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R109.040543
Yang M, Deng K, Pan M, Zhang Y, Sampath W, Zhang W, Mai K (2020) Molecular adaptations of glucose and lipid metabolism to different levels of dietary carbohydrates in juvenile Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquacult Nutr 26(2):516–527. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.13013
Yoshimura A, Wakabayashi Y, Mori T (2010) Cellular and molecular basis for the regulation of inflammation by TGF-β. J Biochem 147(6):781–792. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvq043
Yu S, Meng S, Xiang M, Ma H (2021) Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in cell metabolism: Roles and mechanisms beyond gluconeogenesis. Mol Metab 53:101257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101257
Yuan X, Dong D, Li Z, Wu B (2019) Rev-erbα activation down-regulates hepatic Pck1 enzyme to lower plasma glucose in mice. Pharmacol Res 141:310–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2019.01.010
Zhang Y, Liang X-F, He S, Wang J, Li L, Zhang Z, Li J, Chen X, Li L, Alam MS (2021) Metabolic responses of Chinese perch (Siniperca chuatsi) to different levels of dietary carbohydrate. Fish Physiol Biochem 47(5):1449–1465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-021-00965-2
Zhang Y, Qin C, Yang L, Lu R, Zhao X, Nie G (2018) A comparative genomics study of carbohydrate/glucose metabolic genes: from fish to mammals. BMC Genomics 19:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-4647-4
Zhou S-S, Xu J, Zhu H, Wu J, Xu J-D, Yan R, Li X-Y, Liu H-H, Duan S-M, Wang Z, Chen H-B, Shen H, Li S-L (2016) Gut microbiota-involved mechanisms in enhancing systemic exposure of ginsenosides by coexisting polysaccharides in ginseng decoction. Sci Rep 6(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22474
Acknowledgements
Xu-Fang Liang and Ke Lu designed the experiments and wrote the paper; Ke Lu and Jiaqi Wu performed the experiments and analyzed the data; Ke Lu and Yanpeng Zhang fed fish and sampled; Ke Lu and Wuyuan Zhuang prepared the experimental diets.
Funding
This work was funded by National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFD0900400), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31972809), and Key Research and Development Project of Hubei Province (2020BBA035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, K., Wu, J., Zhang, Y. et al. Role of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 (pck1) in mediating nutrient metabolism in zebrafish. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 67 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-00993-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-00993-6